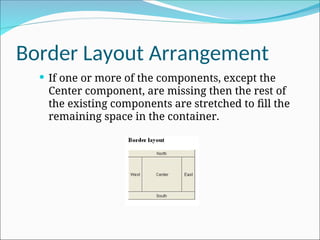
The document outlines various layout managers in GUI design, including Flow Layout, Grid Layout, Border Layout, and Card Layout, each controlling component positioning within containers. It describes how these managers adjust component size and arrangement based on container dimensions and layout specifications. Constructors and alignment options for each layout type are also detailed to guide implementation.