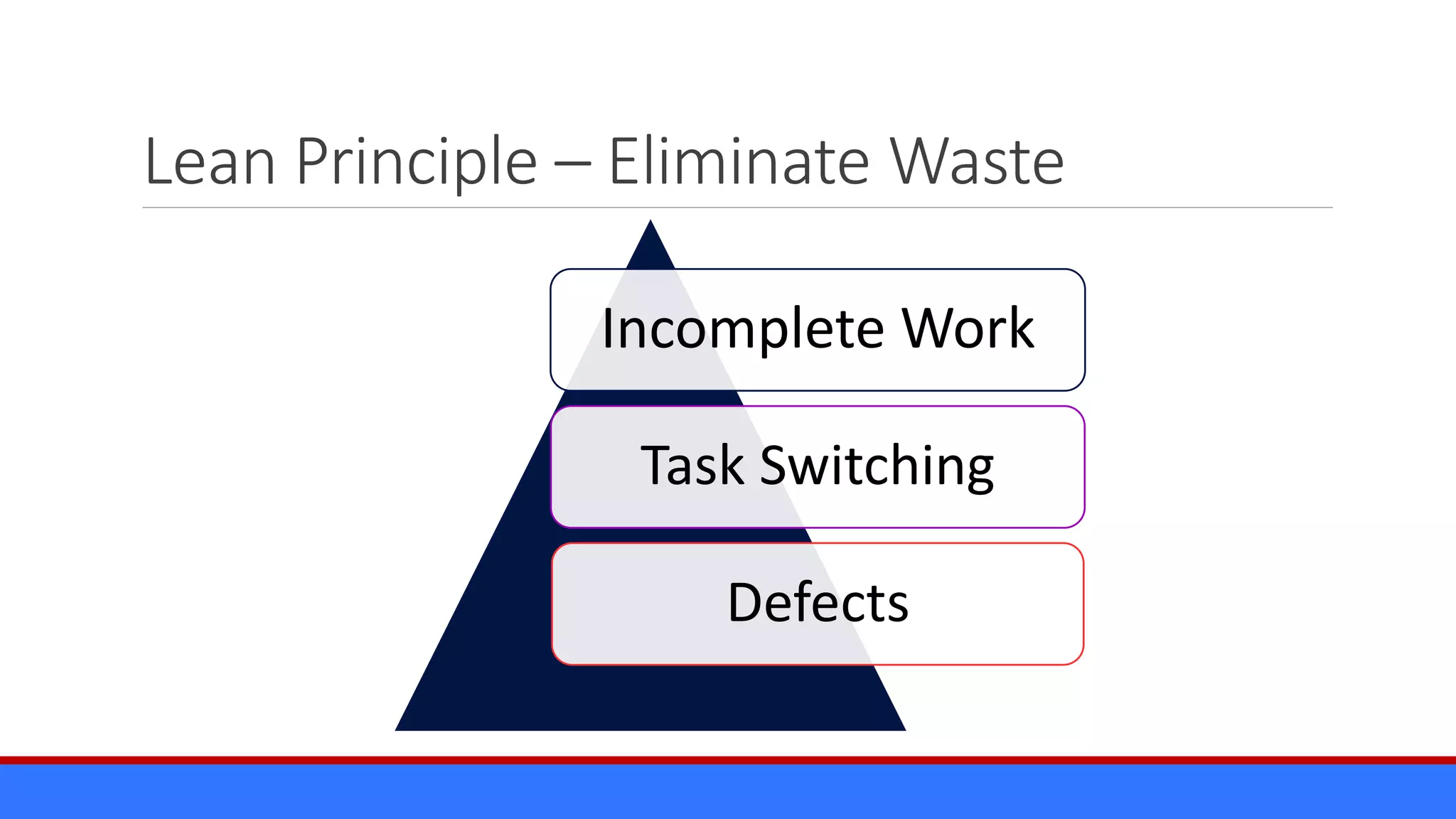
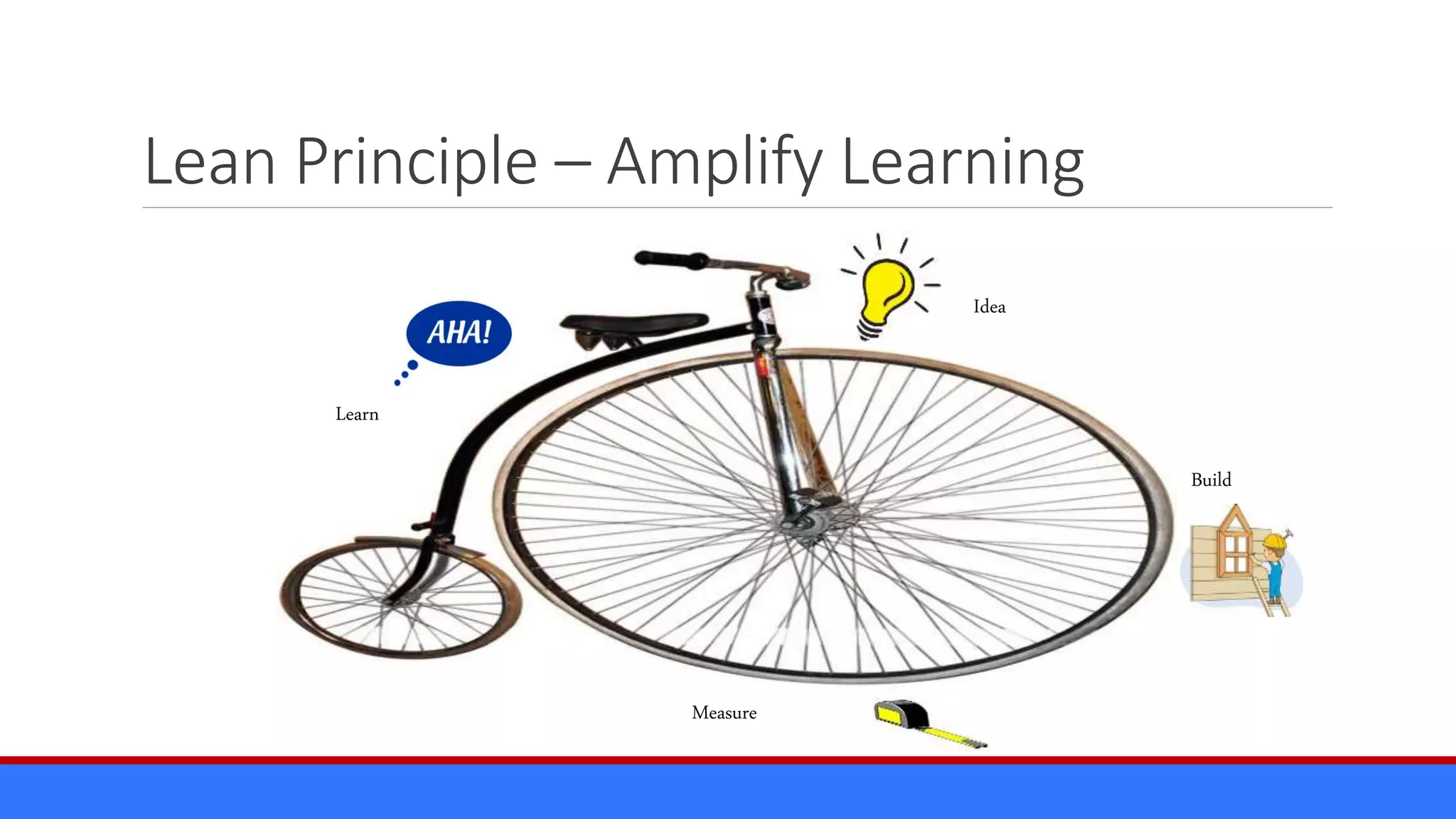
