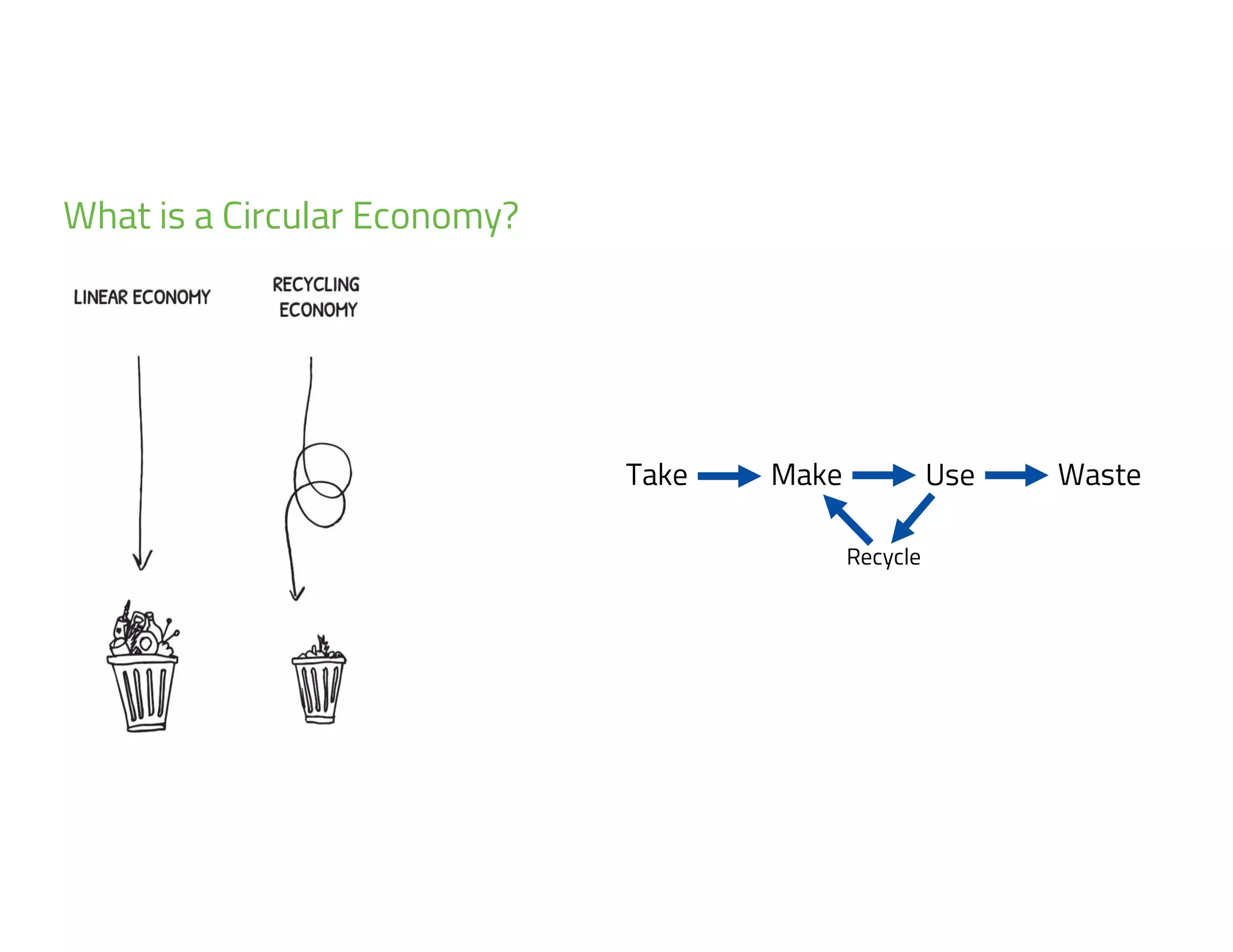
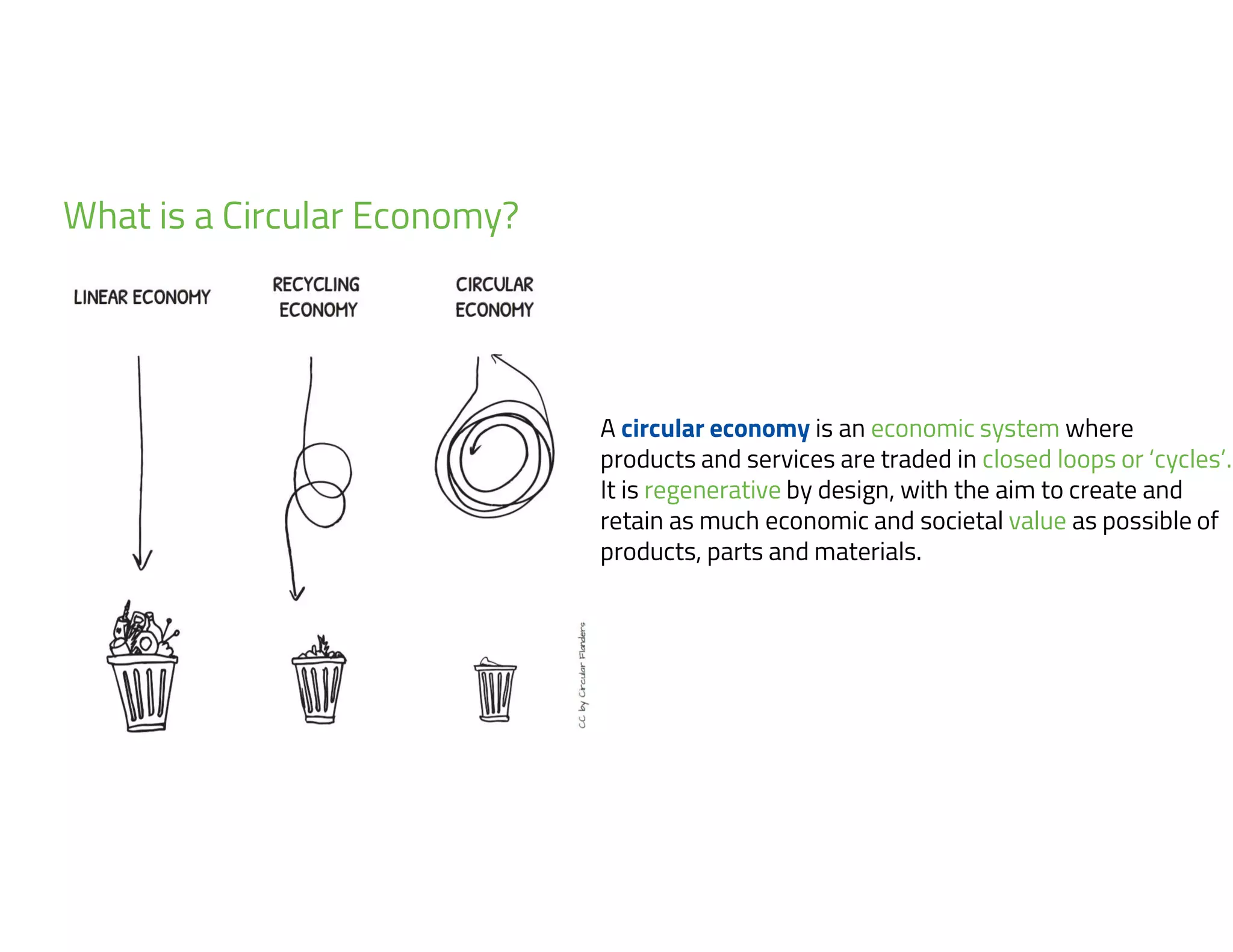
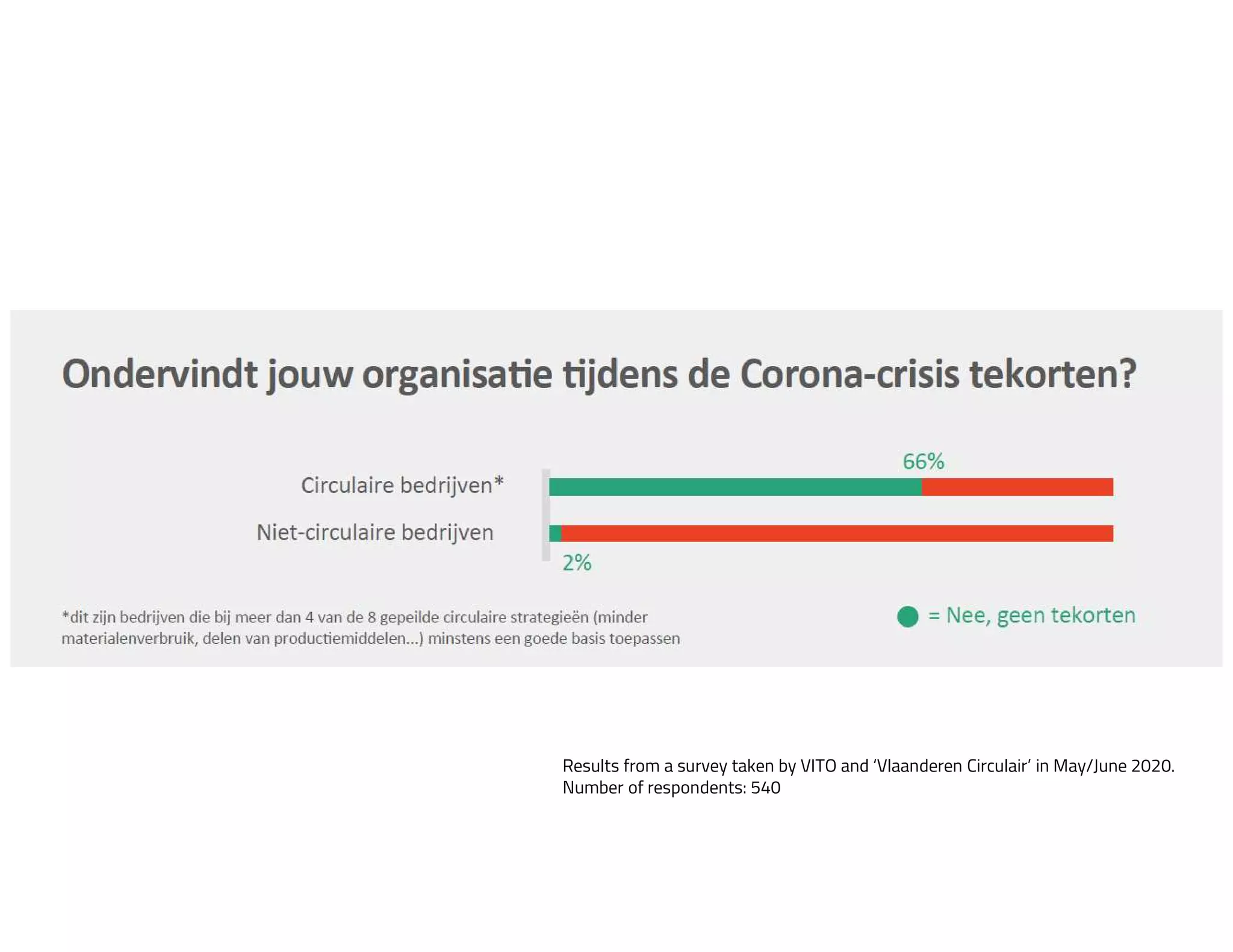
