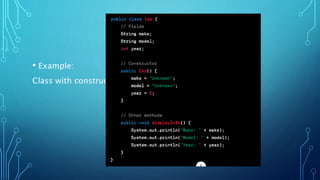
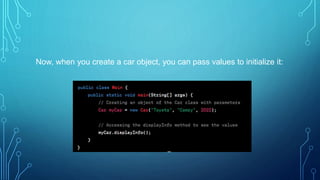
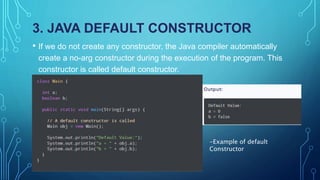
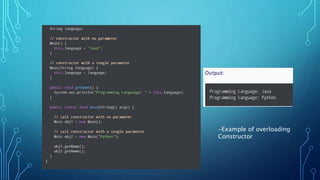
Constructors in Java are special methods that are used to initialize objects. They are invoked when an object is created and have the same name as the class. Constructors can be overloaded and can take parameters to initialize object state. They ensure objects are ready for use by setting initial values and supporting inheritance. Constructors have no return type and implicitly return an instance of the class. If no constructors are defined, a default no-arg constructor is provided.