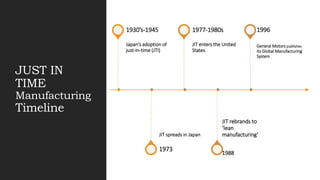
Just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing originated in Japan in the 1930s and was pioneered by Toyota. It aims to reduce waste by receiving materials only as needed in the exact quantities and at the specific times. Key elements of JIT include improved plant layout, reduced setup times, low defect rates, and a flexible workforce. It focuses on eliminating waste and continuous improvement. JIT was implemented through techniques like kanbans, visual controls, preventative maintenance, supplier partnerships, and level loading of production.