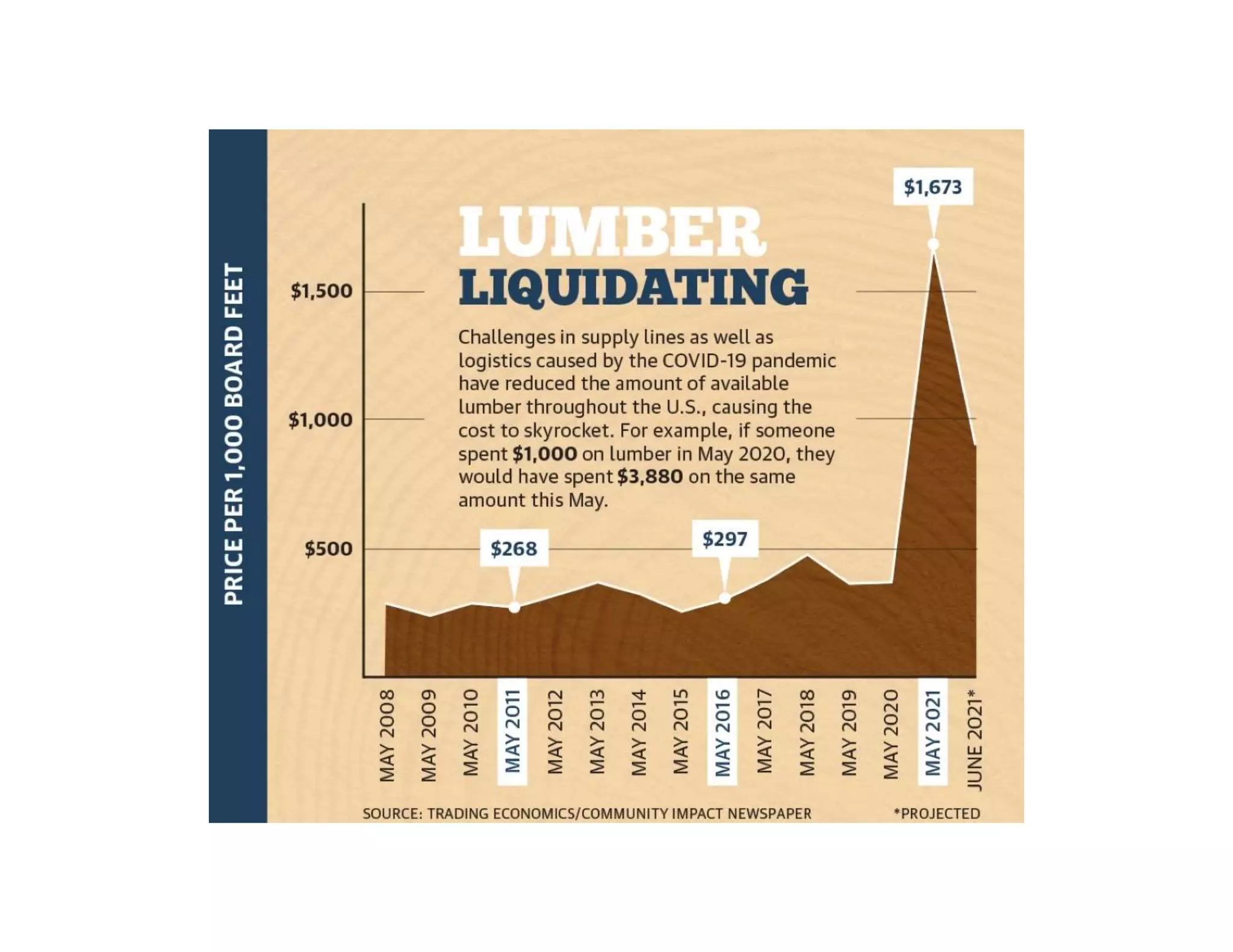
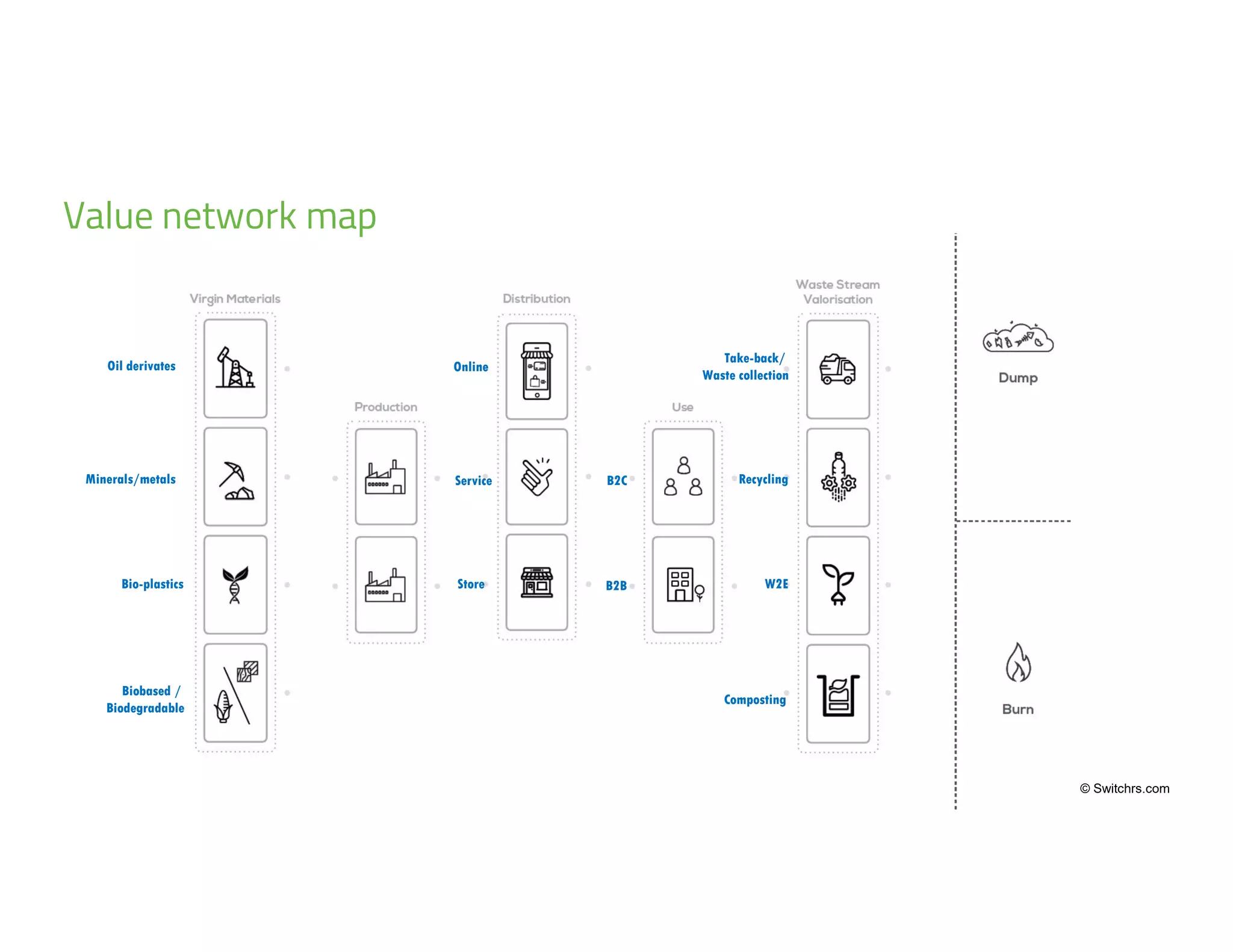
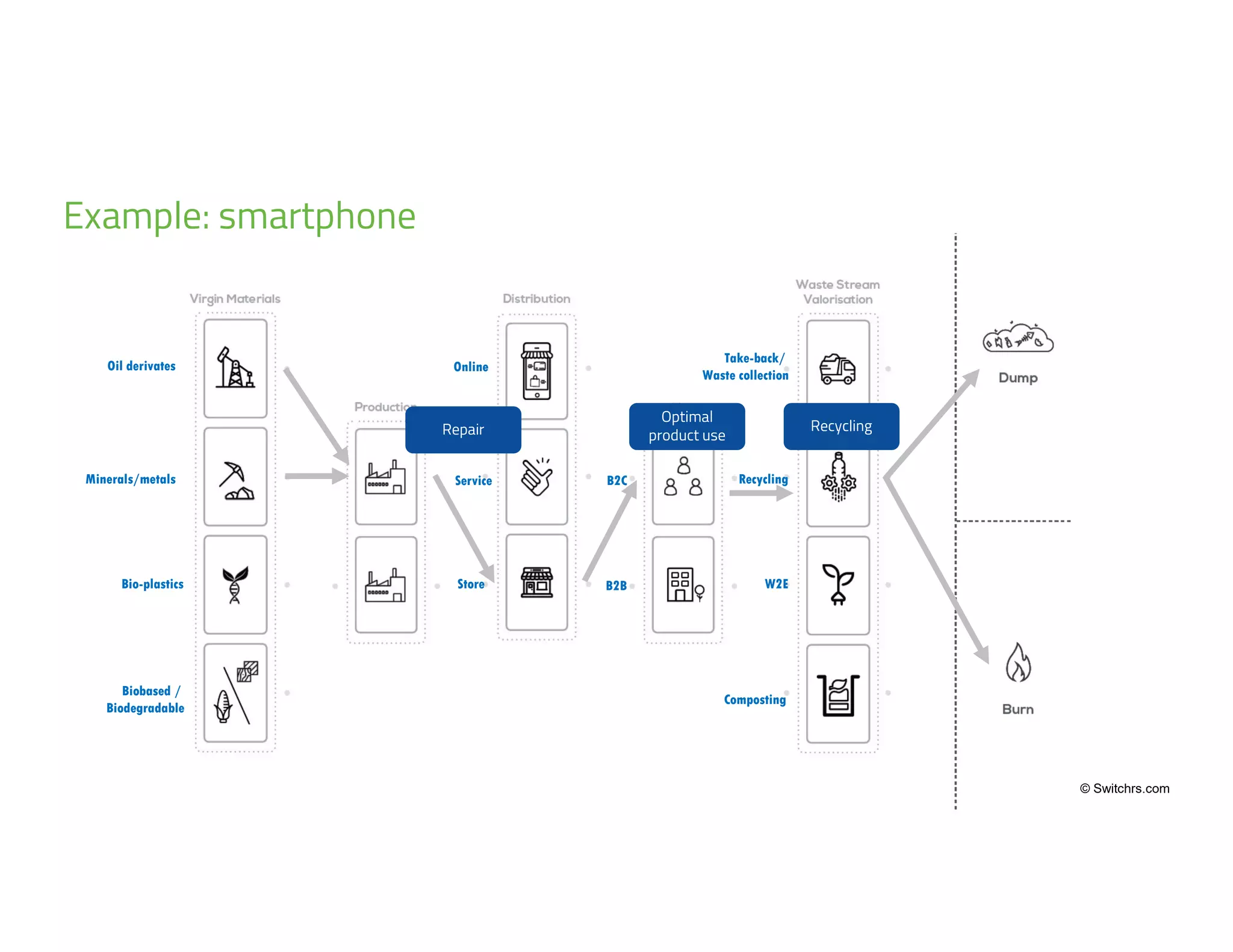
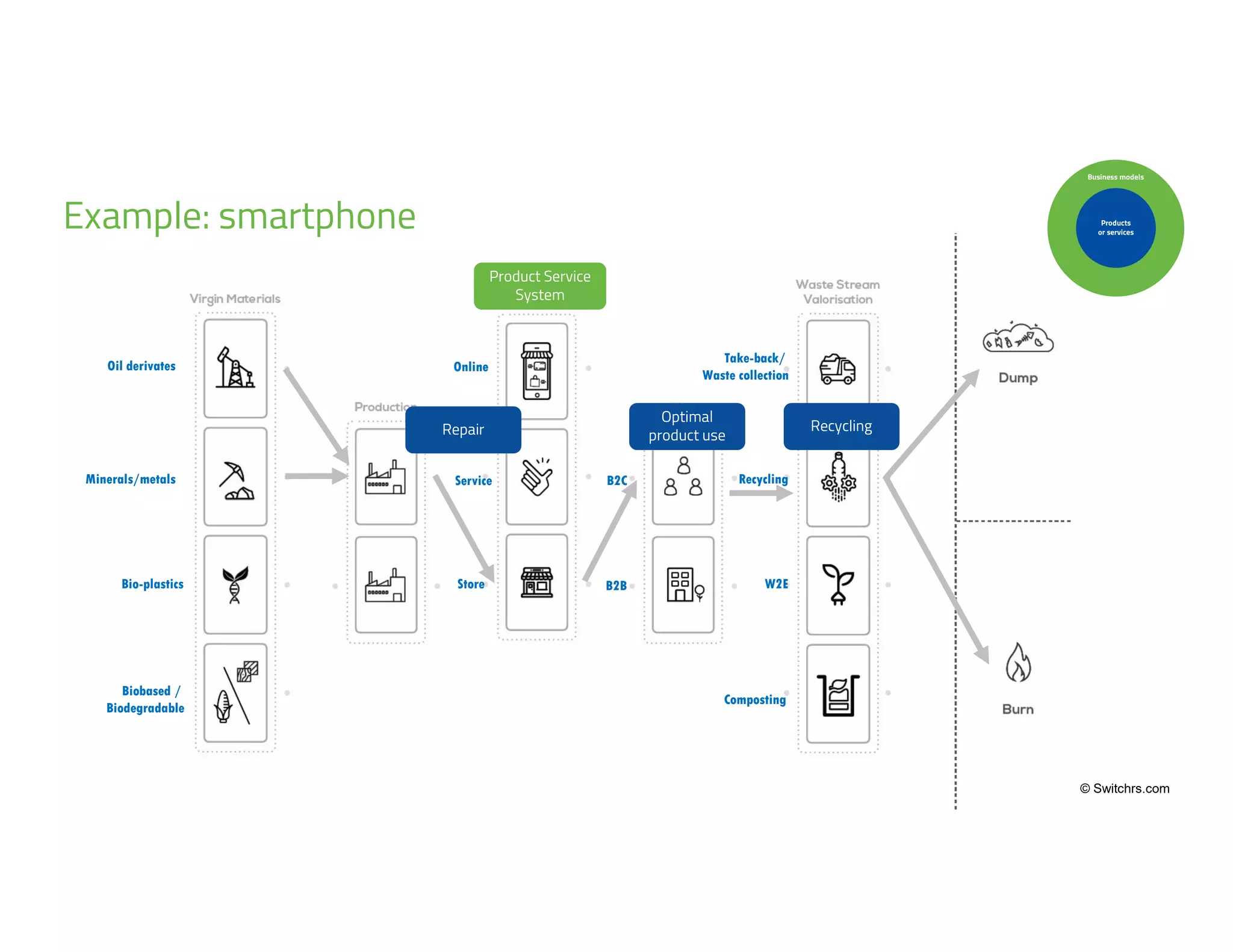