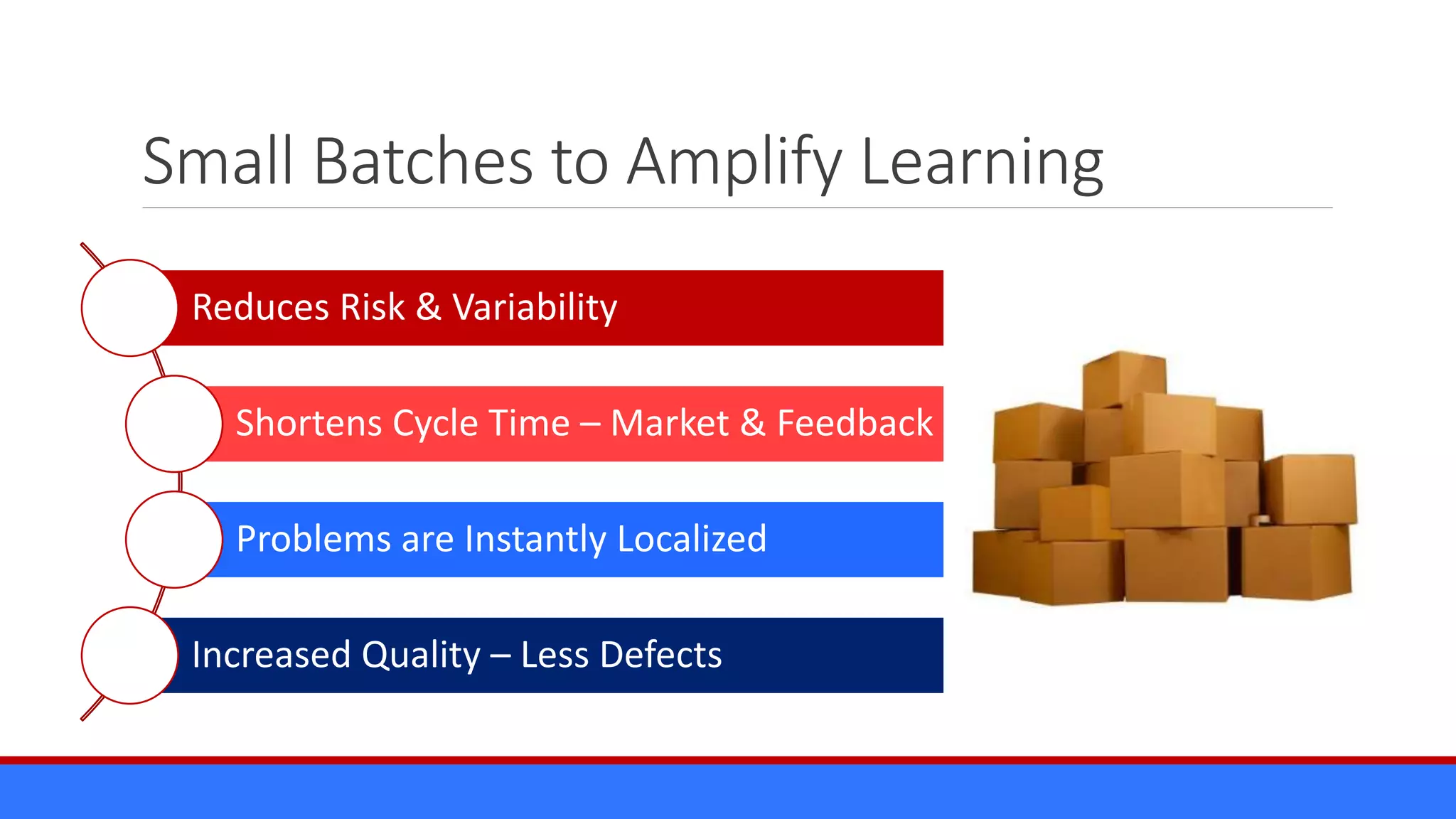
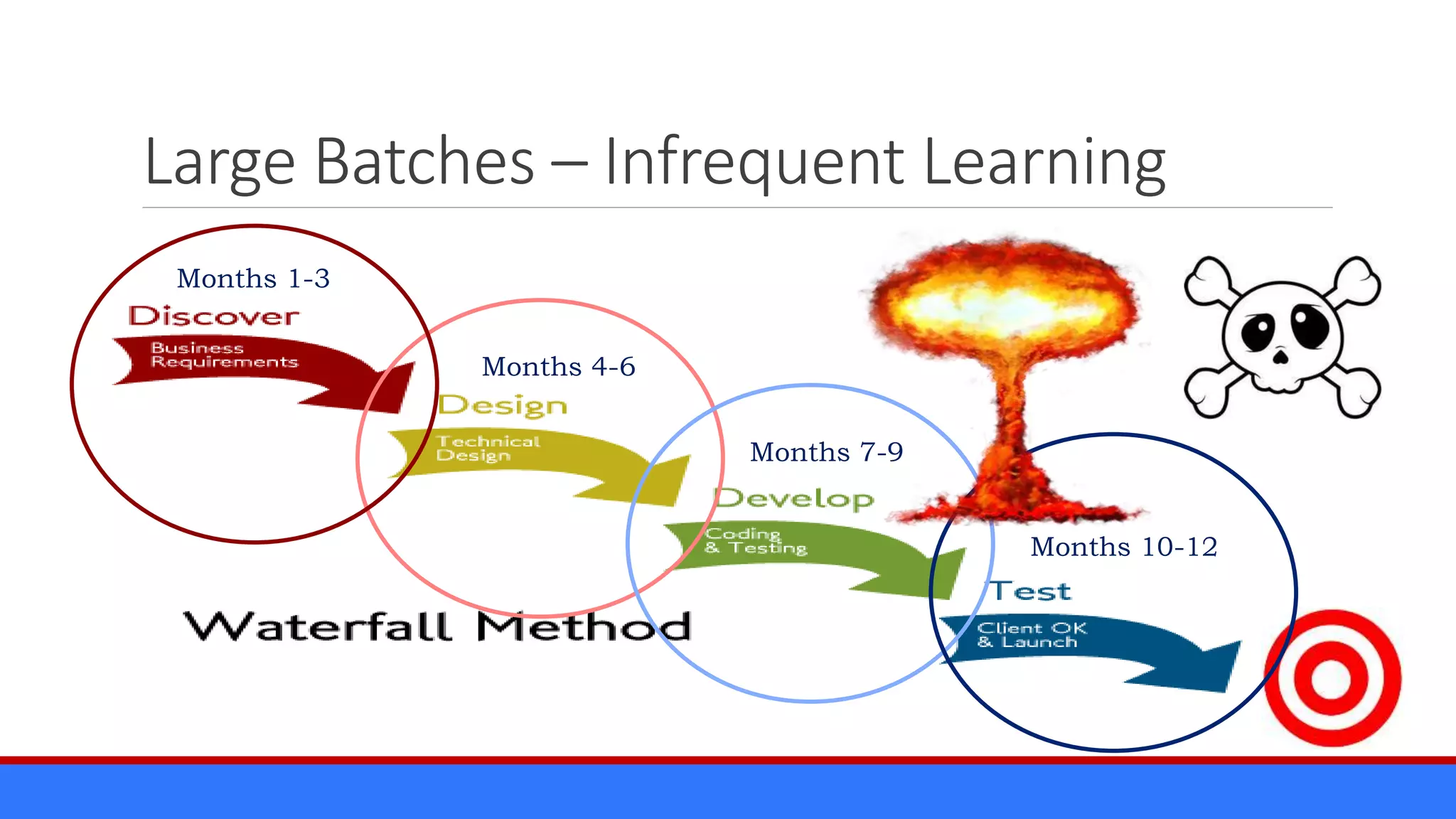
