This document evaluates the performance of deep learning algorithms and data preprocessing for demand power prediction. Experiments were conducted using raw and preprocessed daily electricity load, temperature, and weather data from Australia. Recurrent neural networks and convolutional neural networks generally had better prediction accuracy when trained on preprocessed rather than raw data. Preprocessing scaled the temperature data and increased the data points, leading to more stable and accurate results across all tested algorithms. The best performance was achieved using a recurrent neural network on preprocessed data. Further analysis of extreme learning machine algorithms was recommended.




![Raw vs. Preprocessed
• Given data(Australia NEM data):
• Daily Max and Mean Temperature data ( 2 points/day)
• Daily power load data with 30 mins interval ( 48 points/day)
• Raw data:
• [𝑃𝑟𝑎𝑤
𝑛 ] = 𝑃 𝑛, 𝑇 𝑚𝑎𝑥
𝑛 , 𝑇 𝑚𝑒𝑎𝑛
𝑛 ( 50 points/day)
• Preprocessed data:
• [𝑃𝑝𝑟𝑒
𝑛 ] = 𝑃 𝑛, 𝑃 𝑇.𝑚𝑎𝑥.𝑠𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑑
𝑛
, 𝑃 𝑇.𝑚𝑒𝑎𝑛.𝑠𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑑
𝑛
(144 points/day)
• 𝑃 𝑇.𝑚𝑎𝑥.𝑠𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑑
