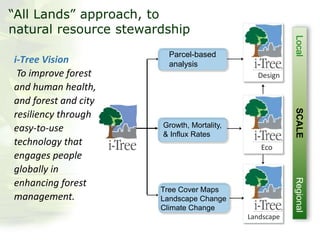
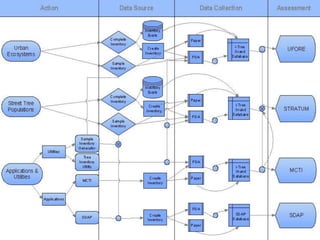
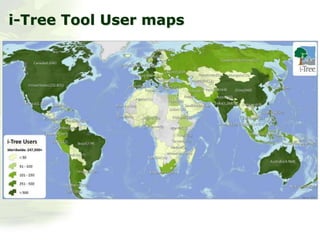
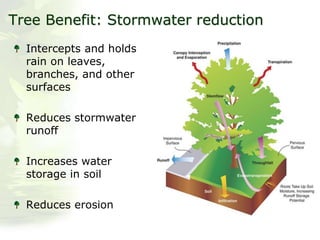
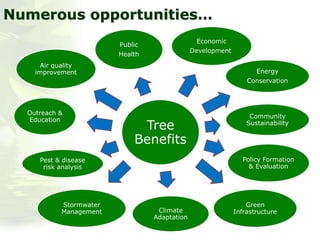
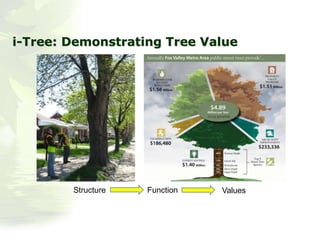
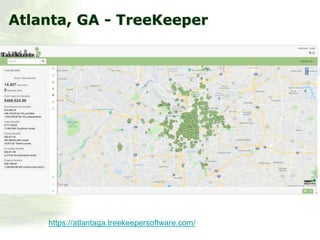
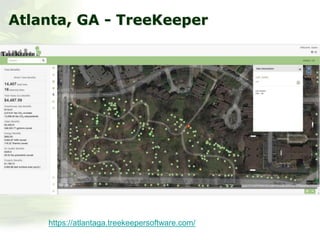
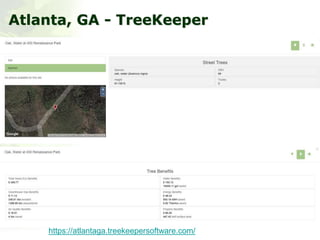
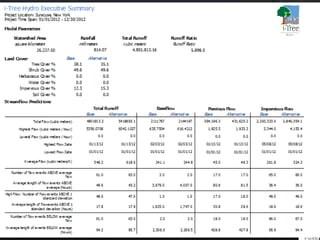
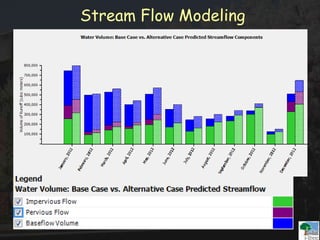
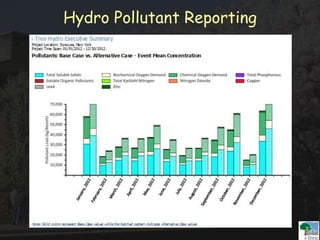
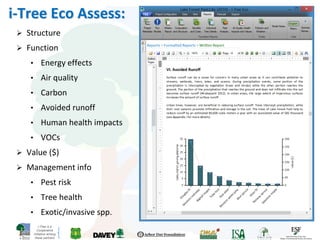
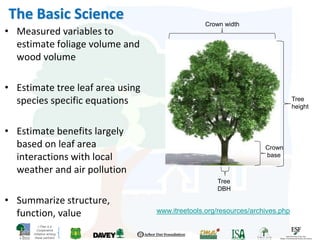
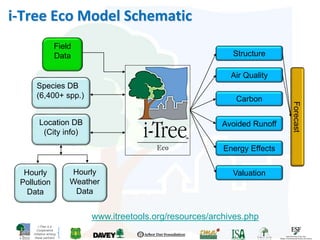
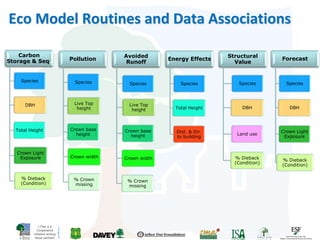
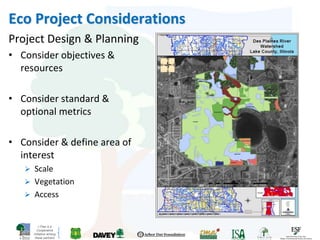
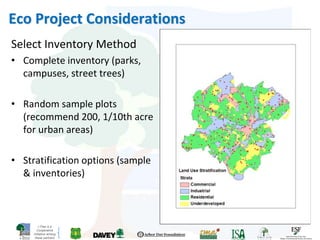
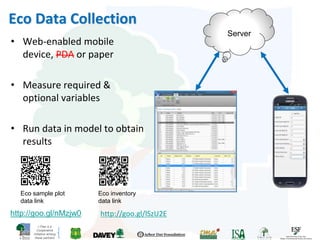
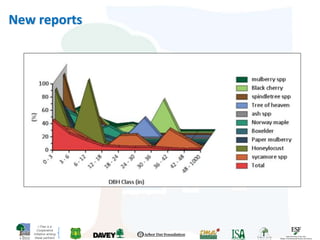
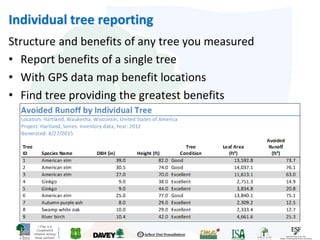
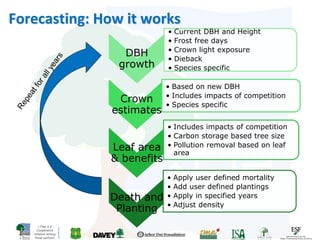
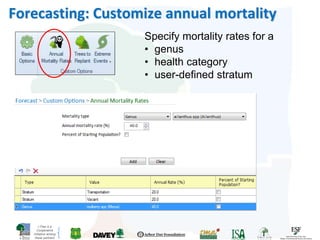
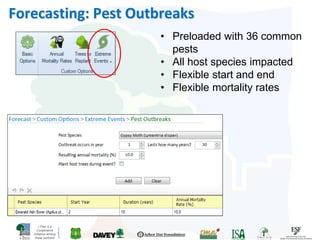
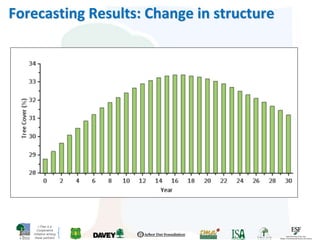
