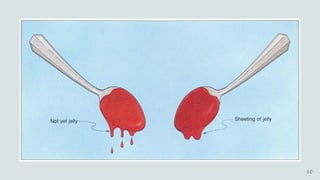
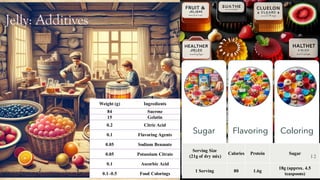
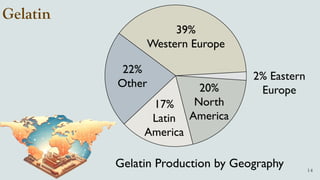
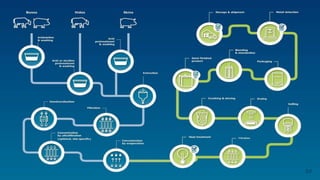
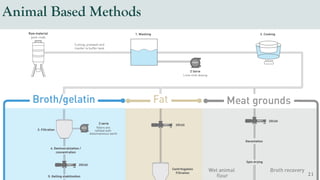
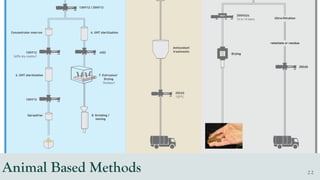
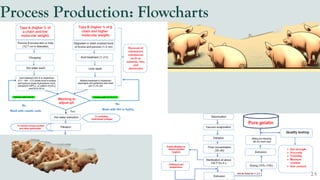
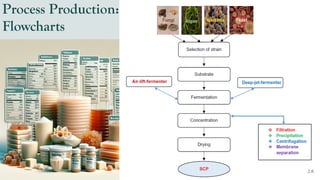
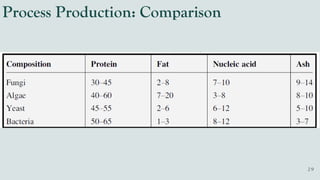
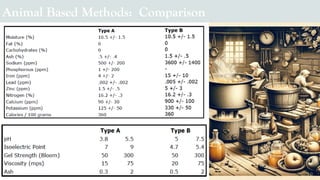
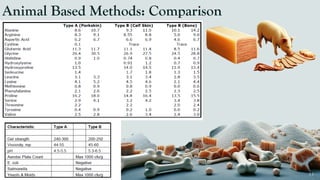
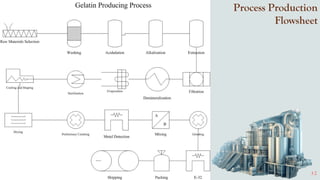
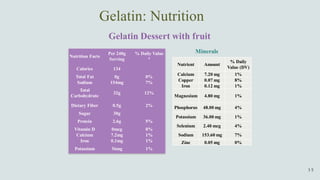
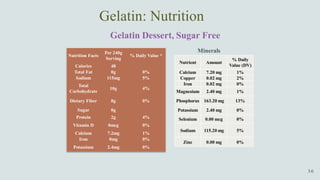
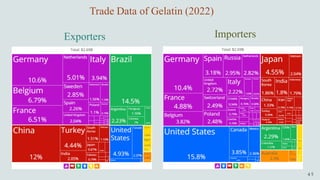
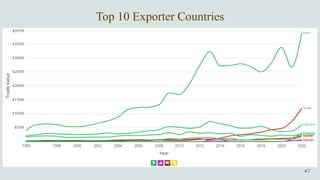
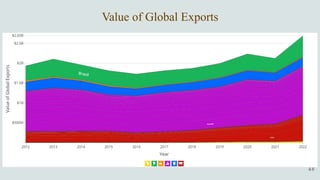
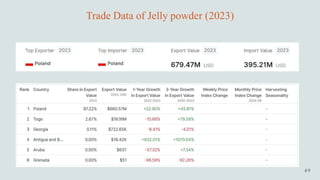
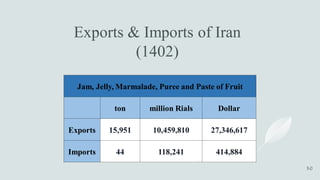
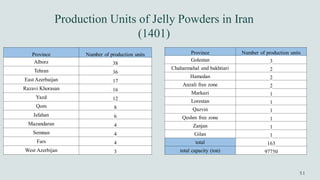
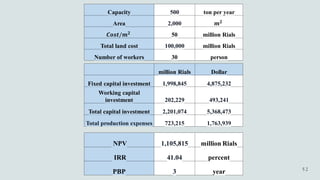
The document details the history and production of gelatin and jelly powders, noting significant milestones from their inception in 1682 to modern-day applications in various industries. It covers nutritional information, production methods, and common substitutes for gelatin, along with its health benefits and disadvantages. Additionally, it includes economic analysis related to gelatin trade and production statistics in Iran.