𝑛
= 𝑃 𝑛
𝑝𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑑 𝑏𝑦 𝑠𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑑 𝑀𝑎𝑥 𝑇𝑒𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑒
• [𝑃 𝑇.𝑚𝑒𝑎𝑛.𝑠𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑑
𝑛
] = 𝑃 𝑛
𝑝𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑑 𝑏𝑦 𝑠𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑑 𝑀𝑒𝑎𝑛 𝑇𝑒𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑒](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kcc201728apr2017-170828235330/75/KCC2017-28APR2017-6-2048.jpg)
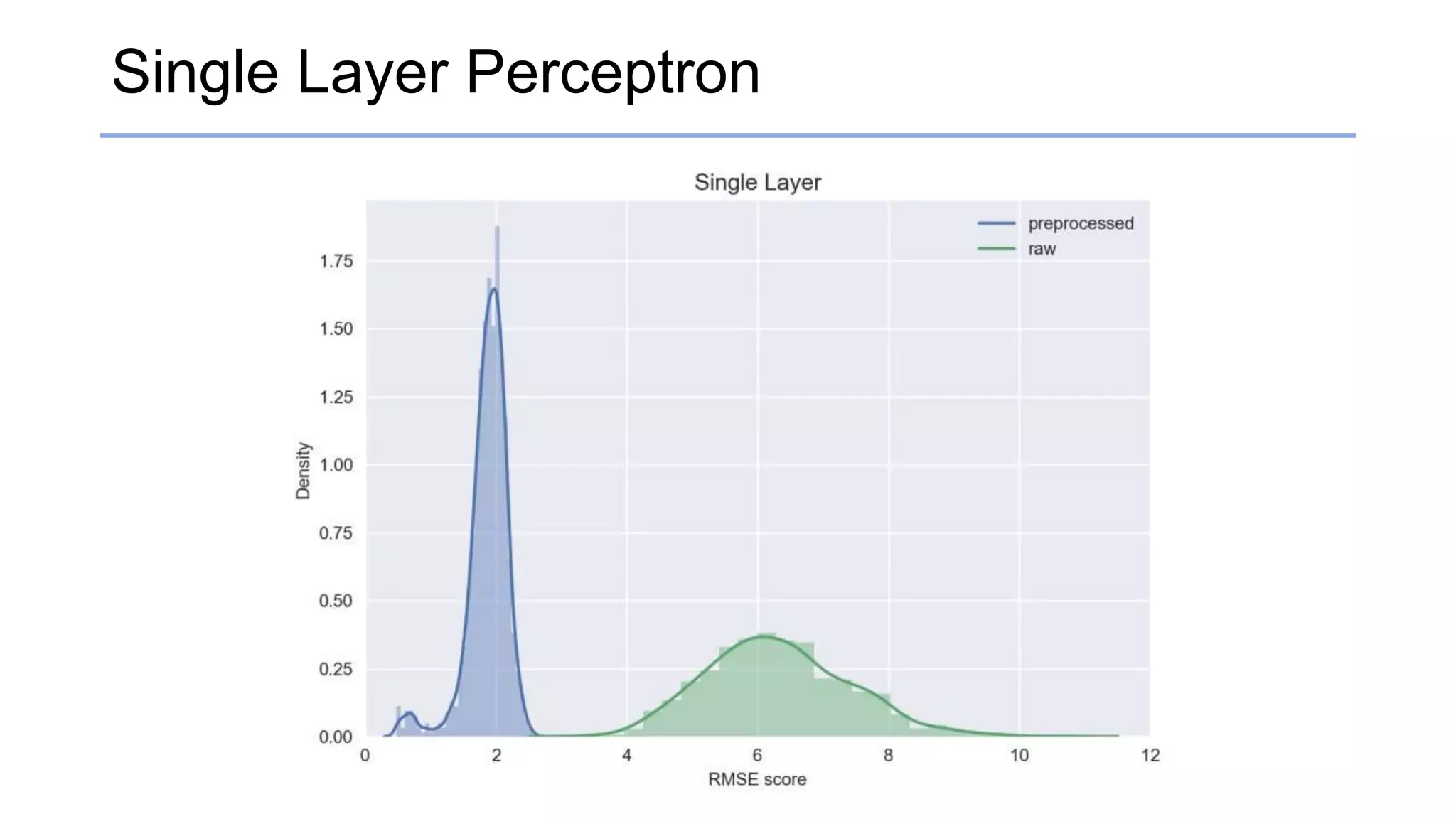