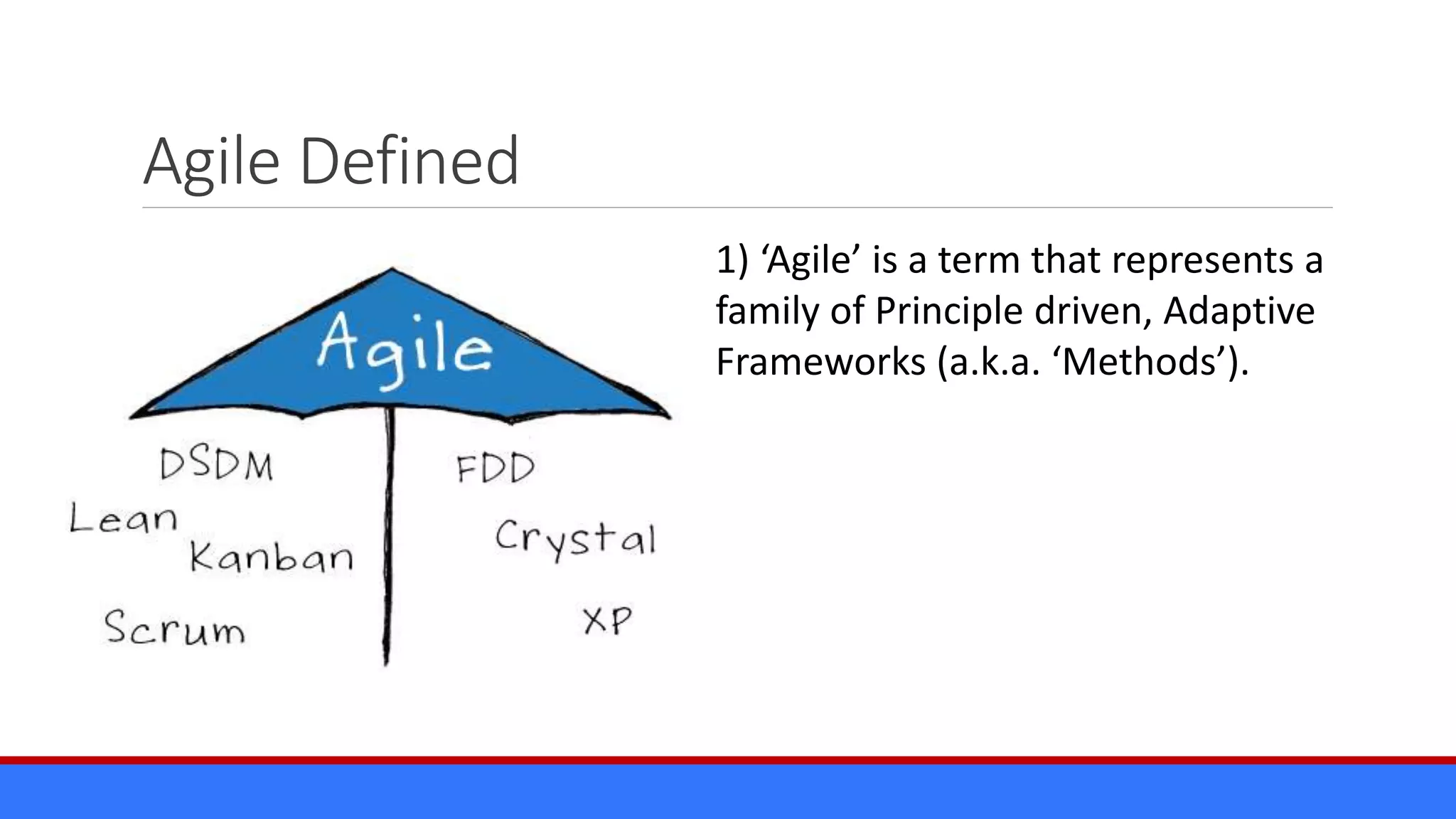
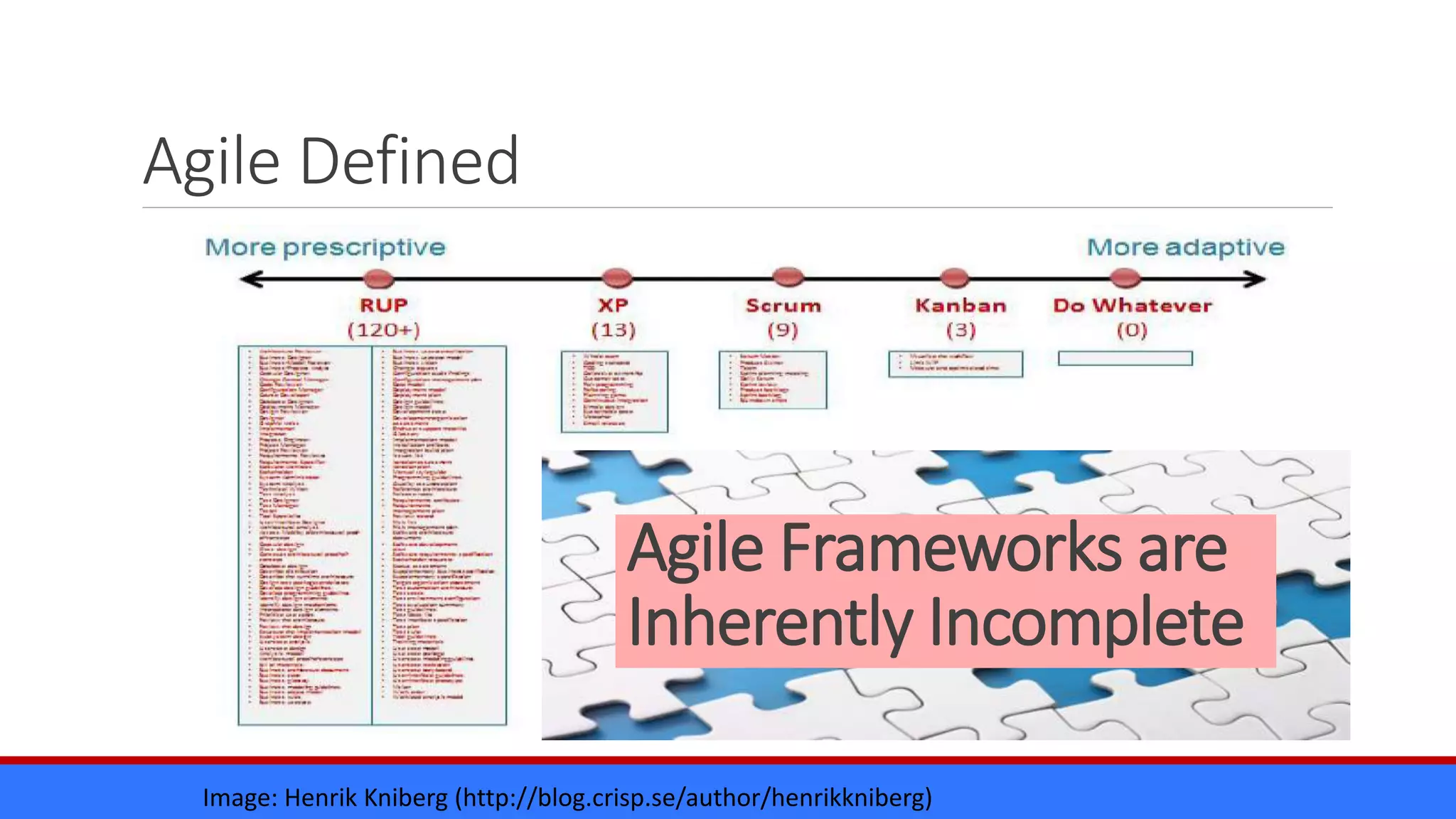
