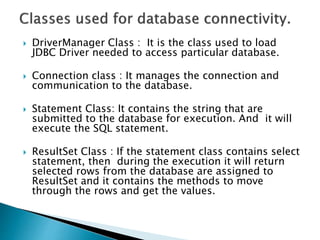
This document discusses the key classes used in Java database programming - DriverManager, Connection, Statement, and ResultSet. It also outlines the basic steps to connect to a database and execute queries: 1) import necessary packages, 2) register the JDBC driver, 3) open a connection, 4) execute queries using Statement or PreparedStatement, 5) extract data from the ResultSet, and 6) close the connection. Finally, it provides examples of using these classes and methods to perform common database operations like selecting, inserting, updating, and deleting data.














![ DefaultTableModel dtm=(javax.swing.table.DefaultTableModel)studenttab.getModel();
int rows=dtm.getRowCount();
if(rows>0)
{
for(int i=0;i<rows;i++)
{
dtm.removeRow(0);
}
}
try
{
Class.forName("java.sql.DriverManager");
Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydbll“,"root","");
Statement stmt=con.createStatement();
String str="select * from student";
ResultSet rs=stmt.executeQuery(str);
while(rs.next())
{
int sid=rs.getInt("stdid");
String sname= rs.getString("stdname");
int mark= rs.getInt(“mark");
Object obj[]={sid,sname,mark};
dtm.addRow(obj);
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javadatabseconnectvity-160528192843/85/Java-Databse-Connectvity-Alex-Jose-16-320.jpg)

