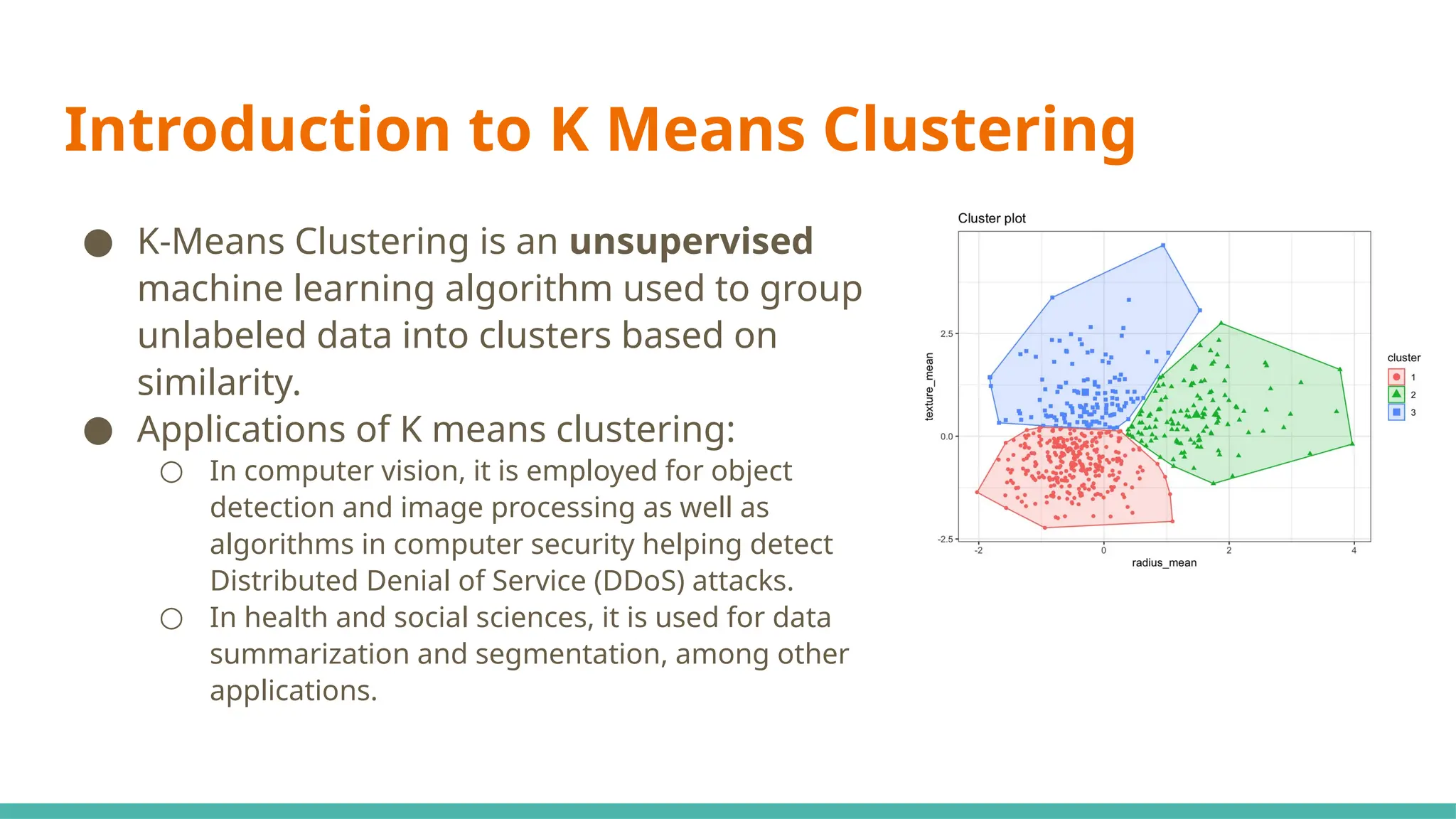
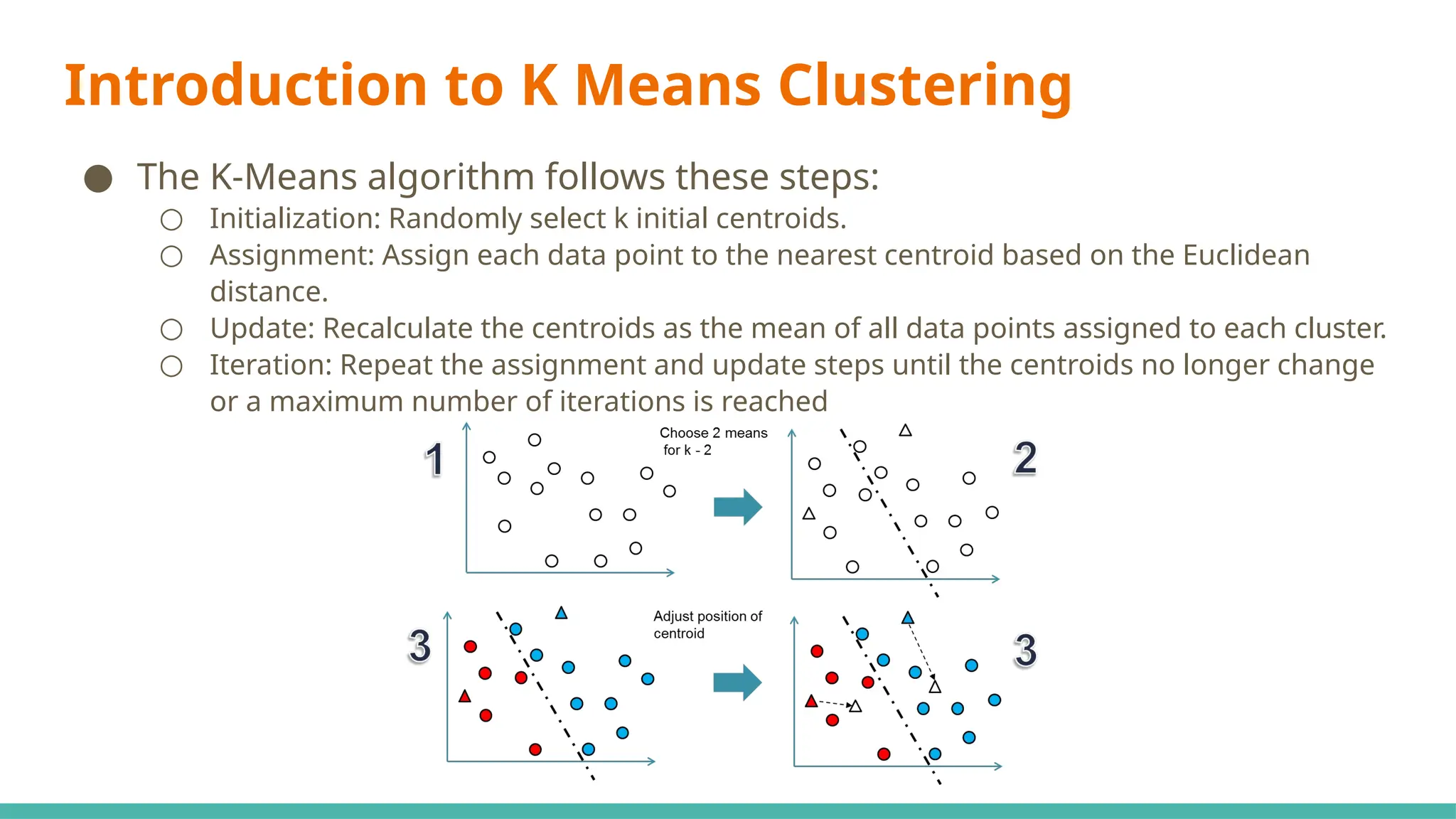
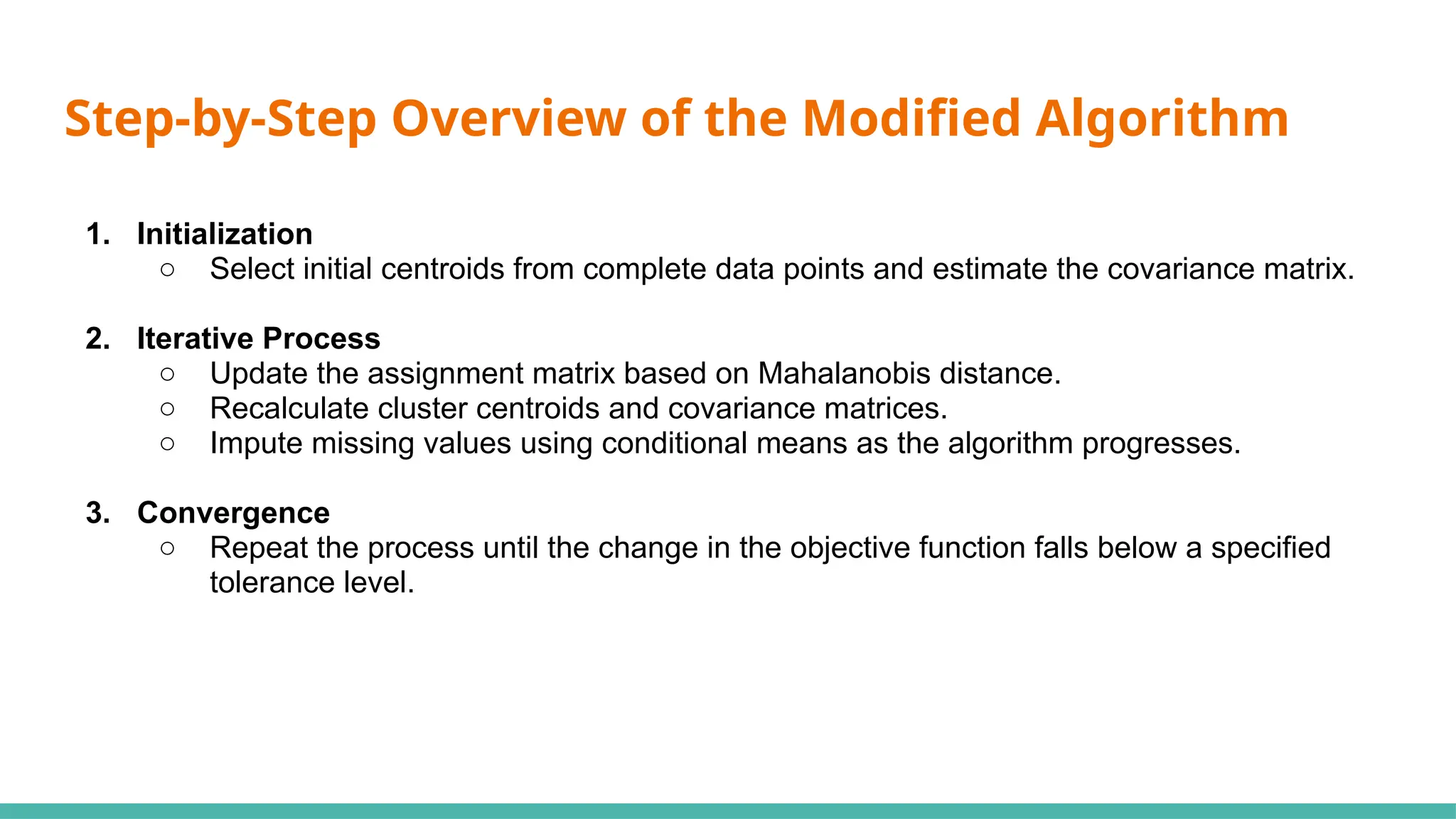
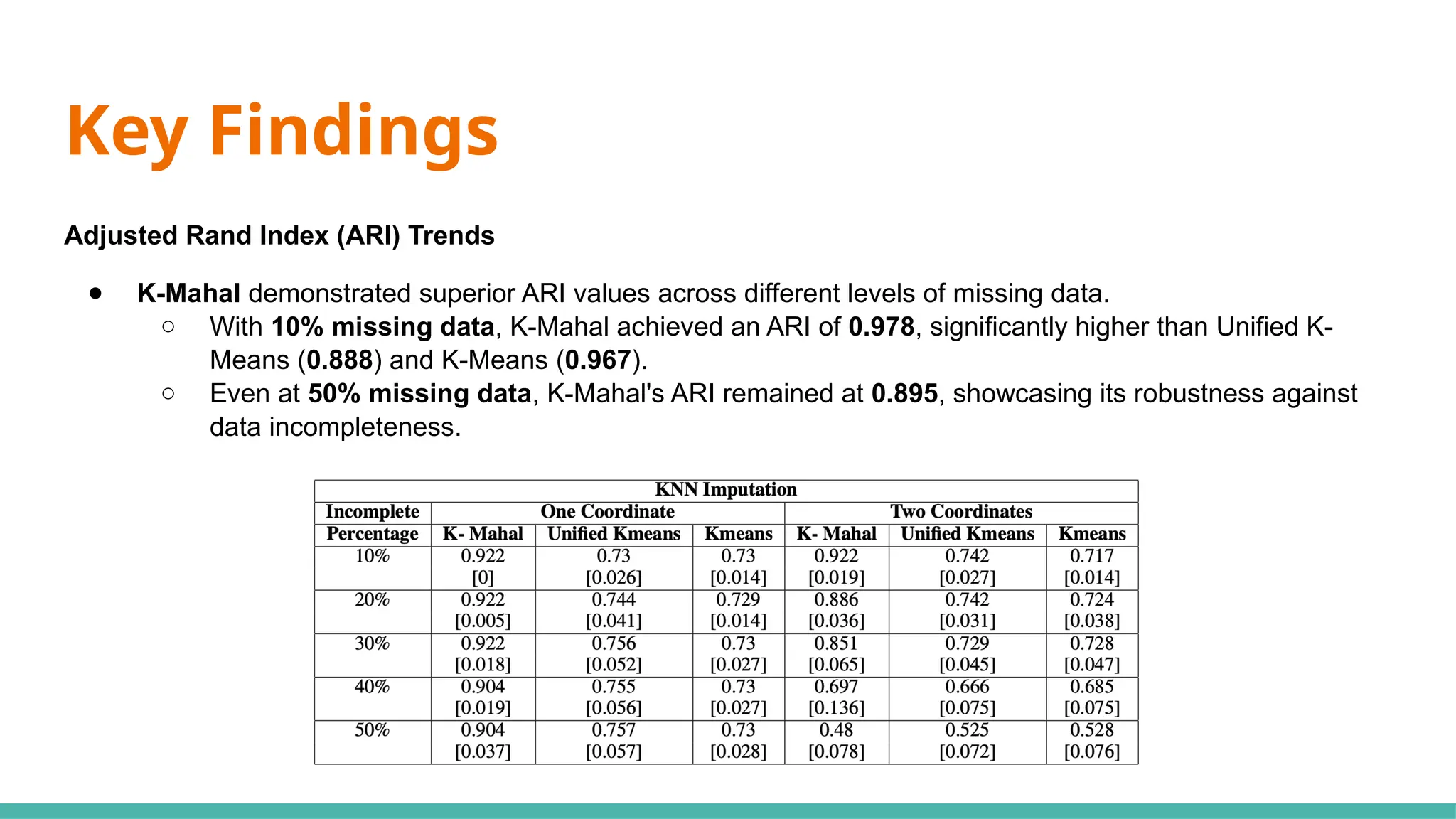
The document discusses a modified k-means clustering algorithm, referred to as k-mahal, which integrates Mahalanobis distance to better handle incomplete datasets and manage non-spherical cluster shapes. Experimental results show that k-mahal significantly outperforms traditional k-means methods, achieving higher adjusted Rand index and normalized mutual information values even with varying levels of data incompleteness. Applications of k-mahal are highlighted across healthcare, finance, and image processing, emphasizing its efficacy in clustering under conditions of missing data.