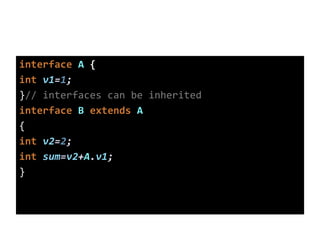
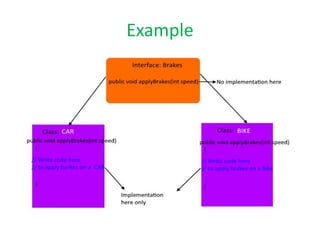
Interfaces in Java provide a common behavior that classes can implement. They declare public abstract methods and public static final variables. Classes that implement interfaces must define the interface's abstract methods but can determine how they are implemented. Interfaces allow for multiple inheritance by allowing classes to implement multiple interfaces and provide a consistent way for unrelated classes to share common behaviors.