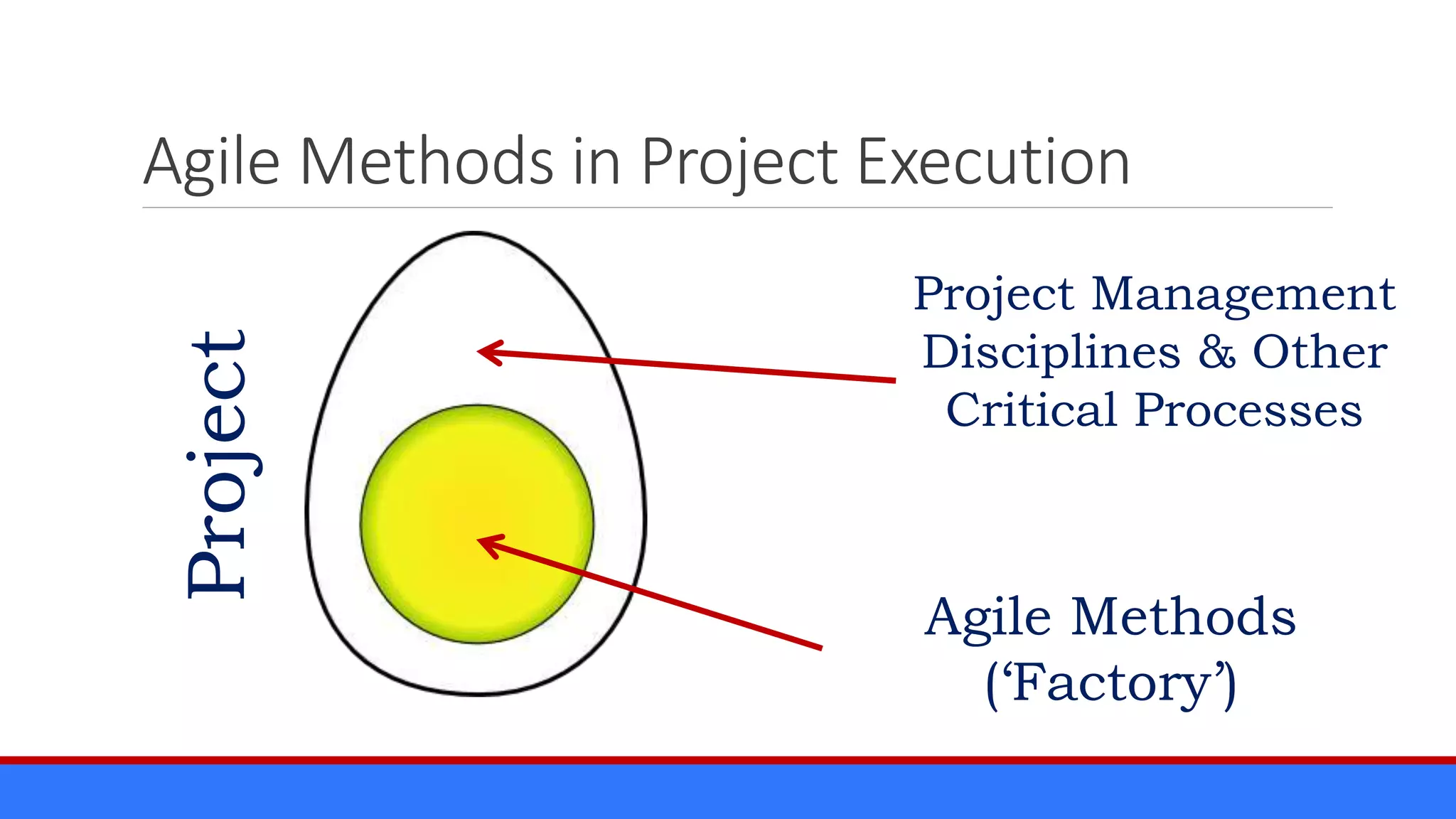
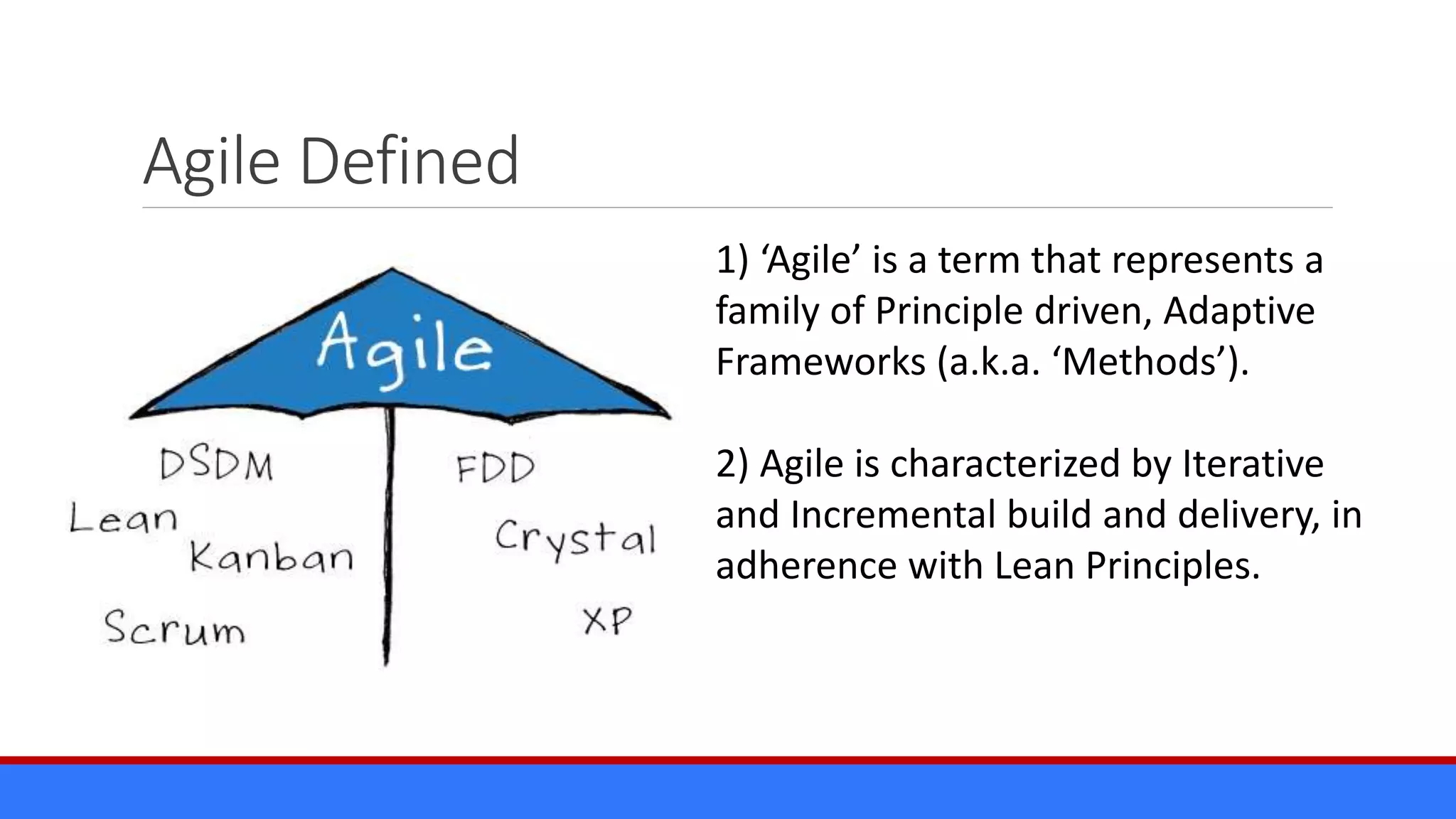
