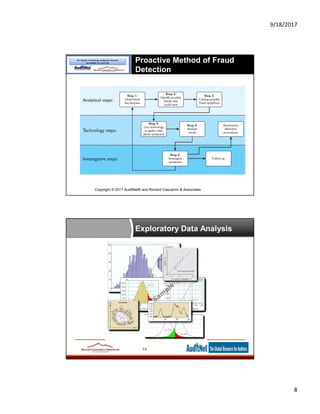
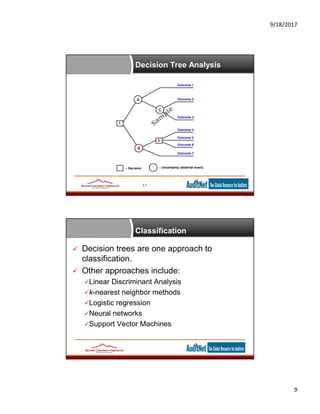
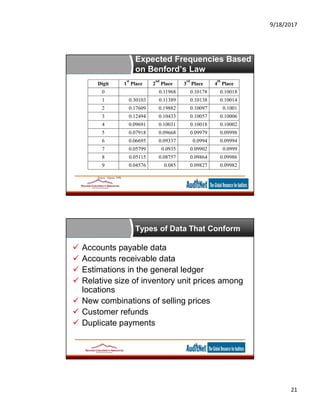
The document provides information about data analytics for auditors, featuring insights from experts Jim Kaplan and Richard Cascarino, along with details about auditnet®, a comprehensive resource for audit professionals. It covers topics such as probability theory, fraud detection techniques, data mining, and statistical analysis relevant to internal audit practices. Furthermore, it outlines the necessary conditions and procedures for obtaining CPE credits during webinars conducted by auditnet®.