The document is a presentation on software engineering that covers topics such as:
- The definitions of engineering and software engineering;
- The process of software evolution;
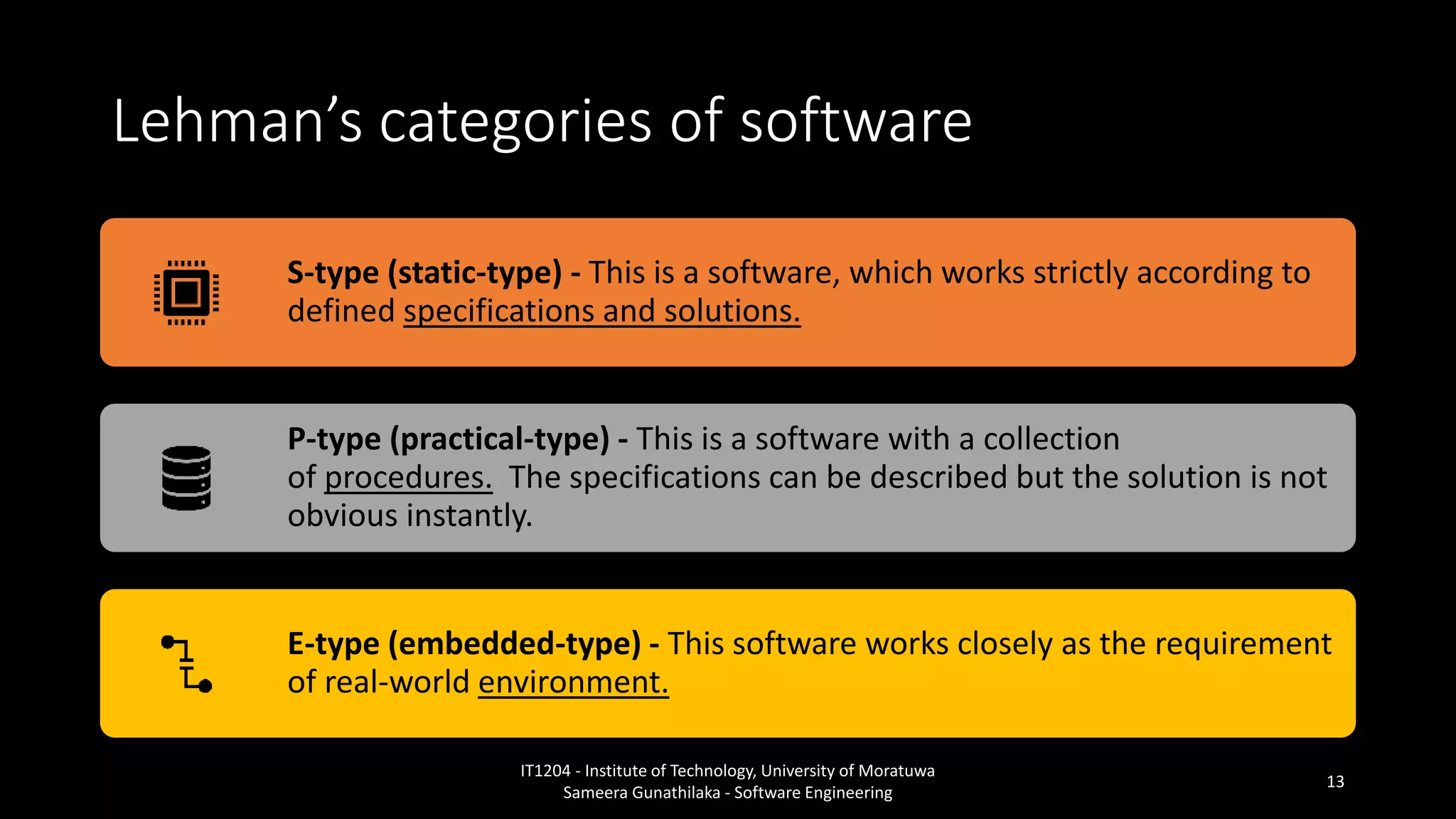
- Categories of software by Lehman;
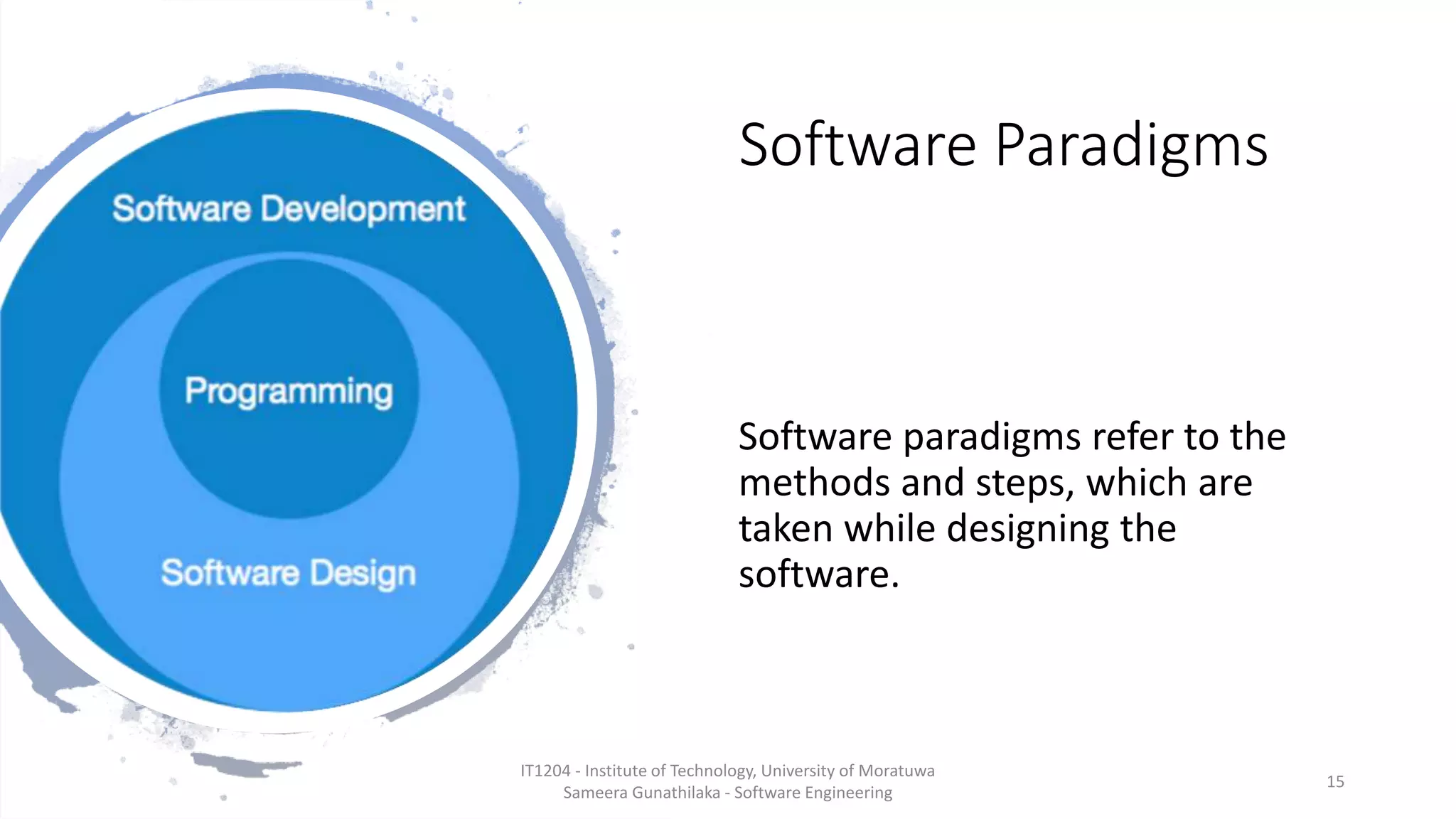
- Software engineering paradigms and the software development life cycle (SDLC);
- Characteristics of good software including operational, transitional, and maintenance characteristics;
- The history of software engineering from 1945 to 2015.

























![History of Software
Engineering
• 1945 to 1965: The origins
• 1965 to 1985: The software crisis
• 1985 to 1989: "No Silver Bullet“
• 1990 to 1999: Prominence of the Internet
• 2000 to 2015: Lightweight methodologies
[Assignment]
IT1204 - Institute of Technology, University of Moratuwa
Sameera Gunathilaka - Software Engineering
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontosoftwareengineering-191023162525/75/IT1204-Introduction-to-software-engineering-L1-32-2048.jpg)