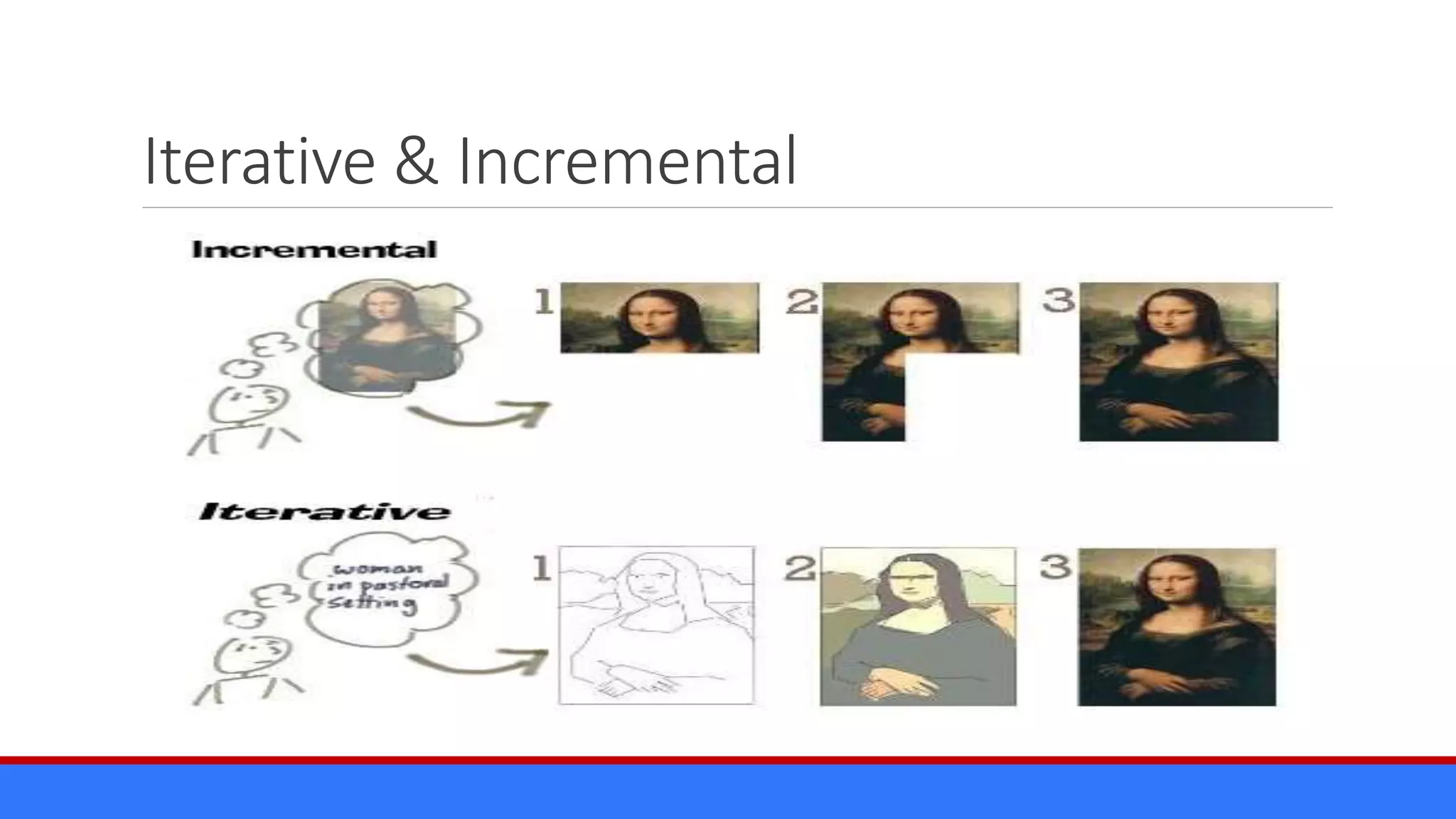
