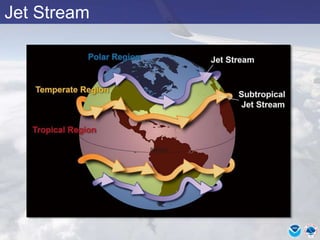
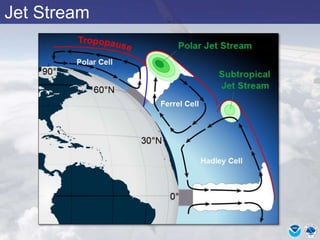
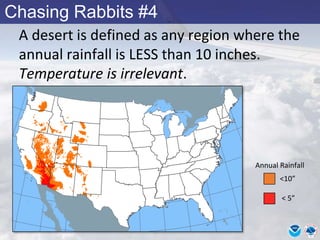
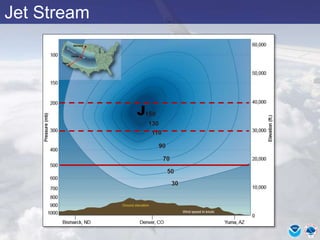
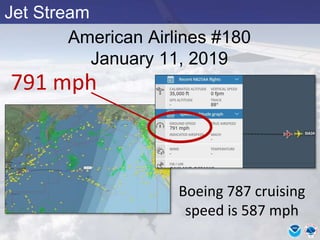
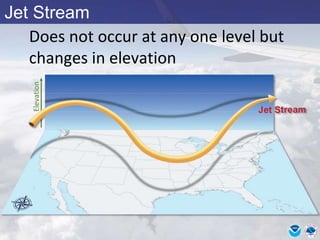
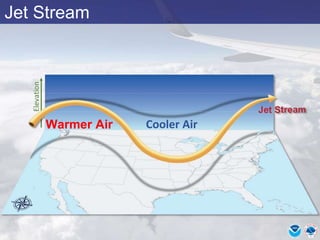
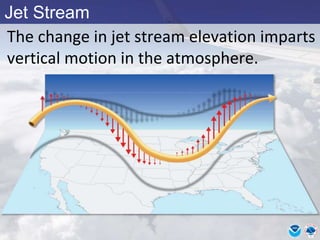
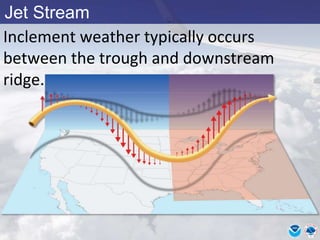
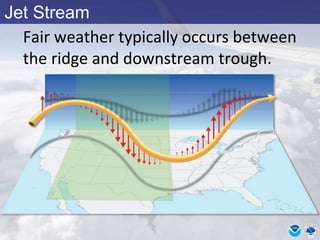
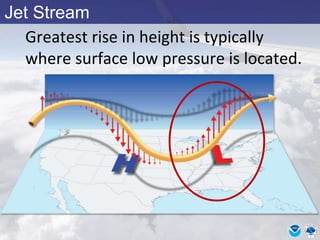
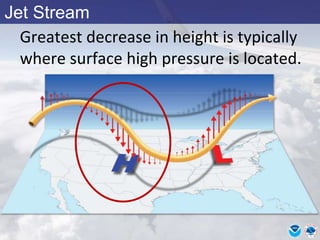
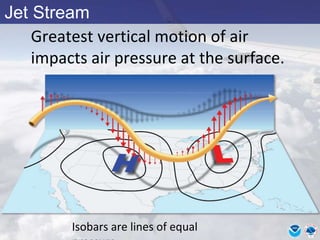
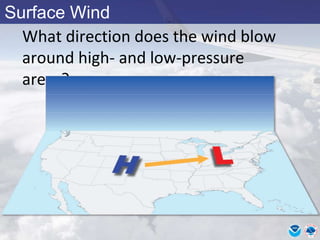
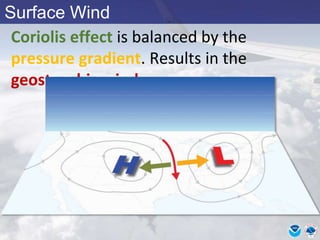
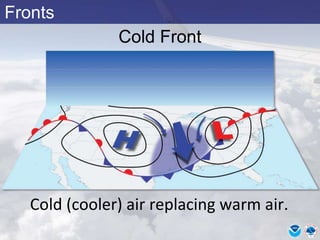
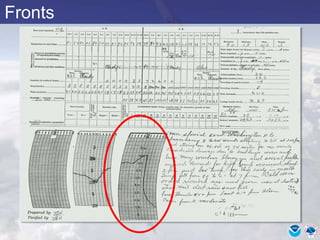
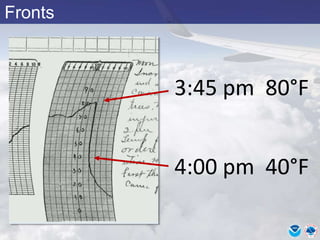
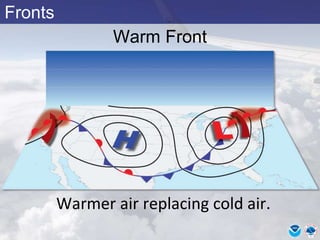
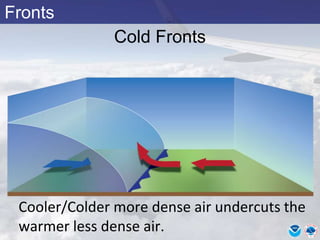
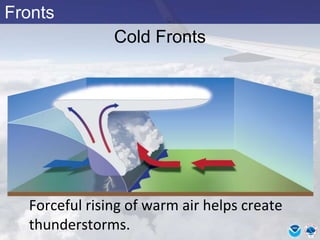
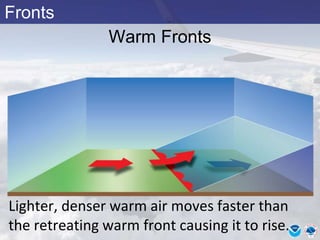
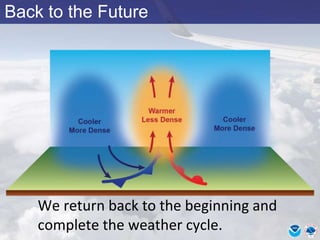
This document provides information about various meteorological concepts including the jet stream, surface winds, high and low pressure systems, and fronts. It defines the jet stream as the atmosphere's response to strong temperature gradients and density changes, occurring where wind speeds are at least 50 knots. It notes that the jet stream elevation is not fixed and can impart vertical motion. Fair weather typically occurs between ridges and troughs while inclement weather is found between troughs and ridges. Cold fronts involve cooler air replacing warm air and may produce thunderstorms, while warm fronts bring warmer air more gradually with clouds and rain ahead of the front.