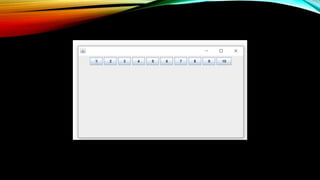
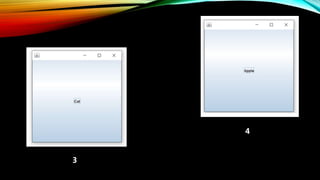
The document discusses Java's CardLayout and FlowLayout classes, detailing their functionalities and how to implement them. CardLayout allows only one component to be visible at a time, utilizing methods to navigate between components, while FlowLayout arranges components in a line with multiple alignment options. It provides example code for both layouts, demonstrating their usage within Java applications.






![37.}
38.public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
39.{
40.
41.crd.next(cPane);
42.}
43.
44.
45.public static void main(String argvs[])
46.{
47.CardLayoutExample1 crdl = new CardLayoutExample1();
48.
49.
50.crdl.setSize(300, 300);
51.crdl.setVisible(true);
52.crdl.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
53.}
54.}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javacardandflowlayout-211115025324/85/Java-card-and-flow-layout-7-320.jpg)



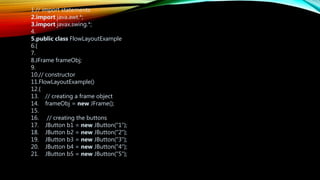
![22. JButton b6 = new JButton("6");
23. JButton b7 = new JButton("7");
24. JButton b8 = new JButton("8");
25. JButton b9 = new JButton("9");
26. JButton b10 = new JButton("10");
27.Public void init (){
28.frameObj.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
29. // adding the buttons to frame
30. frameObj.add(b1); frameObj.add(b2); frameObj.add(b3); frameObj.add(b4);
31. frameObj.add(b5); frameObj.add(b6); frameObj.add(b7); frameObj.add(b8);
32. frameObj.add(b9); frameObj.add(b10);
33. // therefore, alignment is center
34.}
35. // main method
36.public static void main(String argvs[])
37.{
38. new FlowLayoutExample();
39.}
40.}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javacardandflowlayout-211115025324/85/Java-card-and-flow-layout-13-320.jpg)