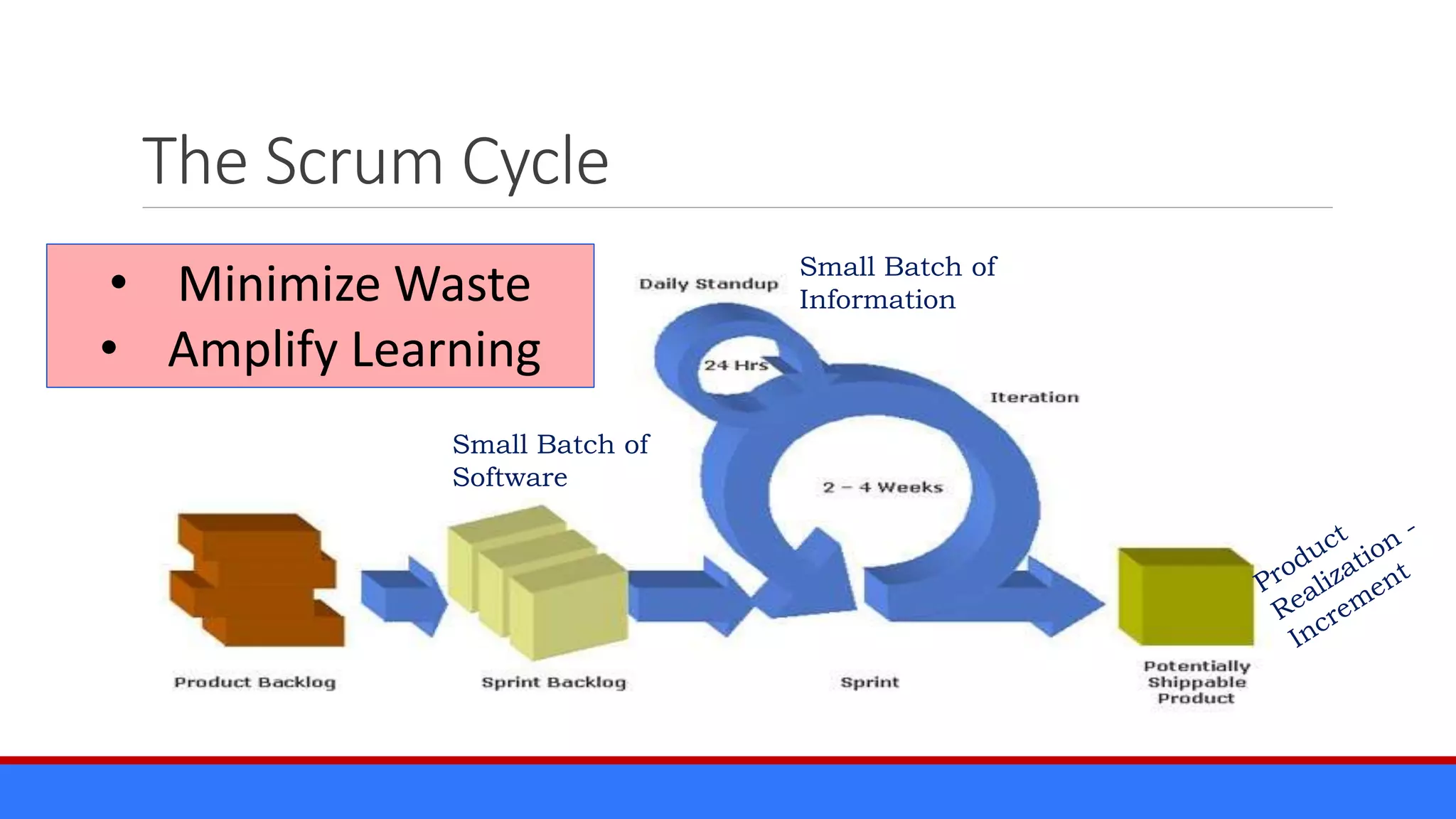
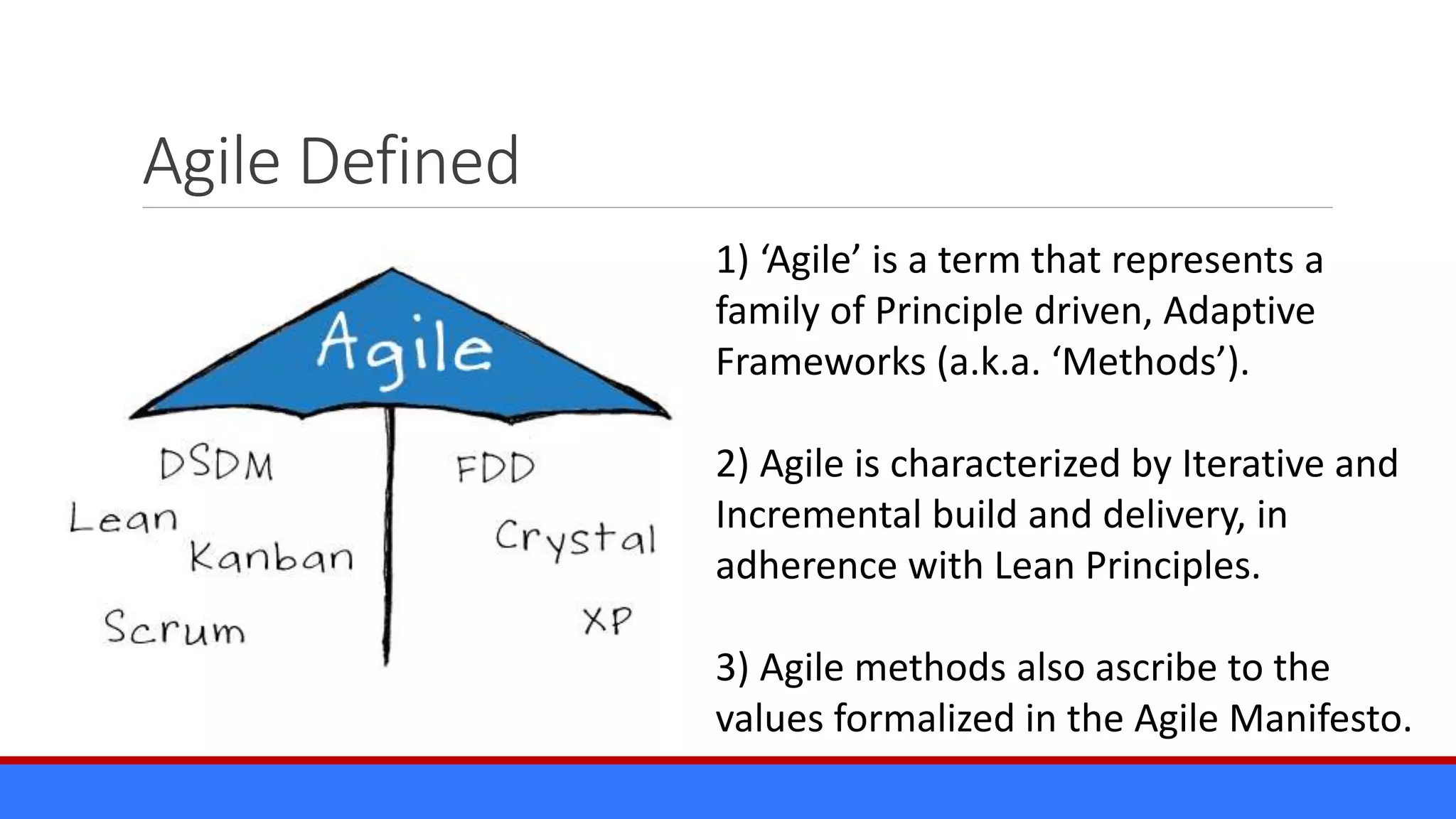
