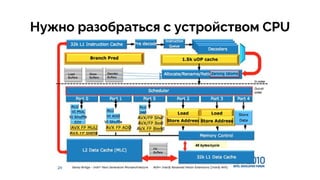
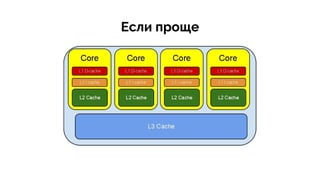
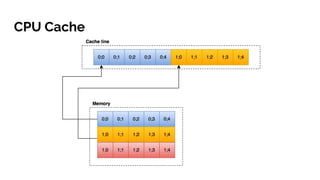
Документ обсуждает оптимизацию производительности CPU в Java с акцентом на важные аспекты, такие как архитектура кода, использование потоков и проблемы, связанные с доступом к кэш-памяти. Проведенные экспериментальные проверки показывают время выполнения различных алгоритмов, включая использование 'false sharing' и 'true sharing', с целью заметного улучшения производительности. Также рассматриваются примеры кода и оптимизации с использованием кастомных объектов и Java 8 функций.



![Задача: Ускорить код
int N = 8192;
byte[][] arr = new byte[N][N];
static boolean check(byte[][] arr, int N)
{
int count = 0;
for(int i=0; i< N; i++)
for(int j=0; j< N; j++)
if(arr[j][i] < 0)
count--;
return count < 0;
}
3_744 ms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-160815094616/85/CPU-Performance-in-Java-4-320.jpg)
![Вариант 1! Уже хорошо.
int N = 8192;
byte[][] arr = new byte[N][N];
static boolean check(byte[][] arr, int N)
{
int count = 0;
for(int i=0; i< N; i++)
for(int j=0; j< N; j++)
if(arr[i][j] < 0)
count--;
return count < 0;
}
264 ms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-160815094616/85/CPU-Performance-in-Java-8-320.jpg)
![Вариант 2! Отлично.
int N = 8192;
byte[][] arr = new byte[N][N];
static boolean check(byte[][] arr, int N)
{
int count = 0;
for(int i=0; i< N; i++)
for(int j=0; j< N; j++)
count += arr[i][j] >> 7;
return count < 0;
}
214 ms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-160815094616/85/CPU-Performance-in-Java-9-320.jpg)


![Работает медленно.
public class IterationThread implements Runnable {
private int index;
private long iterations;
public IterationThread(long iterations, int index) {
this.index = index;
this.iterations = iterations;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(long l = 0; l < iterations; ++l) {
++arr[index];
}
}
}
public class FalseSharing {
private static volatile long arr[] = new long[512];
private static final int THREAD_COUNT = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
private static final long ITERATIONS = 2_000_000_000L;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT];
for(int i = 0; i < THREAD_COUNT; ++i) {
threads[i] = new Thread(new IterationThread(ITERATIONS, i));
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Thread t: threads) {
t.start();
}
for(Thread t: threads) {
t.join();
}
System.out.println("time " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
}
25_406 ms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-160815094616/85/CPU-Performance-in-Java-12-320.jpg)
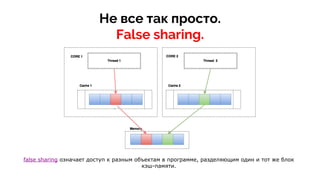
![Работает хорошо.
public class IterationThread implements Runnable {
private int index;
private long iterations;
public IterationThread(long iterations, int index) {
this.index = index;
this.iterations = iterations;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(long l = 0; l < iterations; ++l) {
++arr[index];
}
}
}
public class TrueSharing {
private static volatile long arr[] = new long[512];
private static final int THREAD_COUNT = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
private static final long ITERATIONS = 2_000_000_000L;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT];
for(int i = 0; i < THREAD_COUNT; ++i) {
threads[i] = new Thread(new IterationThread(ITERATIONS, (i+1)*8));
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Thread t: threads) {
t.start();
}
for(Thread t: threads) {
t.join();
}
System.out.println("time " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
}
4_949 ms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-160815094616/85/CPU-Performance-in-Java-14-320.jpg)

![False sharing with custom object
public static class IterationThread implements
Runnable {
private int index;
private long iterations;
public IterationThread(long iterations, int index) {
this.index = index;
this.iterations = iterations;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(long l = 0; l < iterations; ++l) {
++arr[index].val;
}
}
}
public class FalseSharing
{
private static final int THREAD_COUNT = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
private static final long ITERATIONS = 2_000_000_000L;
private static MyObject arr[] = new MyObject[THREAD_COUNT];
static {
for (int i = 0; i <arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = new MyObject();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT];
for(int i = 0; i < THREAD_COUNT; ++i) {
threads[i] = new Thread(new IterationThread(ITERATIONS, i));
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Thread t: threads) {
t.start();
}
for(Thread t: threads) {
t.join();
}
System.out.println("time " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
}
149_743 ms
public static class MyObject{
public volatile long val = 0L;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-160815094616/85/CPU-Performance-in-Java-16-320.jpg)
![Java 7 Padding.
public static class IterationThread implements
Runnable {
private int index;
private long iterations;
public IterationThread(long iterations, int index) {
this.index = index;
this.iterations = iterations;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(long l = 0; l < iterations; ++l) {
arr[index].incrementAndGet();
}
}
}
public class FalseSharing
{
private static final int THREAD_COUNT = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
private static final long ITERATIONS = 2_000_000_000L;
private static MyObject arr[] = new MyObject[THREAD_COUNT];
static {
for (int i = 0; i <arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = new MyObject();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT];
for(int i = 0; i < THREAD_COUNT; ++i) {
threads[i] = new Thread(new IterationThread(ITERATIONS, i));
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Thread t: threads) {
t.start();
}
for(Thread t: threads) {
t.join();
}
System.out.println("time " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
}
14_539 ms
public static class MyObject extends AtomicLong {
public volatile long p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6 = 7L;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-160815094616/85/CPU-Performance-in-Java-17-320.jpg)
![Java 8. @sun.misc.Contended
public static class IterationThread implements
Runnable {
private int index;
private long iterations;
public IterationThread(long iterations, int index) {
this.index = index;
this.iterations = iterations;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(long l = 0; l < iterations; ++l) {
arr[index].incrementAndGet();
}
}
}
public class FalseSharing
{
private static final int THREAD_COUNT = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
private static final long ITERATIONS = 2_000_000_000L;
private static MyObject arr[] = new MyObject[THREAD_COUNT];
static {
for (int i = 0; i <arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = new MyObject();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT];
for(int i = 0; i < THREAD_COUNT; ++i) {
threads[i] = new Thread(new IterationThread(ITERATIONS, i));
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Thread t: threads) {
t.start();
}
for(Thread t: threads) {
t.join();
}
System.out.println("time " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
}
14_983 ms
// unlock JVM option: -XX:-RestrictContended
@Contended
public static class MyObject extends AtomicLong {
public volatile long anyVal;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-160815094616/85/CPU-Performance-in-Java-18-320.jpg)
