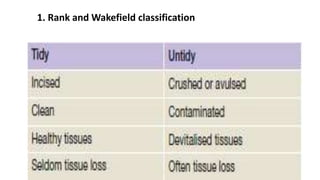
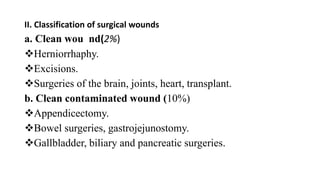
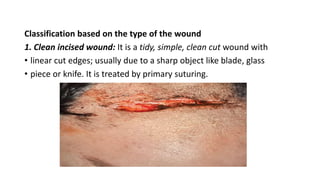
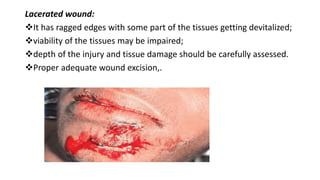
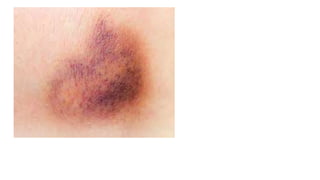
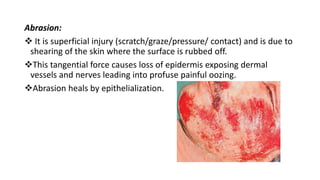
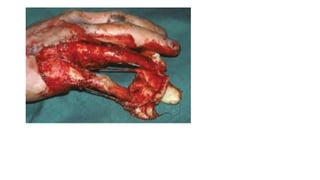
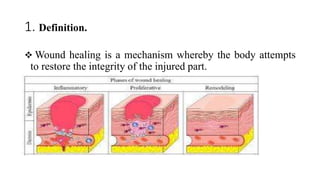
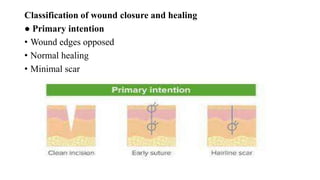
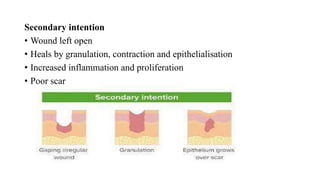
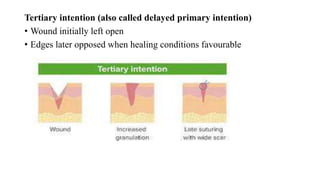
Surgical wounds can be classified based on cleanliness from clean to dirty. Wound healing involves three phases - inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling. The inflammatory phase begins immediately after injury and involves hemostasis and inflammation. The proliferative phase lasts 2-3 weeks and involves granulation tissue formation, angiogenesis, and collagen deposition. During the remodeling phase, collagen matures and wound strength increases. Factors like nutrition, infection, and underlying illness can influence wound healing. Different tissues like bone, nerve, and tendon heal through similar phases but with tissue-specific processes like callus formation or nerve regeneration. Wound closure techniques include primary intention, secondary intention, and tertiary intention.