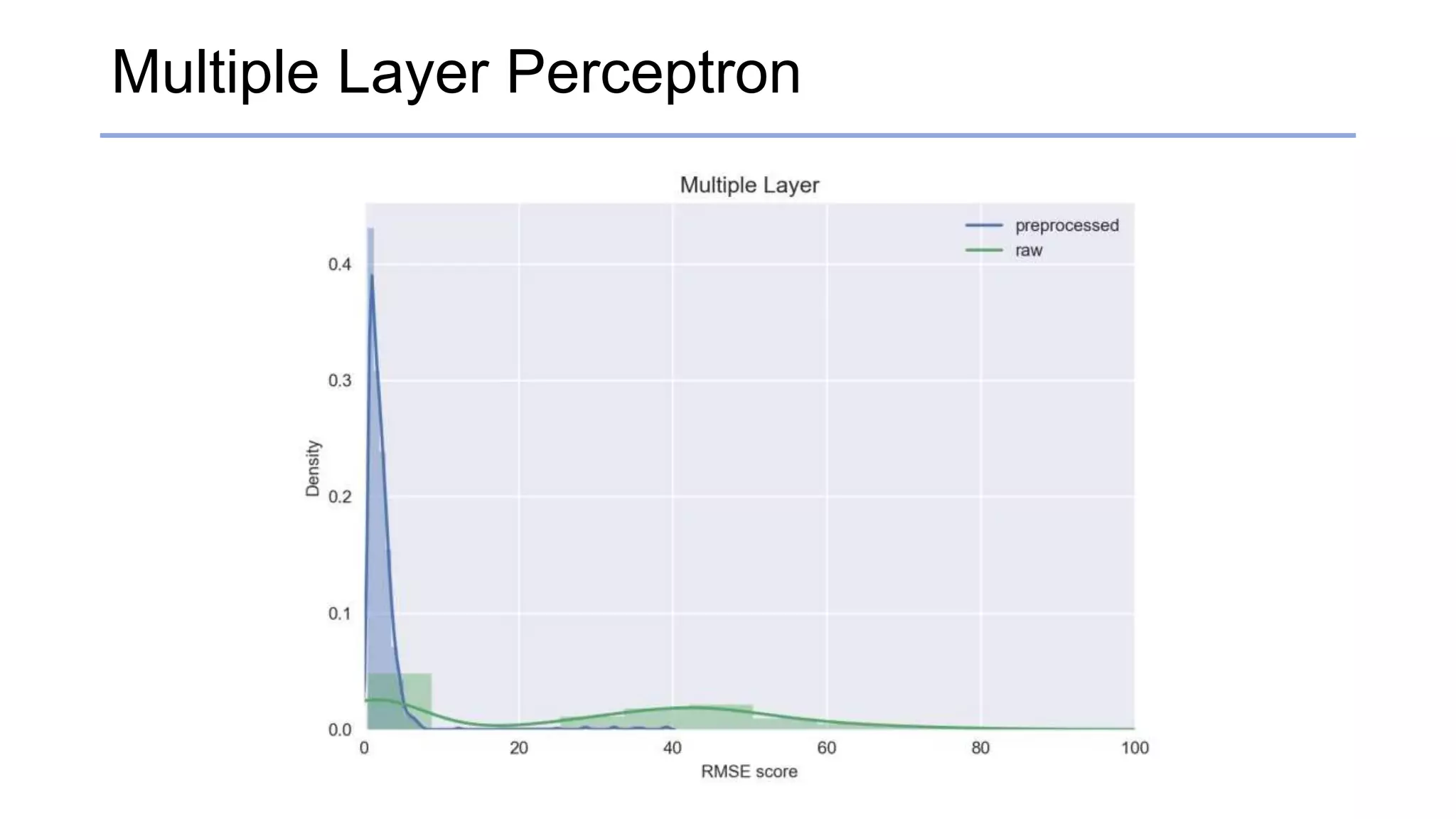
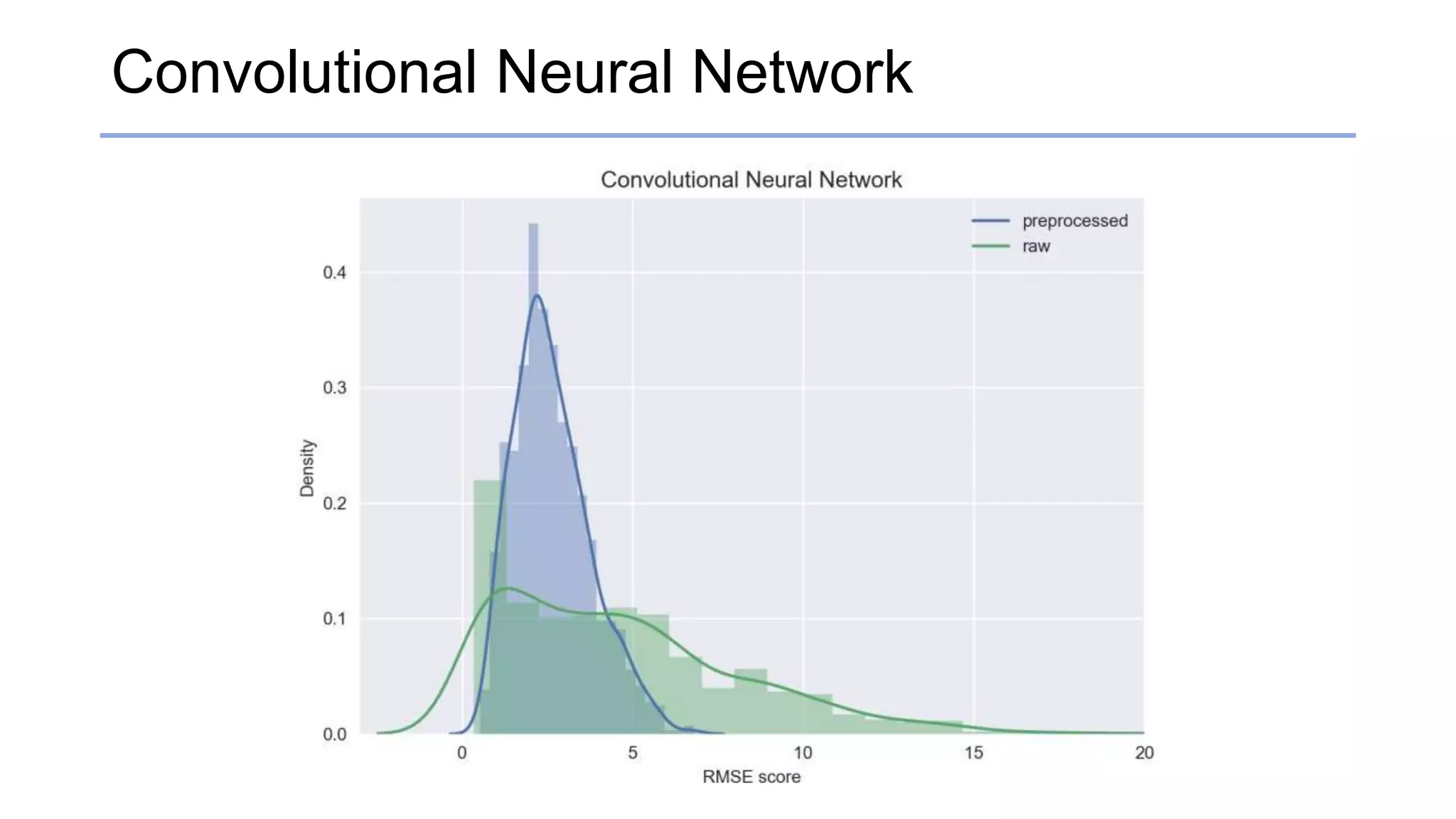
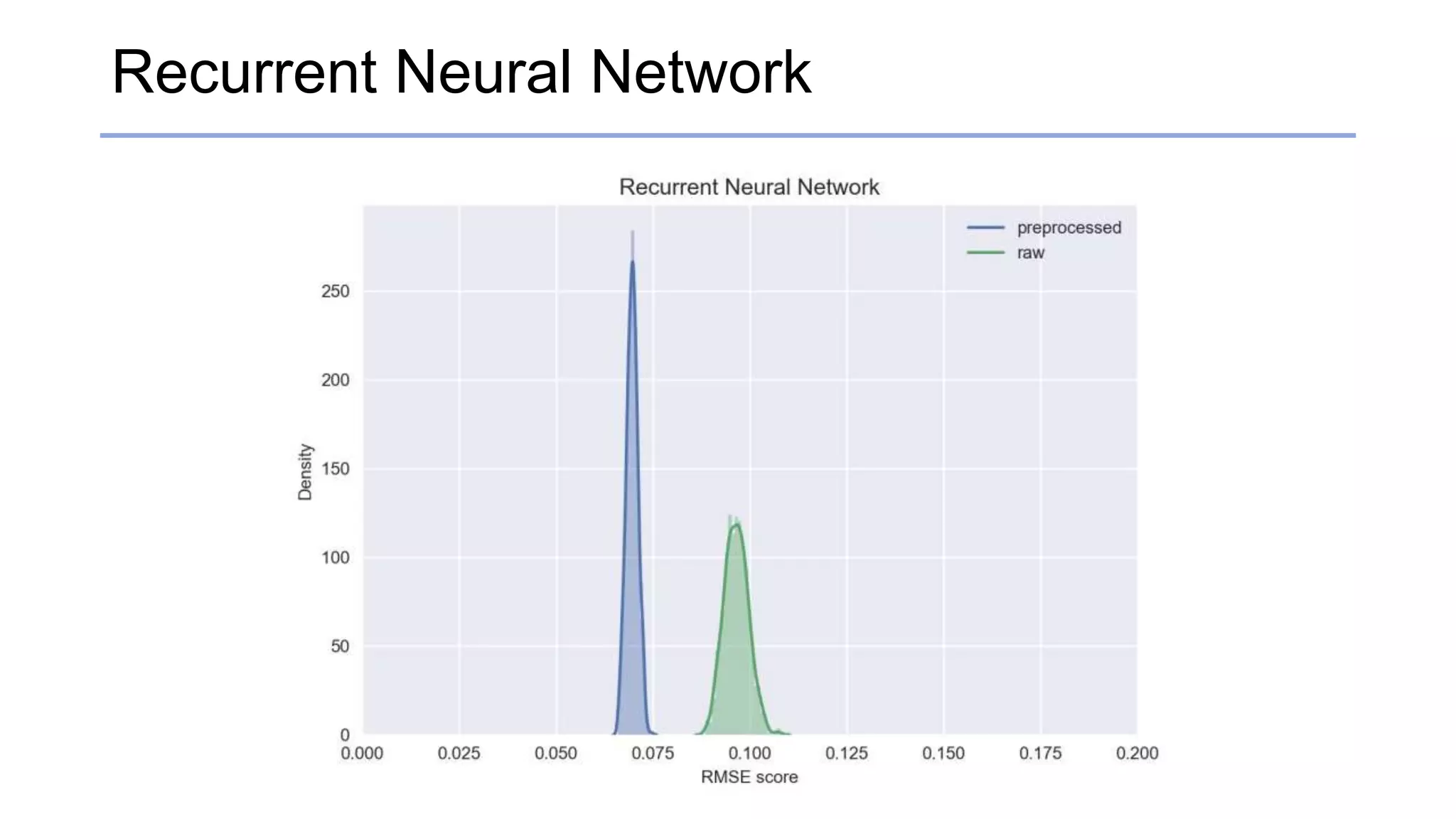
![Results
• RMSE & standard deviation score
Raw [RMSE / std] Preprocessed [RMSE / std]
Single Layer Perceptrons 6.30388 / 1.0803 1.86425 / 0.314612
Multiple Layer Perceptrons 27.0591 / 23.0247 2.2562 / 3.21933
Convolutional Neural Network 4.61754 / 3.52584 2.63669 / 1.11987
Recurrent Neural Network 0.0964969 / 0.00310329 0.0696449 / 0.00145637](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kcc201728apr2017-170828235330/75/KCC2017-28APR2017-7-2048.jpg)