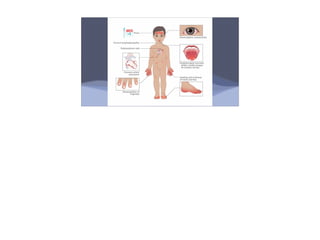
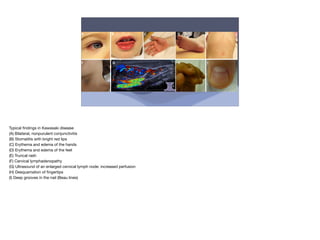
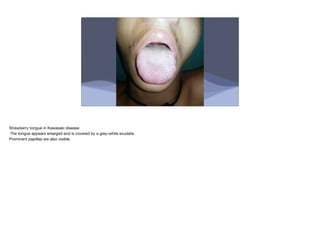
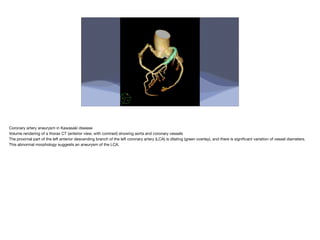
Kawasaki disease is an acute vasculitis that primarily affects children under 5 years of age. It is characterized by fever for at least 5 days and at least 4 of 5 clinical features including rash, conjunctivitis, mouth changes, swelling of hands and feet, and cervical lymphadenopathy. If left untreated, it can lead to coronary artery aneurysms in 15-25% of cases. Treatment involves intravenous immunoglobulin and aspirin which are most effective within the first 10 days of symptoms to reduce the risk of aneurysms and complications like myocardial infarction.