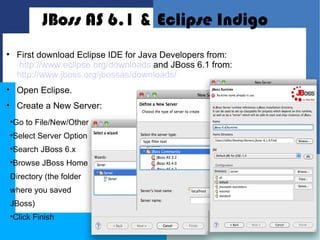
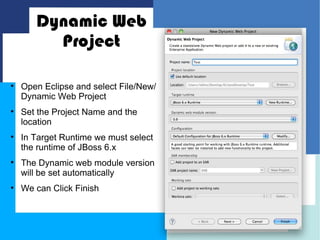
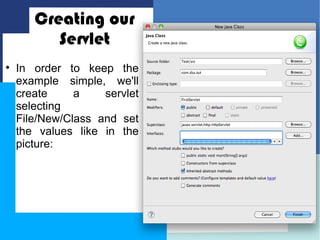
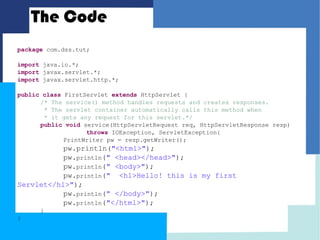
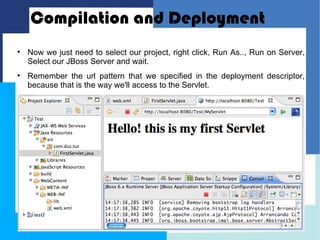
This document discusses how to configure JBoss Application Server within Eclipse to develop Java EE applications. It describes how to download and set up Eclipse and JBoss AS, create a dynamic web project in Eclipse, write a simple servlet class, and define the servlet in a web deployment descriptor. The next steps of compiling, deploying to JBoss AS, and accessing the servlet via its defined URL are also outlined.