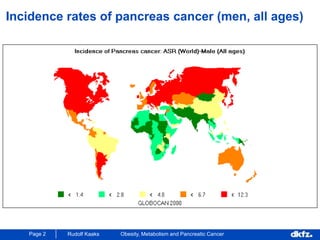
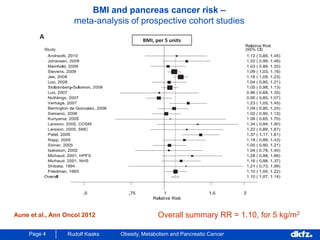
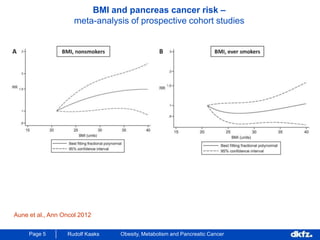
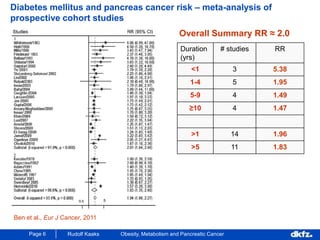
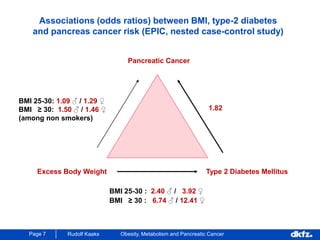
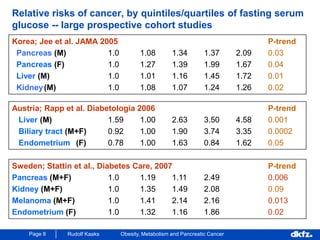
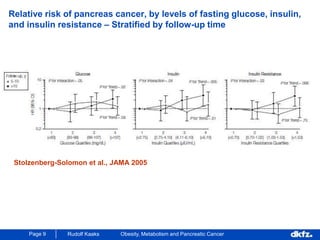
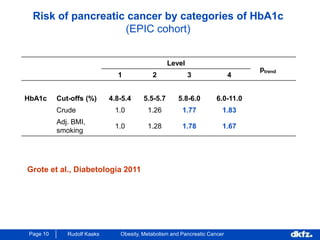
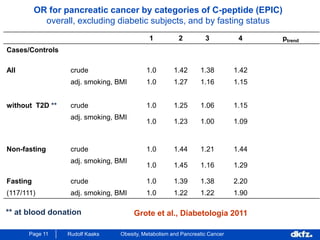
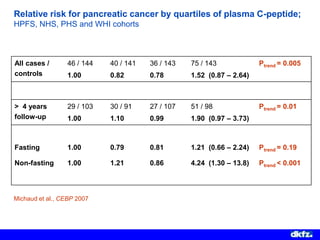
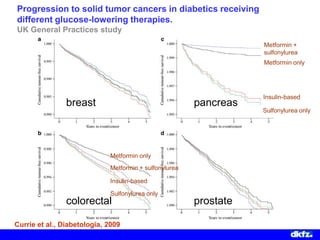
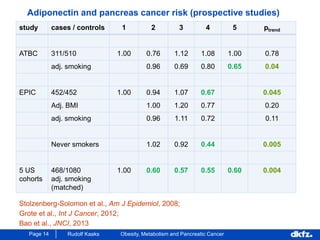
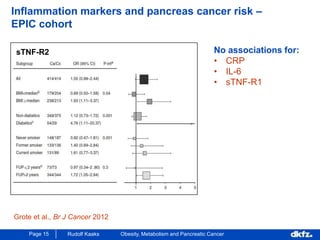
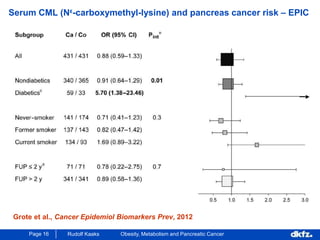
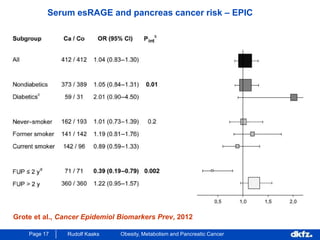
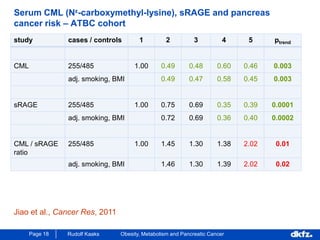
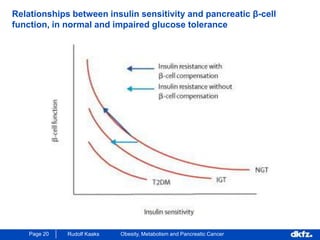
This document discusses the relationship between excess body weight, metabolic risk factors, and pancreatic cancer. It summarizes several meta-analyses and prospective cohort studies that found increased risks of pancreatic cancer associated with higher BMI, diabetes, and blood glucose levels. Specifically, a BMI over 30 was associated with a 6-12 times increased risk of pancreatic cancer. Diabetes was also found to double the risk of pancreatic cancer. Multiple biomarkers related to inflammation and glucose metabolism were also found to correlate with higher risks of pancreatic cancer. However, the document notes that the exact mechanisms linking metabolic factors and pancreatic cancer require further study.