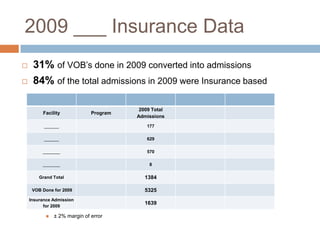
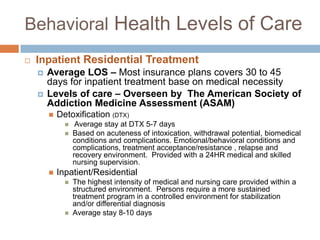
This document summarizes insurance eligibility, coverage, and benefits for residential behavioral health settings. It finds that 84% of admissions in 2009 were insurance-based. It describes differences between in-network and out-of-network coverage for major insurance providers, as well as plan types like PPO, HMO, EPO, and POS. The document also outlines eligibility criteria, covered benefits, and patient financial responsibility. Finally, it reviews behavioral health levels of care and pre-admission screening information required.