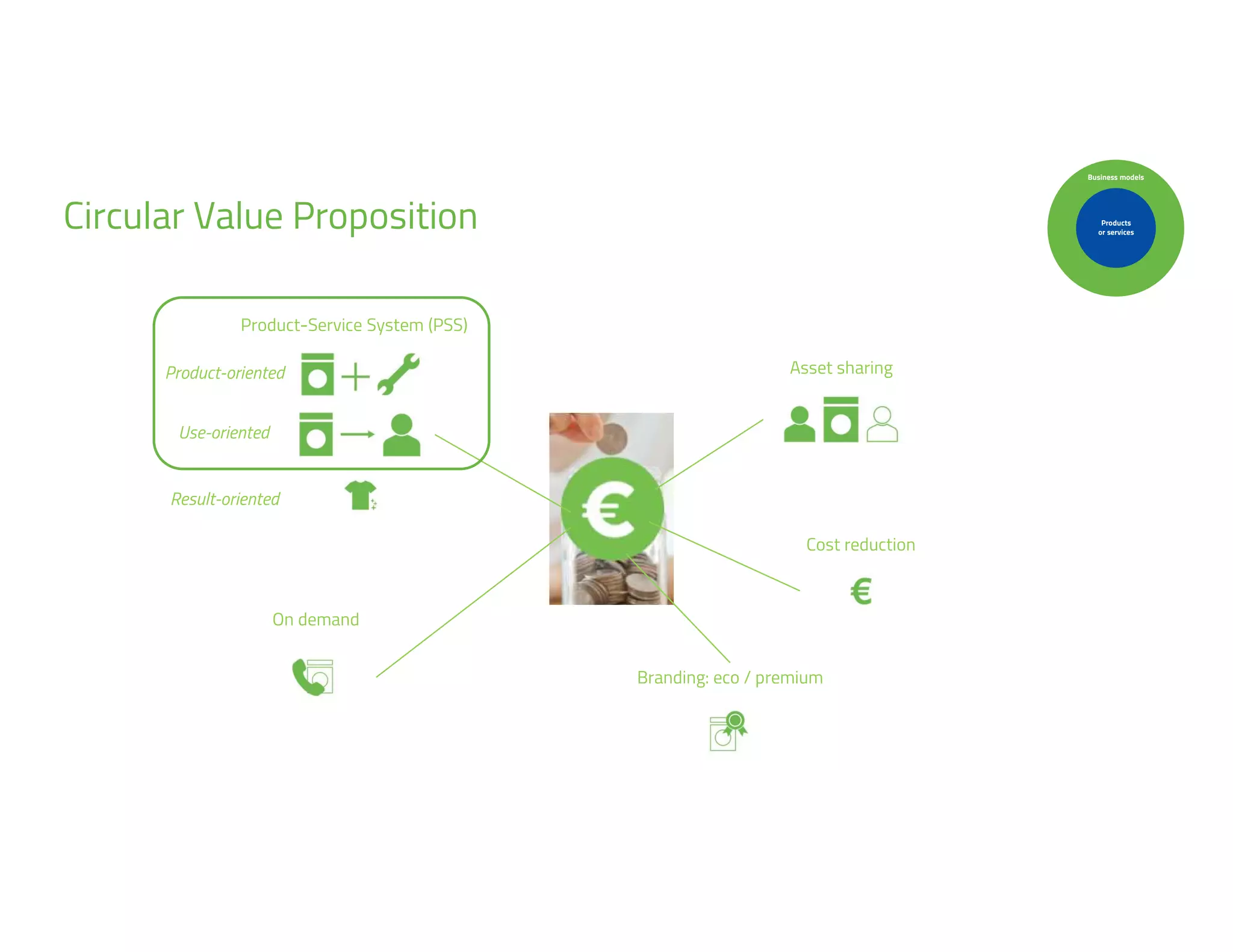
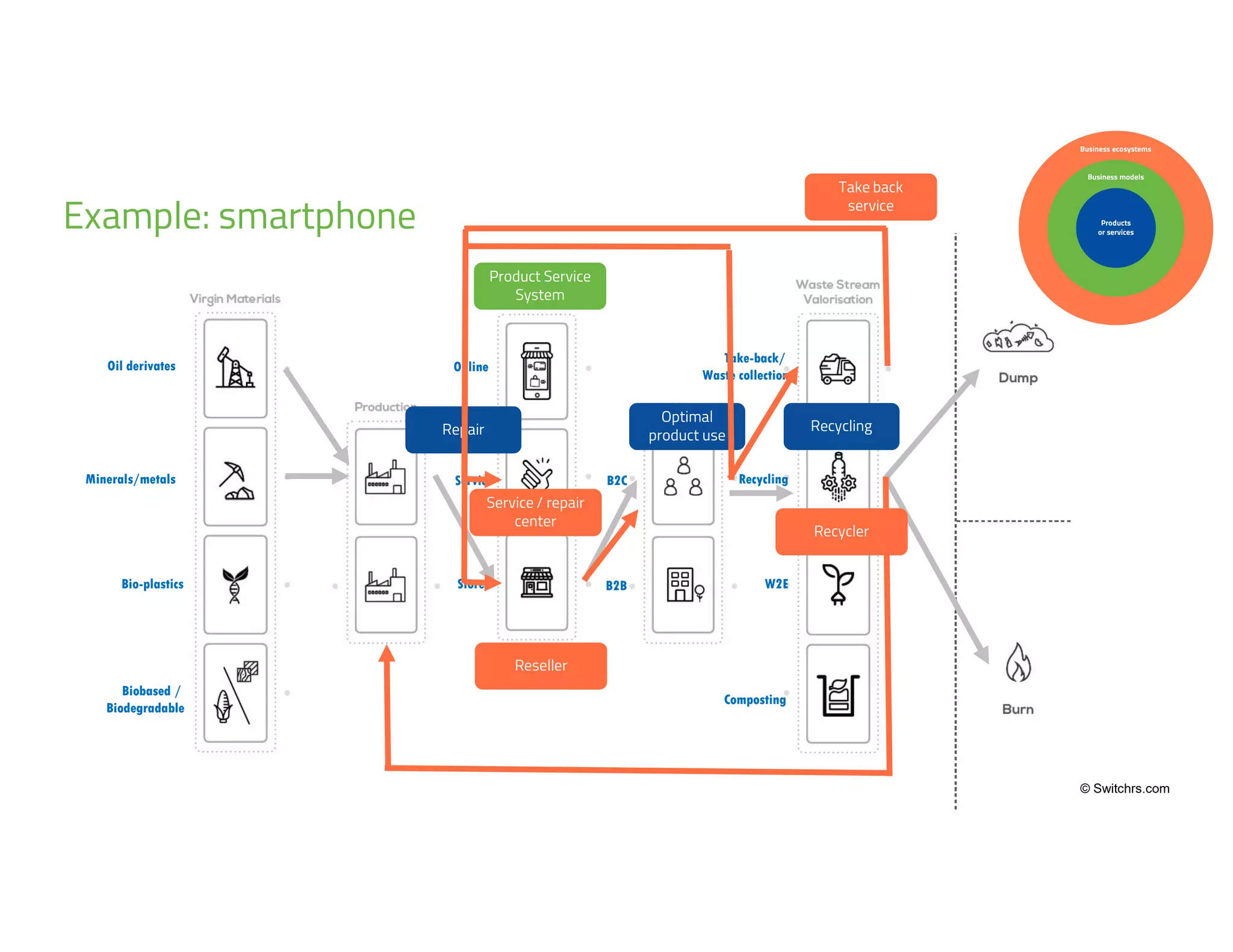
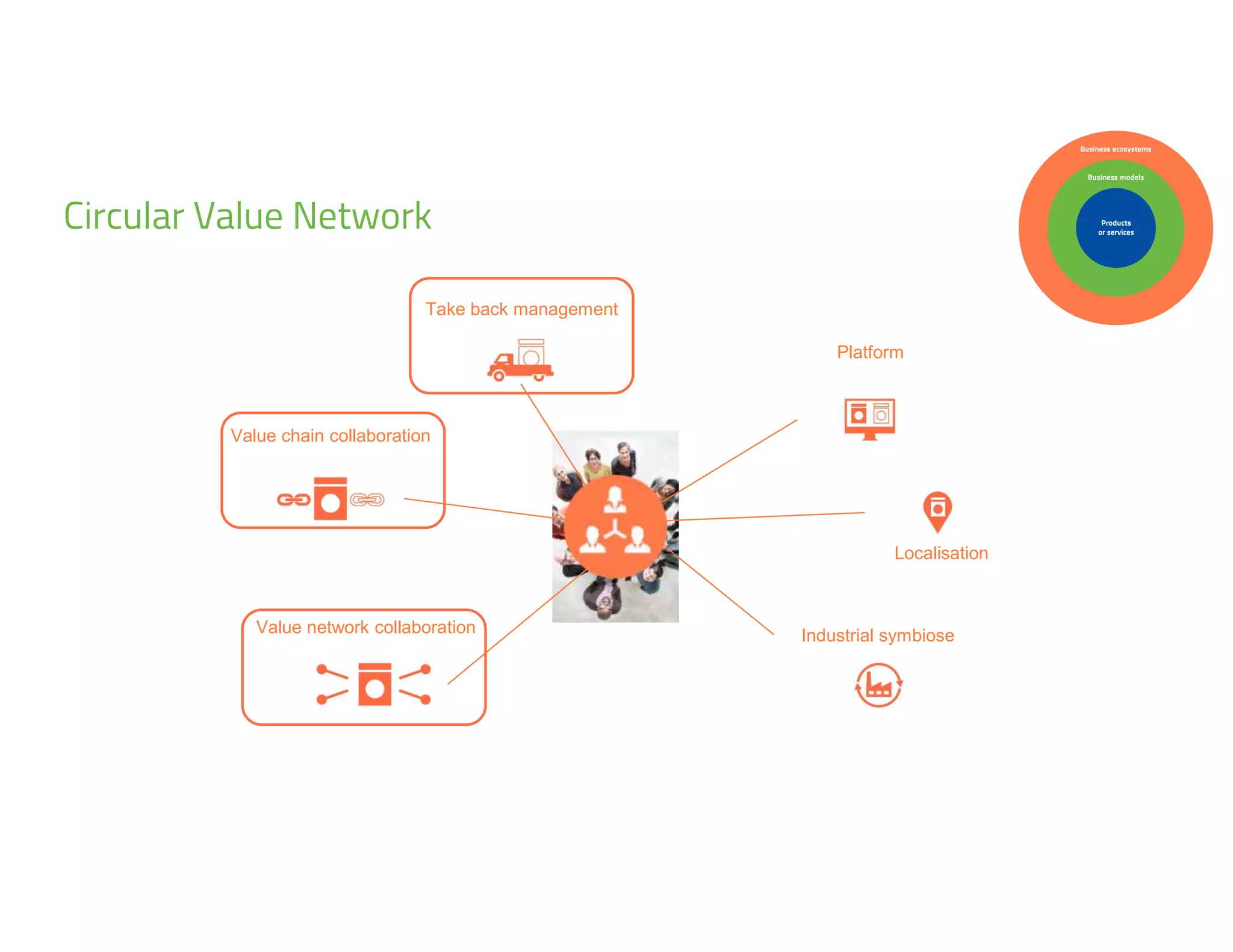
