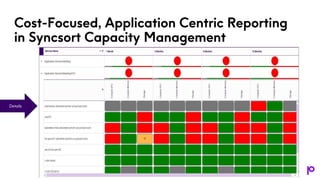
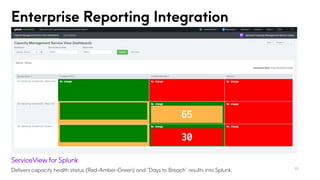
The document discusses the significance of capacity management in IT, highlighting trends for 2024 such as the integration of AI and machine learning, cloud-based tools, and proactive planning for unexpected demand. It emphasizes the importance of formal capacity management to optimize performance, prevent outages, reduce costs, and enable strategic planning, while also detailing the stakeholders involved and the return on investment. Real-world examples illustrate the successful implementation of capacity management insights for improved decision-making and resource allocation.