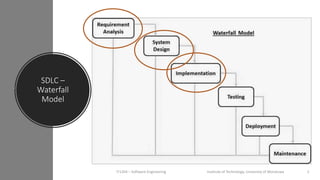
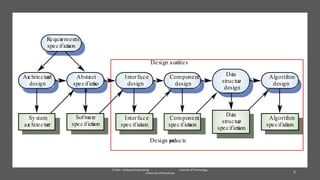
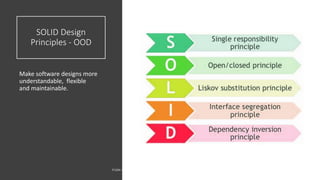
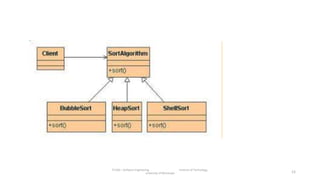
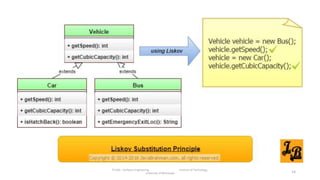
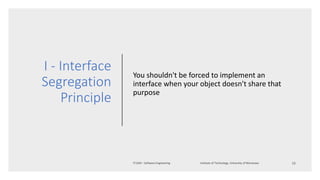
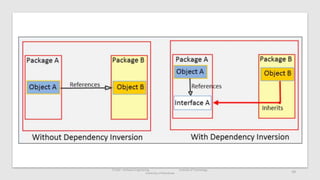
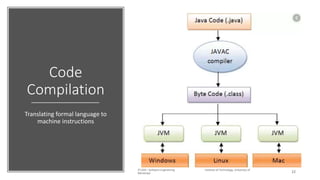
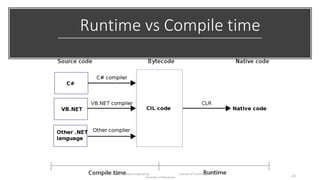
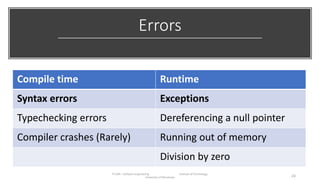
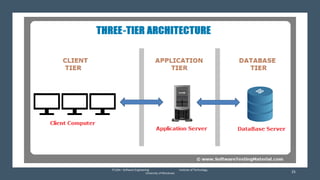
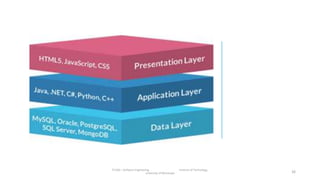
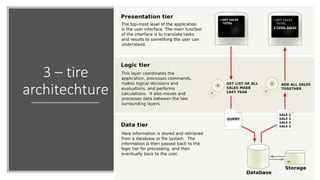
The document discusses the software engineering process, focusing on the waterfall model and various design strategies such as functional and object-oriented design. It outlines essential design principles, including the Single Responsibility Principle and Dependency Inversion Principle, which improve code maintainability. The document also mentions the importance of testing, including both manual and automated approaches, to identify errors and ensure software quality.