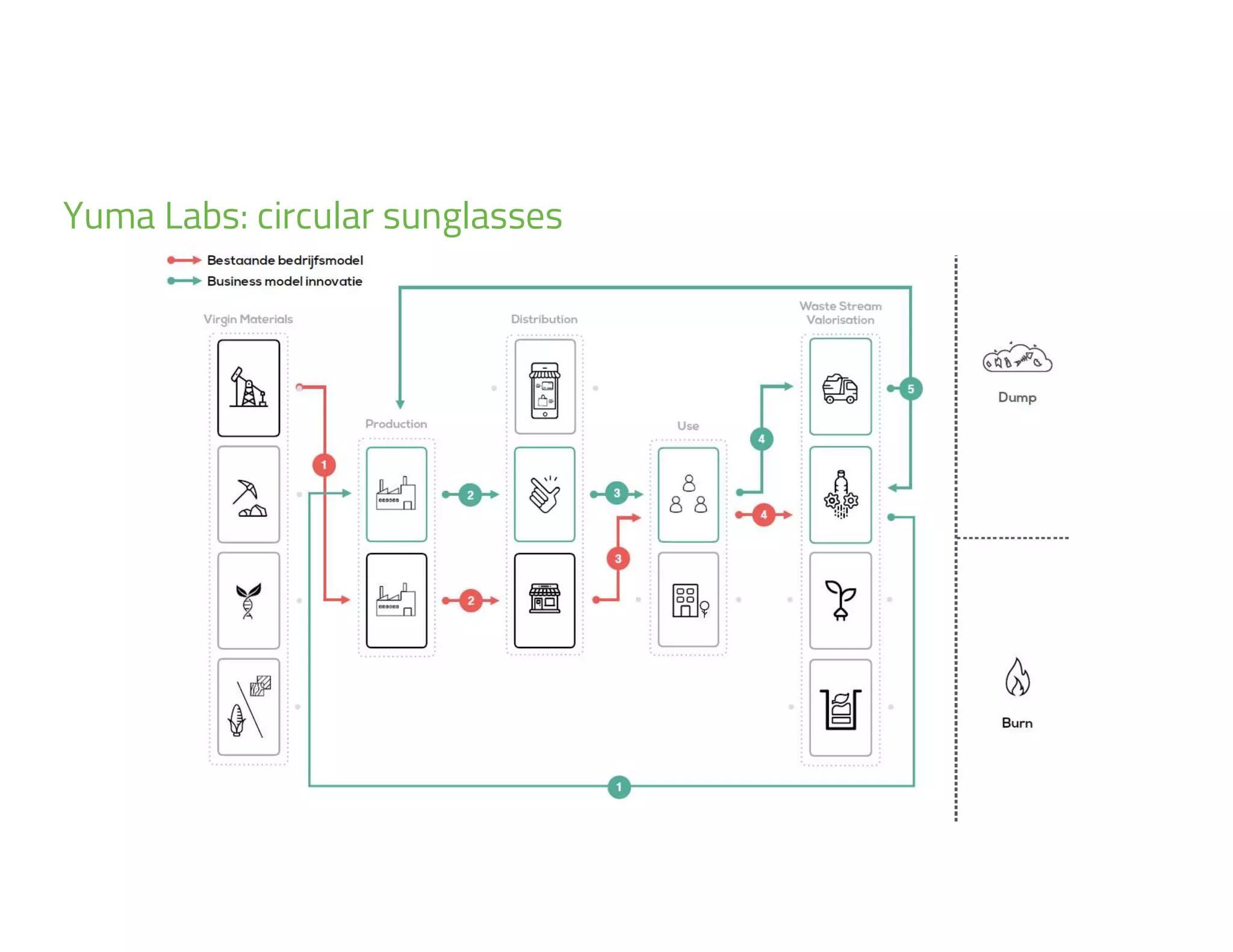
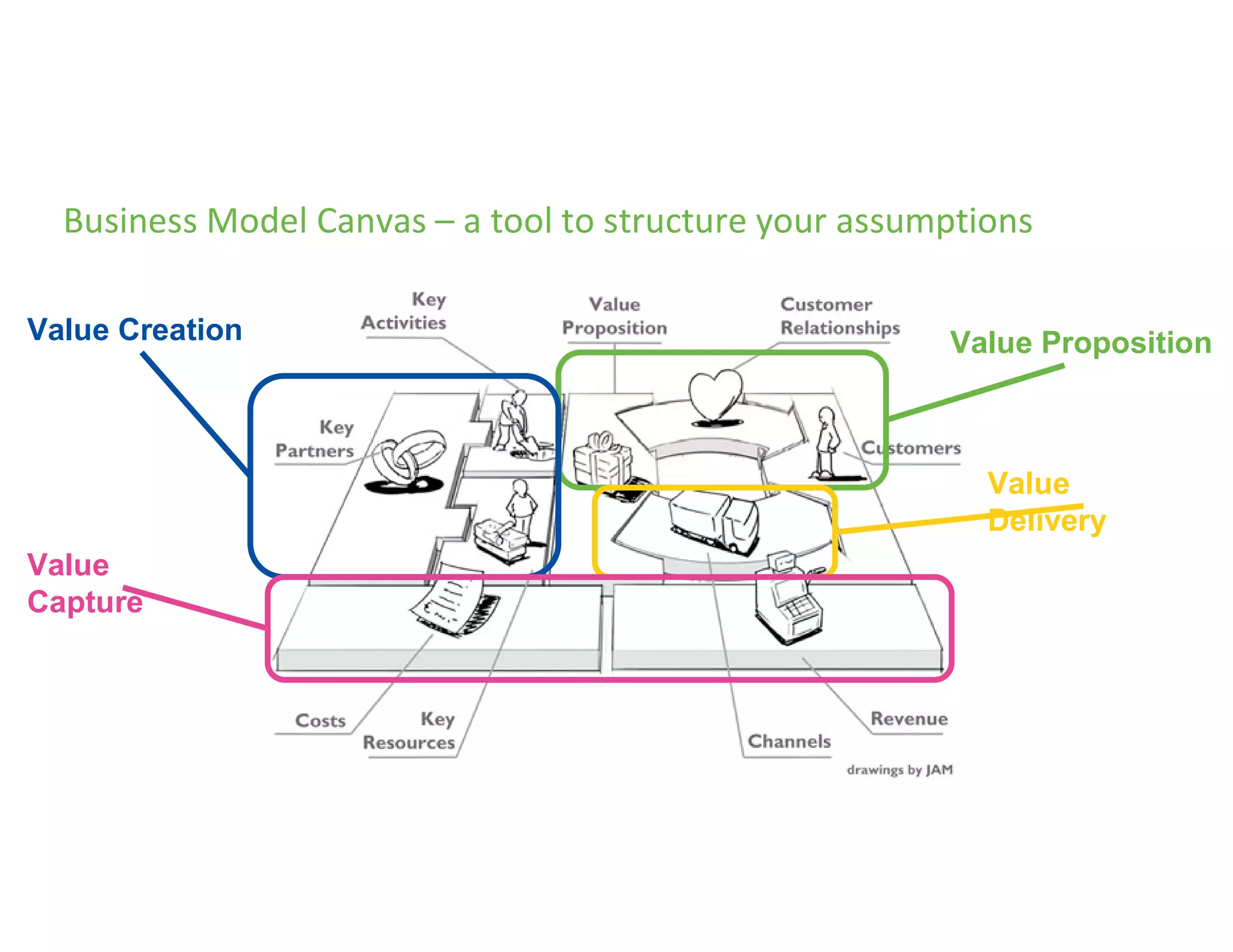
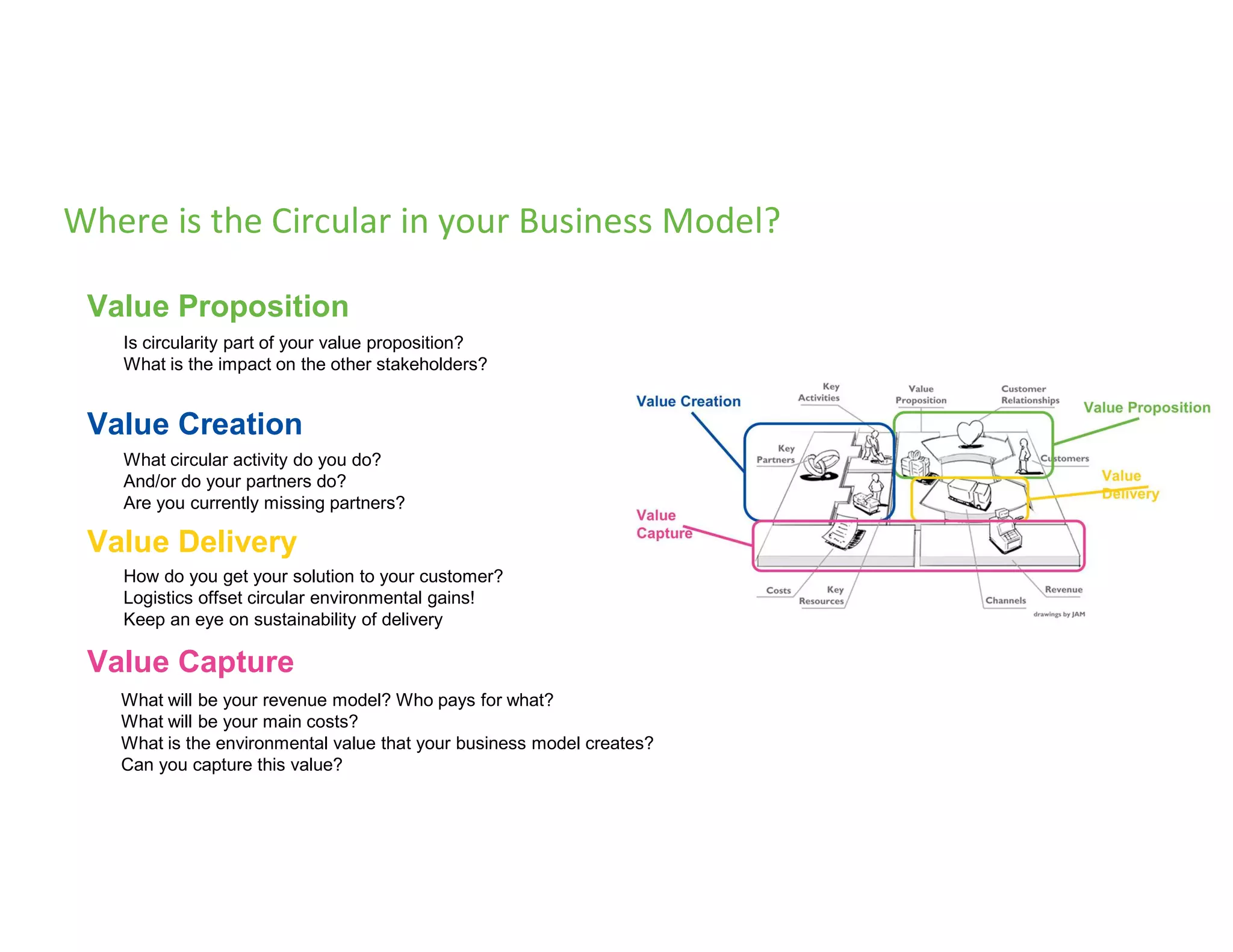