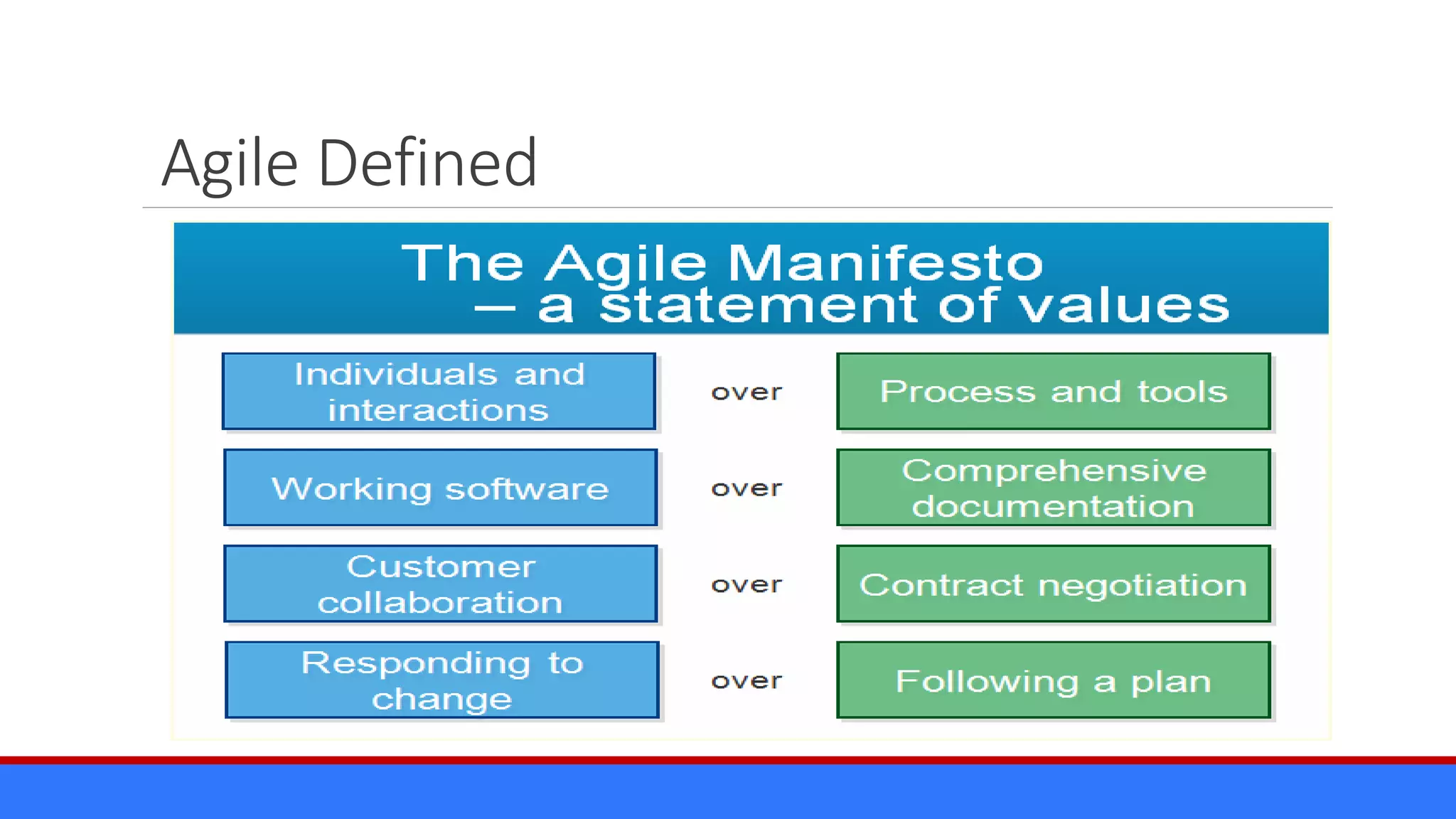
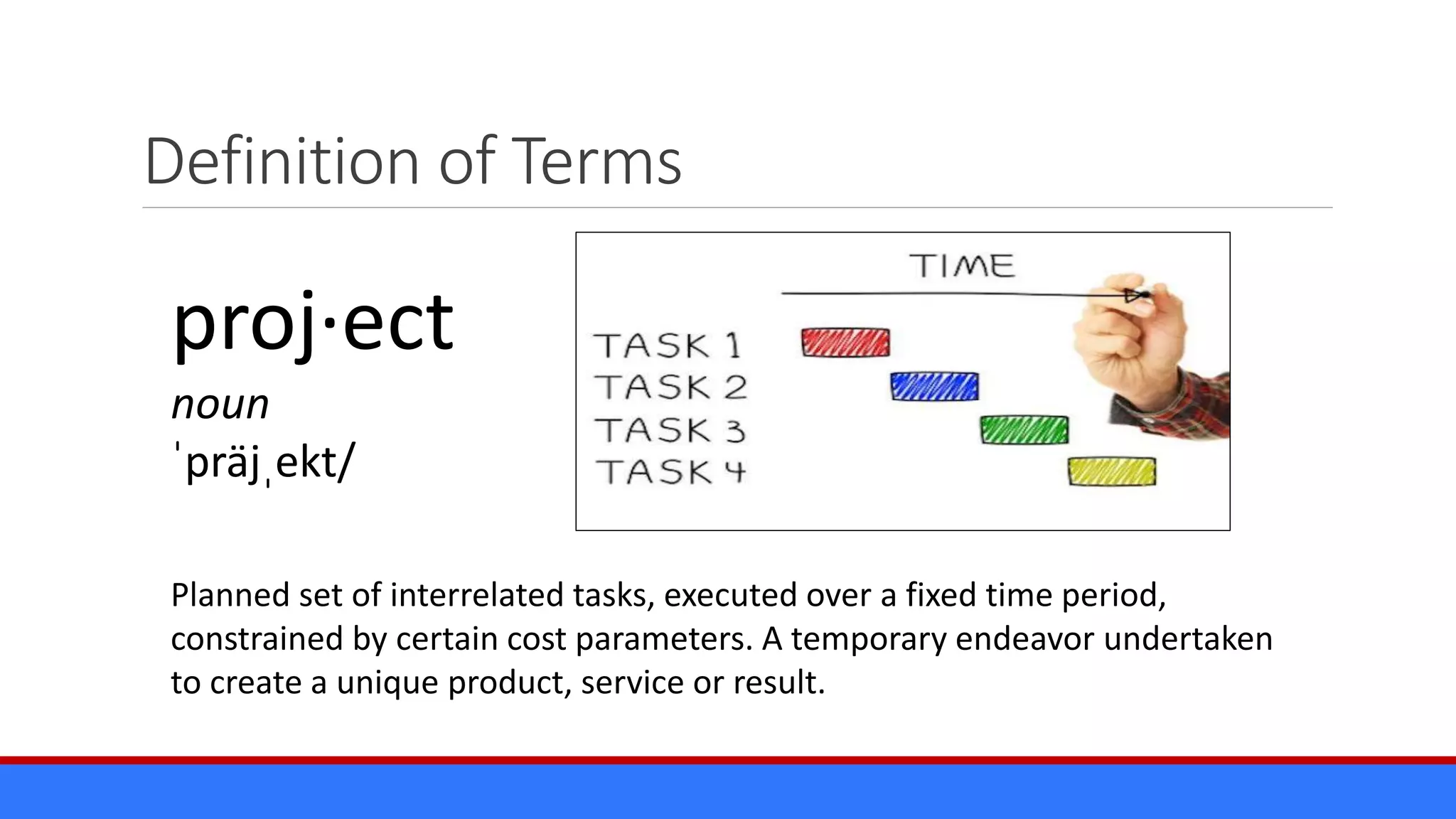
