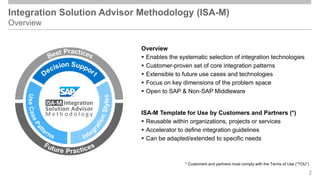
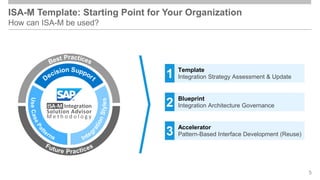
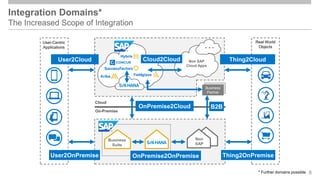
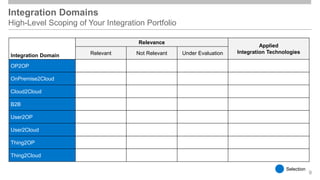
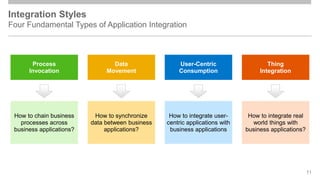
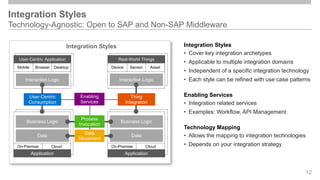
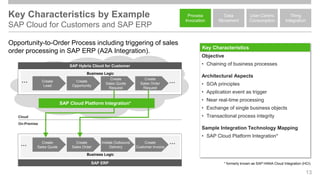
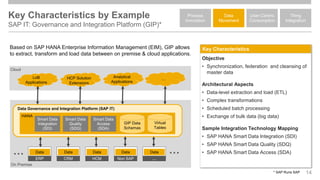
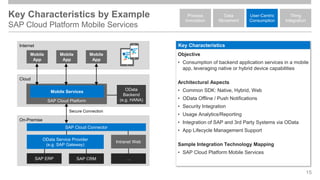
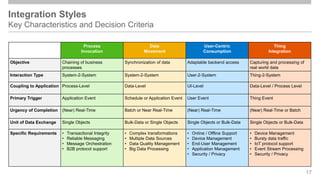
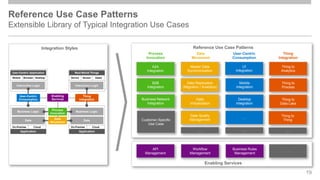
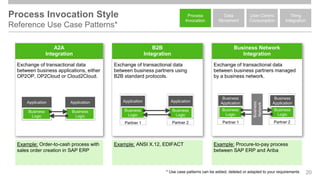
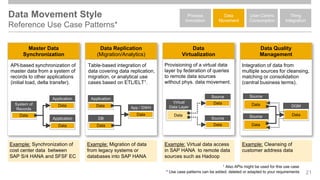
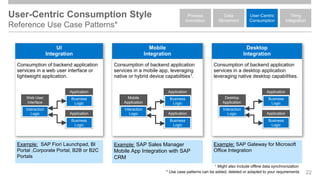
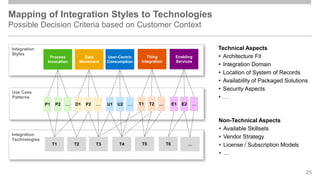
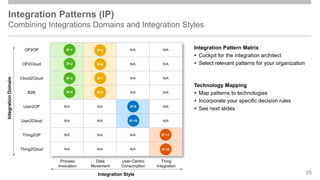
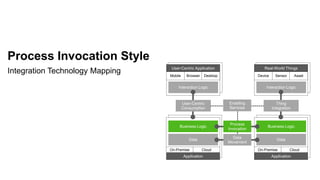
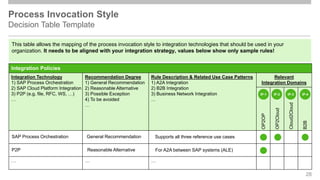
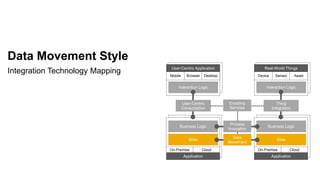
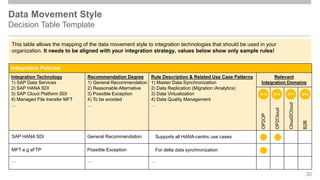
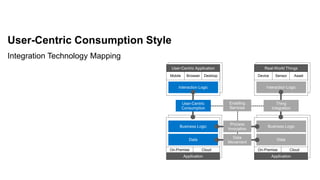
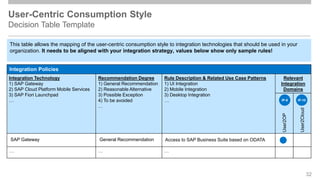
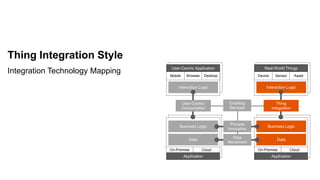
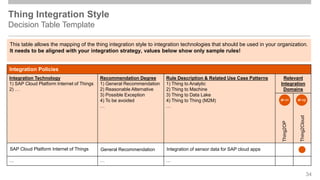
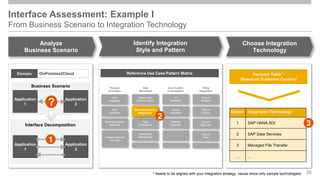
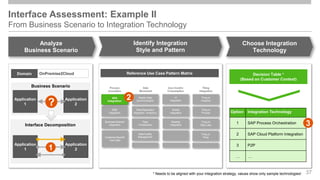
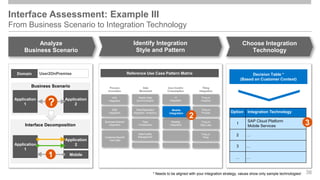
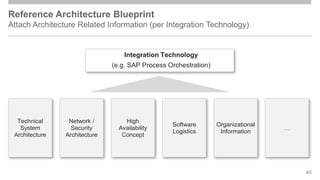
The document outlines the Integration Solution Advisor Methodology (ISA-M) provided by SAP SE, which offers templates for systematic integration technology selection, core integration patterns, and guidelines for integration projects. It includes terms of use that users must comply with when using the ISA-M templates, clarifying SAP's lack of responsibility for content and liability for damages. Additionally, the document elaborates on various integration styles, technologies, and use case patterns relevant to modern integration strategies.