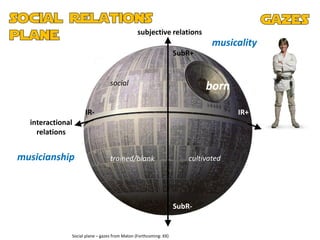
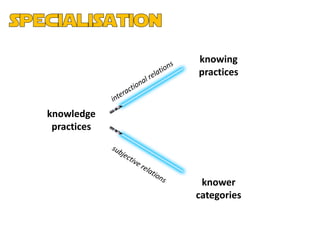
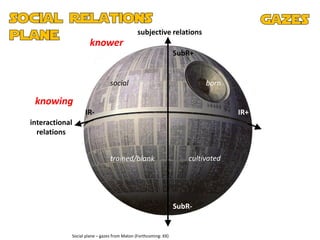
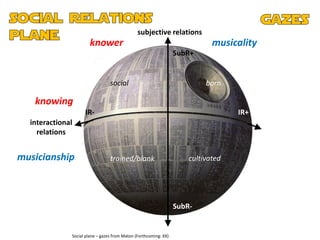
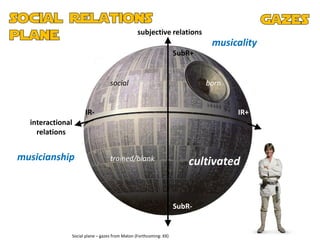
The document discusses the presentation and positioning of knowers in jazz performance student texts, focusing on knowledge practices and epistemic relations in music education. It emphasizes the role of social relations and individual musicality in understanding and producing jazz. The analysis includes various examples of students' interactions with jazz standards and their development as musicians through influences and personal expression.











![Prominence:
‘greatest’, ‘famous’, ‘established’
Normality 28
Individuality:
‘unique’, ‘virtuoso’, ‘prodigy’
Judgement Capacity 39
“[each solo] is executed with
unfathomably virtuosic
technique”
“Elliot Mason can only be
described as a musical prodigy”
Tenacity 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isfcjazzisstrongpdf-120715220352-phpapp02/85/The-Jazz-is-strong-in-this-one-ISFC-21-320.jpg)
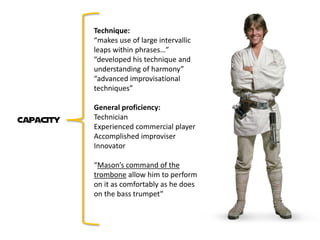
![This command [judg: cap] of advanced [judg: cap]
improvisational techniques coupled with a strong
sense of musicality [judg: cap] makes him an
impressive [app: reac: imp] musician to behold and one
of the most formidable [app: reac: imp]
trombonists/bass trumpeters in the world today.
Further still, he manages [judg: cap] to have a
completely unique [judg: norm] musical voice.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isfcjazzisstrongpdf-120715220352-phpapp02/85/The-Jazz-is-strong-in-this-one-ISFC-23-320.jpg)
![Regardless of the instruments he plays, and perhaps
most [grad: force: int] importantly [app: val], Mason is
an exceptionally [judg: norm; grad: force: int] musical
player [judg: cap], not just [grad: force: int] an
impressive [judg: norm] technician [judg: cap].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isfcjazzisstrongpdf-120715220352-phpapp02/85/The-Jazz-is-strong-in-this-one-ISFC-24-320.jpg)