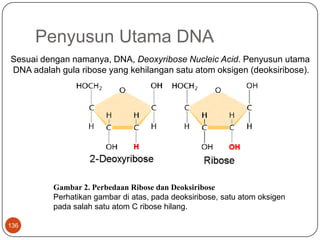
This document summarizes a study that developed and evaluated a quantitative PCR (qPCR) method for rapid detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from positive blood cultures. The qPCR method targeted the ecfX gene and was able to identify P. aeruginosa from blood cultures in less than 1.5 hours with 97% sensitivity and 100% specificity. The qPCR method demonstrated improved speed and equivalent performance compared to conventional identification methods and could help clinicians initiate appropriate antibiotic therapy more quickly.











![12Tabel 1 PrimeroligonukleotidadanProbehibridisasiLightCycler yang digunakandalampemeriksaanPCRa [FAM], fluorescein; [LC705], LightCycler™-Red 705; Ph, 3’-phosphate. b Extracytoplasmic function gene(GenBank accession no. DQ996551).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/j-pi5-110910001251-phpapp02/85/J-pi5-12-320.jpg)

























![KANAMYCINKanamycin is used in molecular biology as a selective agent most commonly to isolate bacteria (e.g., E. coli) which have taken up genes (e.g., of plasmids) coupled to a gene coding for kanamycin resistance (primarily Neomycin phosphotransferase II [NPT II/Neo]). Bacteria that have been transformed with a plasmid containing the kanamycin resistance gene are plated on kanamycin (50-100ug/ml) containing agar plates or are grown in media containing kanamycin (50-100ug/ml). Only the bacteria that have successfully taken up the kanamycin resistance gene become resistant and will grow under these conditions. As a powder kanamycin is white to off-white and is soluble in water (50mg/ml).38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/j-pi5-110910001251-phpapp02/85/J-pi5-38-320.jpg)












![TREATMENTaminoglycosides (gentamicin, amikacin, tobramycin)quinolones (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, and moxifloxacin)cephalosporins (ceftazidime, cefepime, cefoperazone, cefpirome, but notcefuroxime, ceftriaxone, cefotaxime)antipseudomonalpenicillins: ureidopenicillins and carboxypenicillins (piperacillin, ticarcillin: P. aeruginosa is intrinsically resistant to all other penicillins)carbapenems (meropenem, imipenem, doripenem, but notertapenem)polymyxins (polymyxin B and colistin)[31]monobactams (aztreonam)In the rare occasions where infection is superficial and limited (for example, ear infections or nail infections), topicalgentamicin or colistin may be used.50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/j-pi5-110910001251-phpapp02/85/J-pi5-51-320.jpg)






































































![Preparation of the stripPrepare an incubation box (tray and lid) and distribute about 5 ml of distilled water or demineralized water [or any water without additives or chemicals which may release gases (e.g., Cl2, CO2, etc.)] into the honeycombed wells of the tray to create a humid atmosphere.Record the strain reference on the elongated flap of the tray.Remove the strip from its packaging.Place the strip in the tray.Perform the oxidase test on a colony identical to the colony which will be tested.Refer to the Oxidase Test Kit Package Insert.This reaction should be recorded on the result sheet as it constitutes the 21st test.117](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/j-pi5-110910001251-phpapp02/85/J-pi5-123-320.jpg)











![16 S rRNA12616S ribosomal RNA (or 16SrRNA) is a component of the 30S subunit of prokaryoticribosomes. It is 1,542 nucleotides in length.Multiple sequences of 16S rRNA can exist within a single bacterium.[2]In addition to highly conserved primer binding sites, 16S rRNA gene sequences contain hypervariable regions that can provide species-specific signature sequences useful for bacterial identification. As a result, 16S rRNA gene sequencing has become prevalent in medical microbiology as a rapid, accurate alternative to phenotypic methods of bacterial identification[9].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/j-pi5-110910001251-phpapp02/85/J-pi5-135-320.jpg)