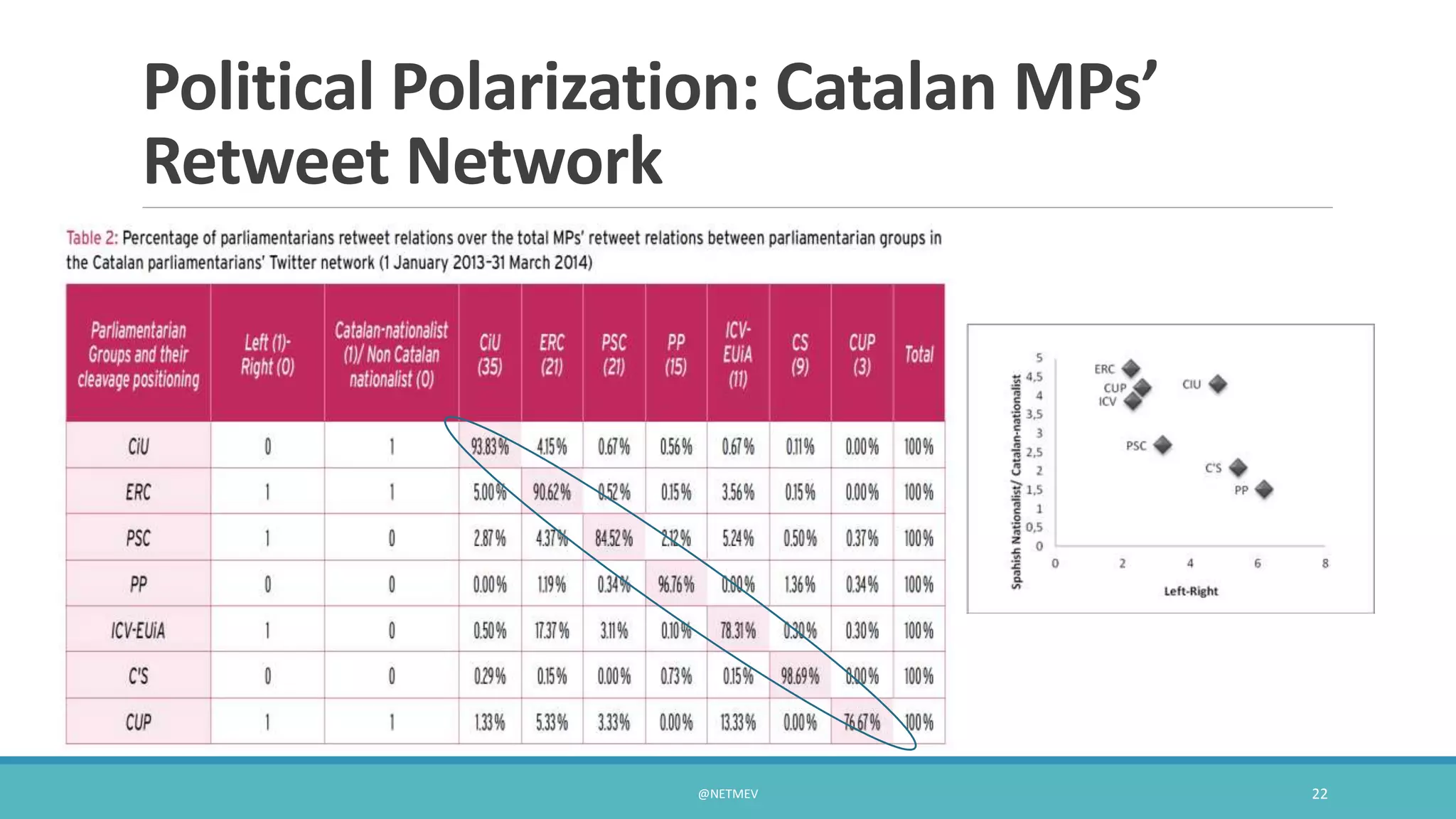
The document explores the impact of social media, particularly Twitter, on traditional politics, focusing on a case study of the Catalan Parliament. It examines how social media facilitates communication between politicians of differing ideologies and identifies new opinion leaders emerging from ordinary members of parliament. The study finds that social media is challenging traditional political hierarchies, but also notes limitations in the analysis of communication content.