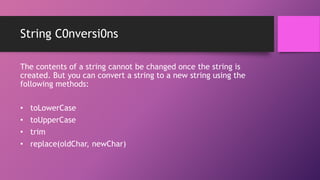
String is an object that represents a sequence of characters. The three main String classes in Java are String, StringBuffer, and StringTokenizer. String is immutable, while StringBuffer allows contents to be modified. Common string methods include length(), charAt(), substring(), indexOf(), and equals(). The StringBuffer class is similar to String but more flexible as it allows adding, inserting and appending new contents.


![Introduction
• A string is sequence (series) of characters.
• A string is NOT an array of characters.
E.g. in C/C++:
char s[20];
• In Java, A String is an object.
• Java has 3 String classes:
• String
• StringBuffer
• StringTokenizer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strings-140114225057-phpapp01/85/Java-Strings-3-320.jpg)
![String Class(2)
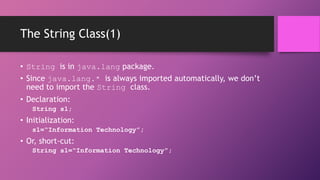
• Because String is a class, then s1 is an object.
• So there should be constructors, methods, or properties.
• String constructors:
• String()
• String(String value)
• String(char[] value)
Ex: String s1 = new String(“IT”);
• You just say:
String s1 = “IT”;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strings-140114225057-phpapp01/85/Java-Strings-5-320.jpg)

![The String Class
• How do I get those methods to use?
• A. You just declare a variable as String.
String s1=“”;
Then, you call a method, say length().
System.out.println(s1.length());
• Let’s try this out:
Public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args){
String s1=“npic”;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strings-140114225057-phpapp01/85/Java-Strings-8-320.jpg)
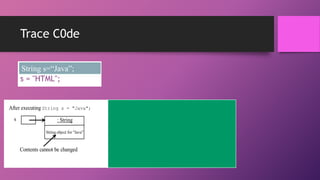
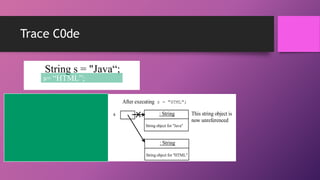

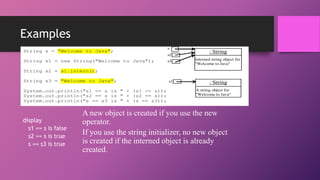

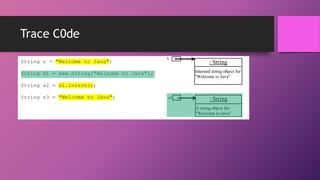
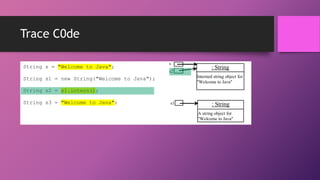
![Retrieving Individual Characters in a String
• Do not use message[0]
• Use message.charAt(index)
• Index starts from 0
Indices
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
message
W
e
l
c
o
m
e
message.charAt(0)
7
8
9
t
o
message.length() is 15
10 11 12 13 14
J
a
v
a
message.charAt(14)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strings-140114225057-phpapp01/85/Java-Strings-19-320.jpg)




![java.lang.StringBuffer
+StringBuffer()
Constructs an empty string buffer with capacity 16
+StringBuffer(capacity: int)
Constructs a string buffer with the specified capacity
+StringBuffer(str: String)
Constructs a string buffer with the specified string
+append(data: char[]): StringBuffer
Appends a char array into this string buffer
+append(data: char[], offset: int, len: int): StringBuffer
Appends a subarray in data into this string buffer
+append(v: aPrimitiveType): StringBuffer
Appends a primitive type value as string to this buffer
+append(str: String): StringBuffer
Appends a string to this string buffer
+capacity(): int
Returns the capacity of this string buffer
+charAt(index: int): char
Returns the character at the specified index
+delete(startIndex: int, endIndex: int): StringBuffer
Deletes characters from startIndex to endIndex
+deleteCharAt(int index): StringBuffer
Deletes a character at the specified index
+insert(index: int, data: char[], offset: int, len: int):
StringBuffer
Inserts a subarray of the data in the array to the buffer at
the specified index
+insert(offset: int, data: char[]): StringBuffer
Inserts data to this buffer at the position offset
+insert(offset: int, b: aPrimitiveType): StringBuffer
Inserts a value converted to string into this buffer
+insert(offset: int, str: String): StringBuffer
Inserts a string into this buffer at the position offset
+length(): int
Returns the number of characters in this buffer
+replace(int startIndex, int endIndex, String str):
StringBuffer
Replaces the characters in this buffer from startIndex to
endIndex with the specified string
+reverse(): StringBuffer
Reveres the characters in the buffer
+setCharAt(index: int, ch: char): void
Sets a new character at the specified index in this buffer
+setLength(newLength: int): void
Sets a new length in this buffer
+substring(startIndex: int): String
Returns a substring starting at startIndex
+substring(startIndex: int, endIndex: int): String
Returns a substring from startIndex to endIndex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strings-140114225057-phpapp01/85/Java-Strings-28-320.jpg)




