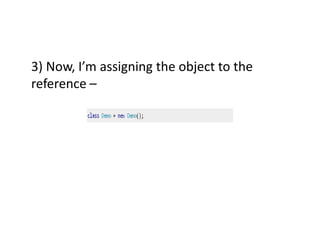
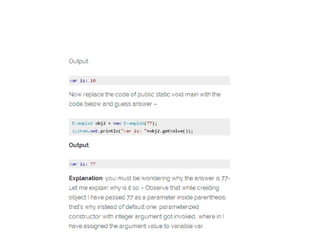
The document provides an introduction to constructors in Java programming, explaining their purpose, types, and how to call them. It details the differences between default and parameterized constructors, constructor chaining, and important points regarding access specifiers and inheritance. Additionally, it clarifies misconceptions regarding constructor existence and functionality within objects and classes.