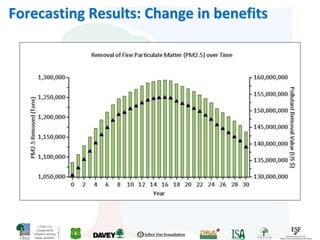
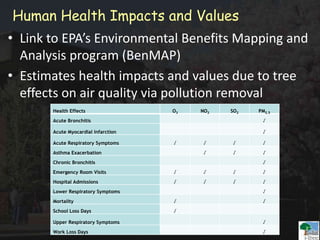
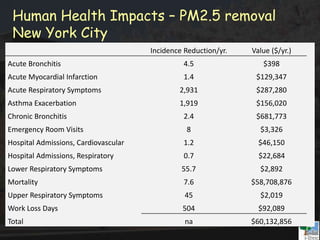
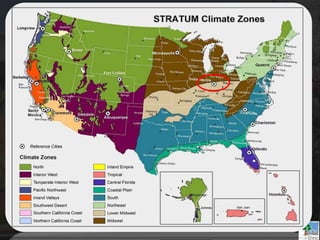
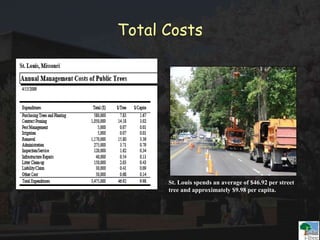
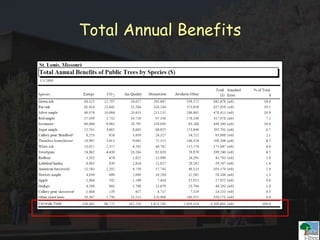
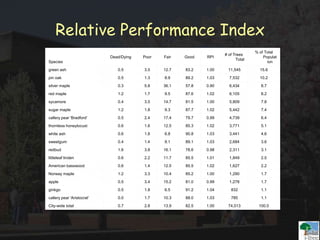
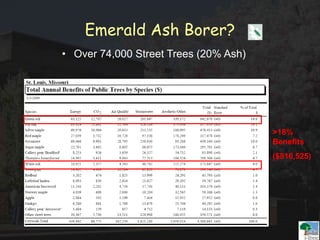
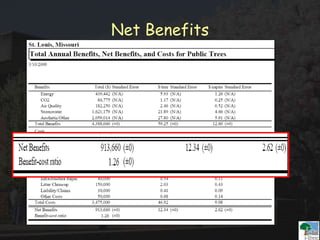
The i-Tree initiative, launched by the Georgia Urban Forestry Council, aims to enhance urban forest management through a suite of web-based tools that assess tree structure, function, and value. The program provides detailed management guides, including recommendations for tree planting and maintenance to improve forest and human health, while also addressing urban challenges like stormwater management and air quality. i-Tree serves various stakeholders, including governments, non-profits, universities, and ecological consultants, offering insights into the benefits of trees, such as carbon sequestration and energy conservation.