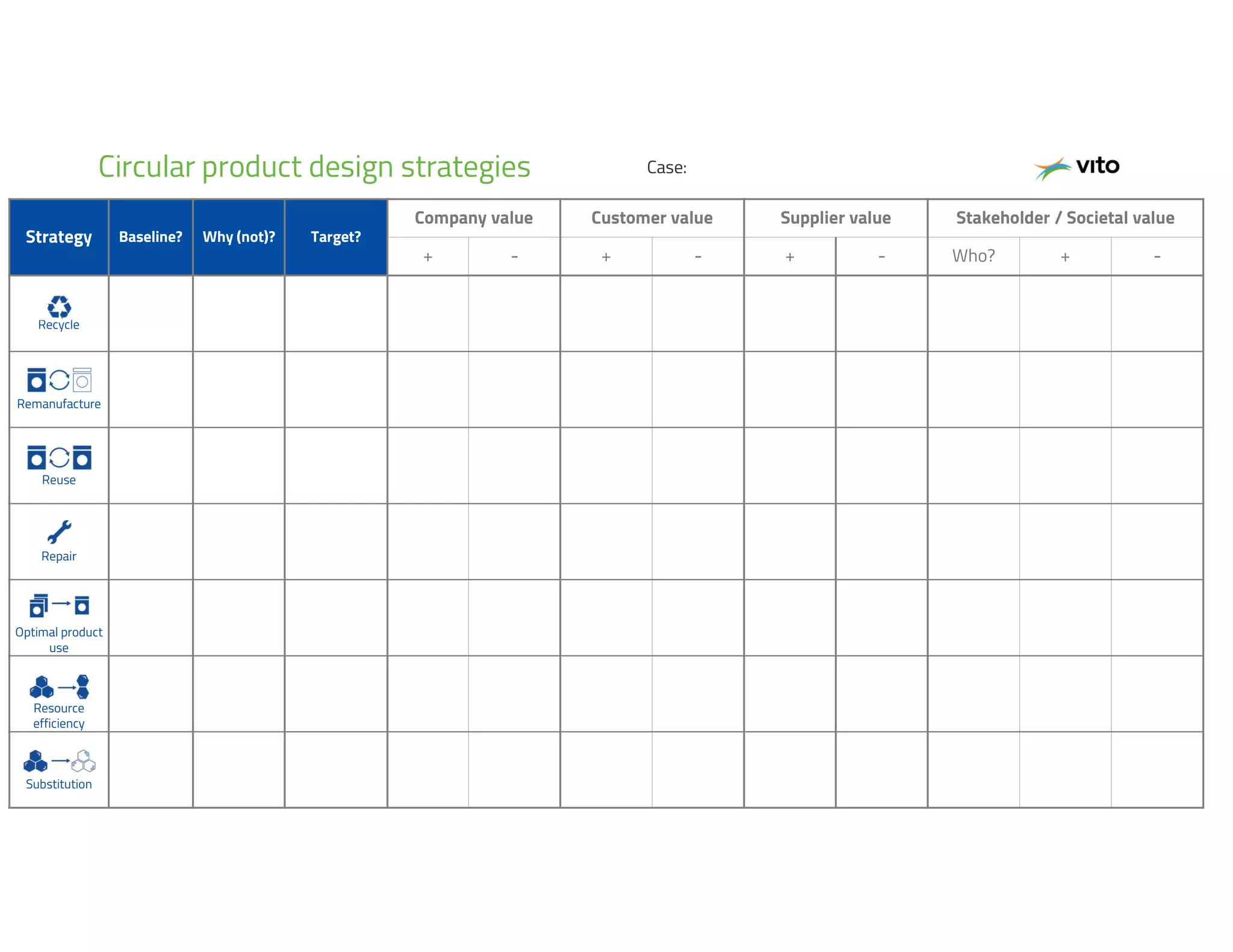
The document provides an overview of circular economy principles and their application in business models, emphasizing the importance of closed-loop systems where products and resources are reused. It highlights various strategies, tools, and real-world examples to enhance circularity, such as product-service systems and resource efficiency. Challenges, stakeholder cooperation, and value proposition development are also discussed in the context of creating sustainable and economically viable businesses.