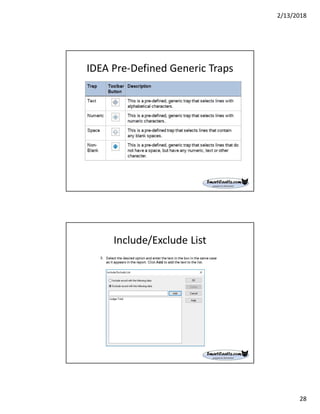
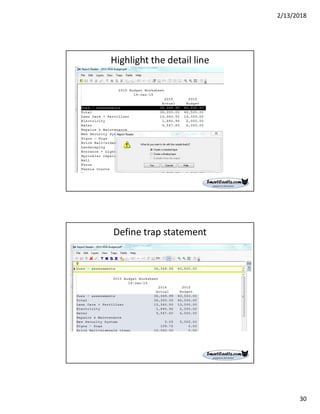
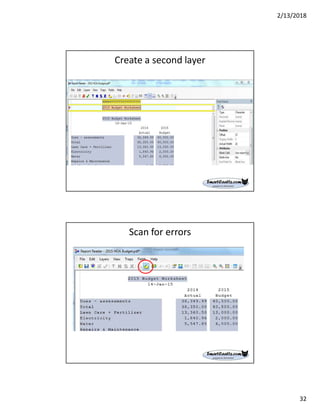
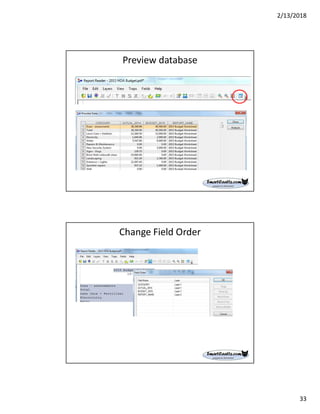
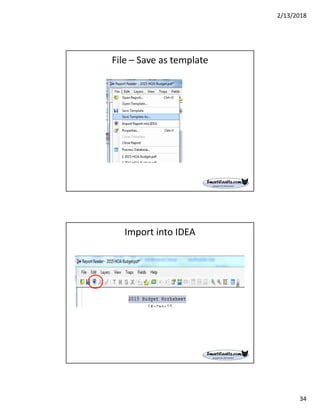
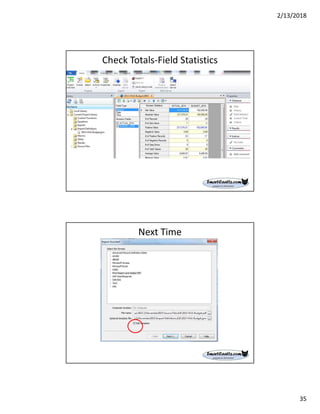
The document discusses best practices for internal auditors on data mining print reports, emphasizing the need for accurate data extraction and the importance of data governance and management. It outlines the resources available through auditnet®, including templates, webinars, and tools for auditing technology. Additionally, it highlights the critical aspects of obtaining, validating, and documenting data analysis processes to improve the effectiveness of audits.