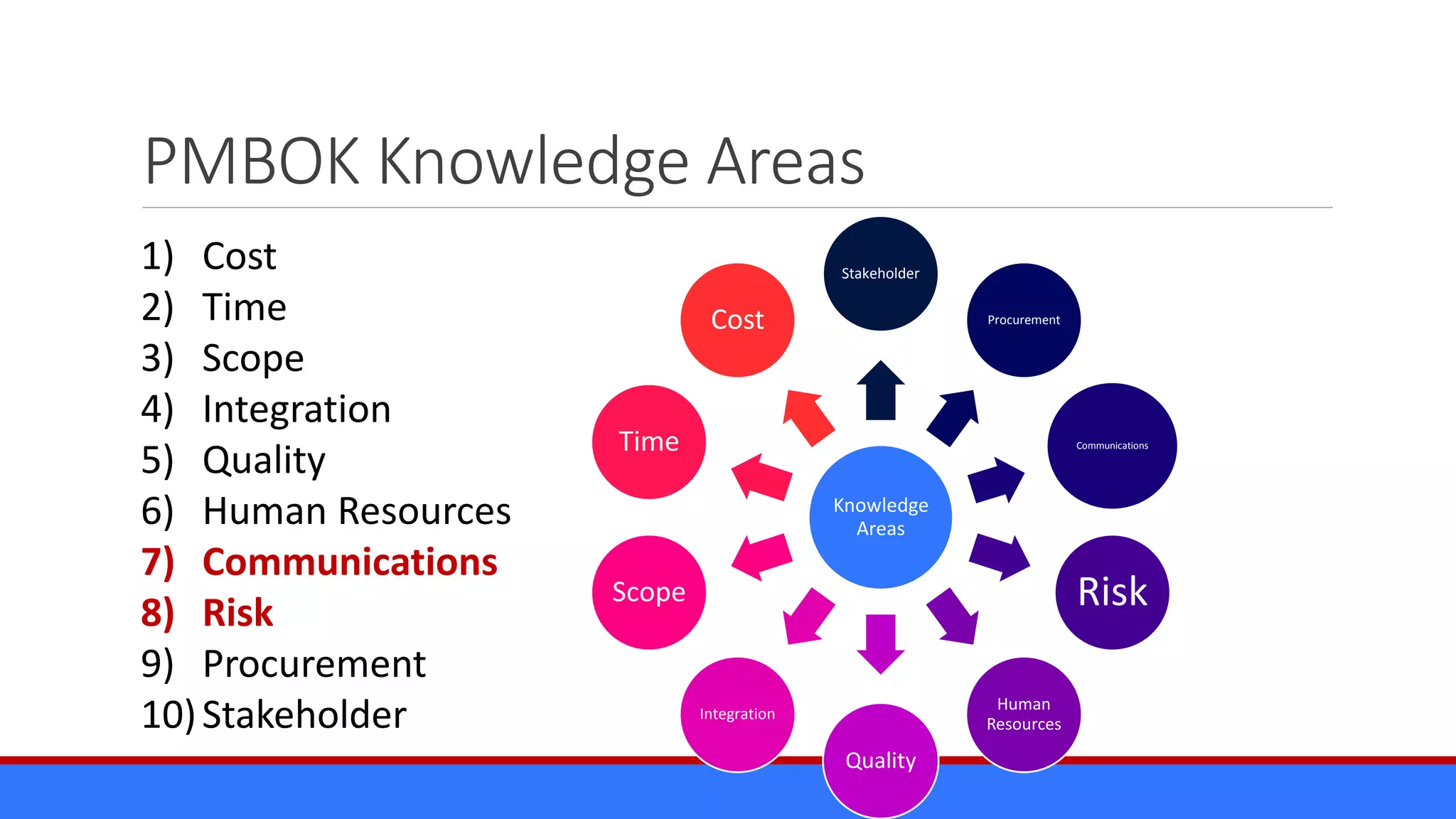
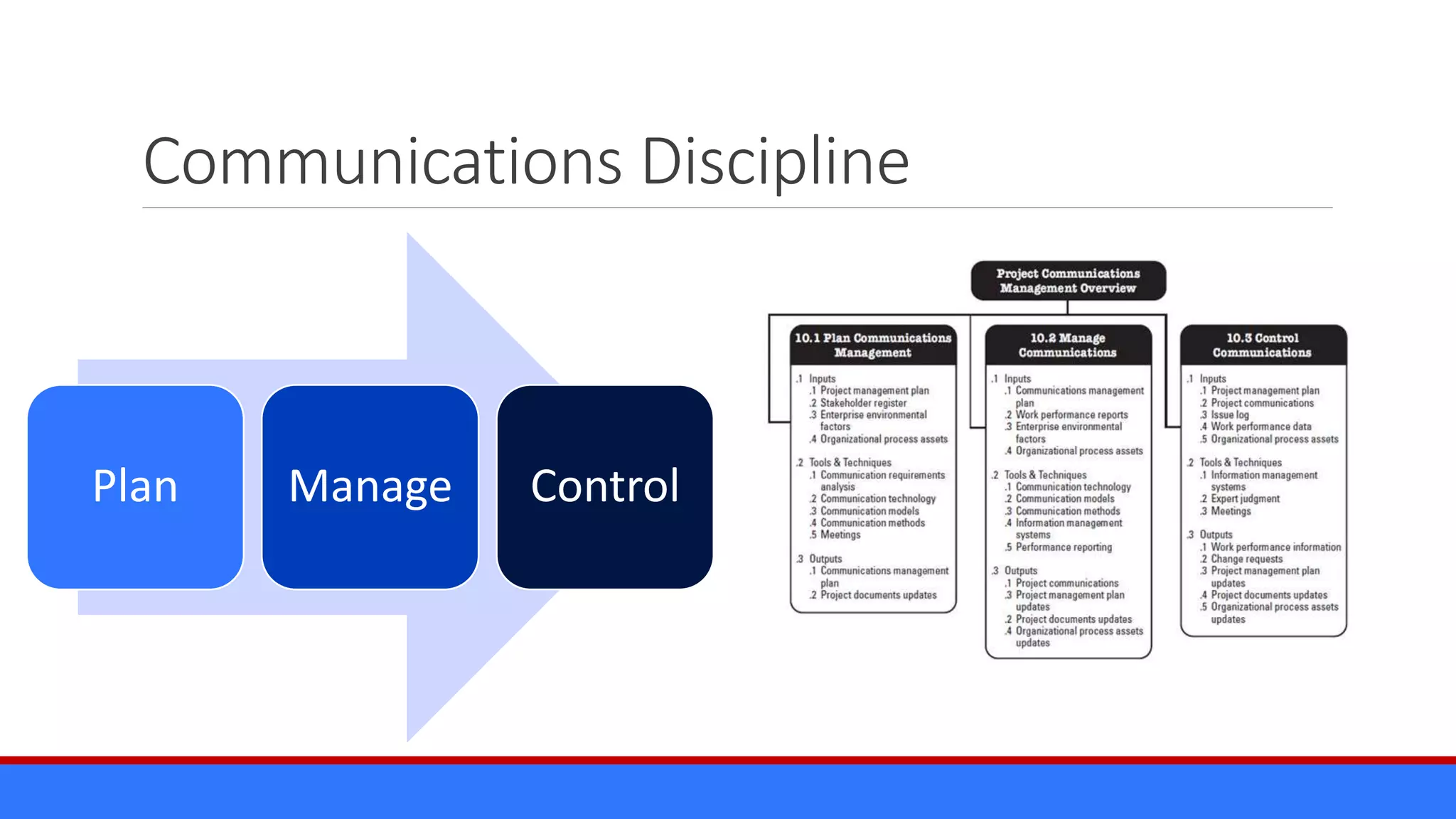
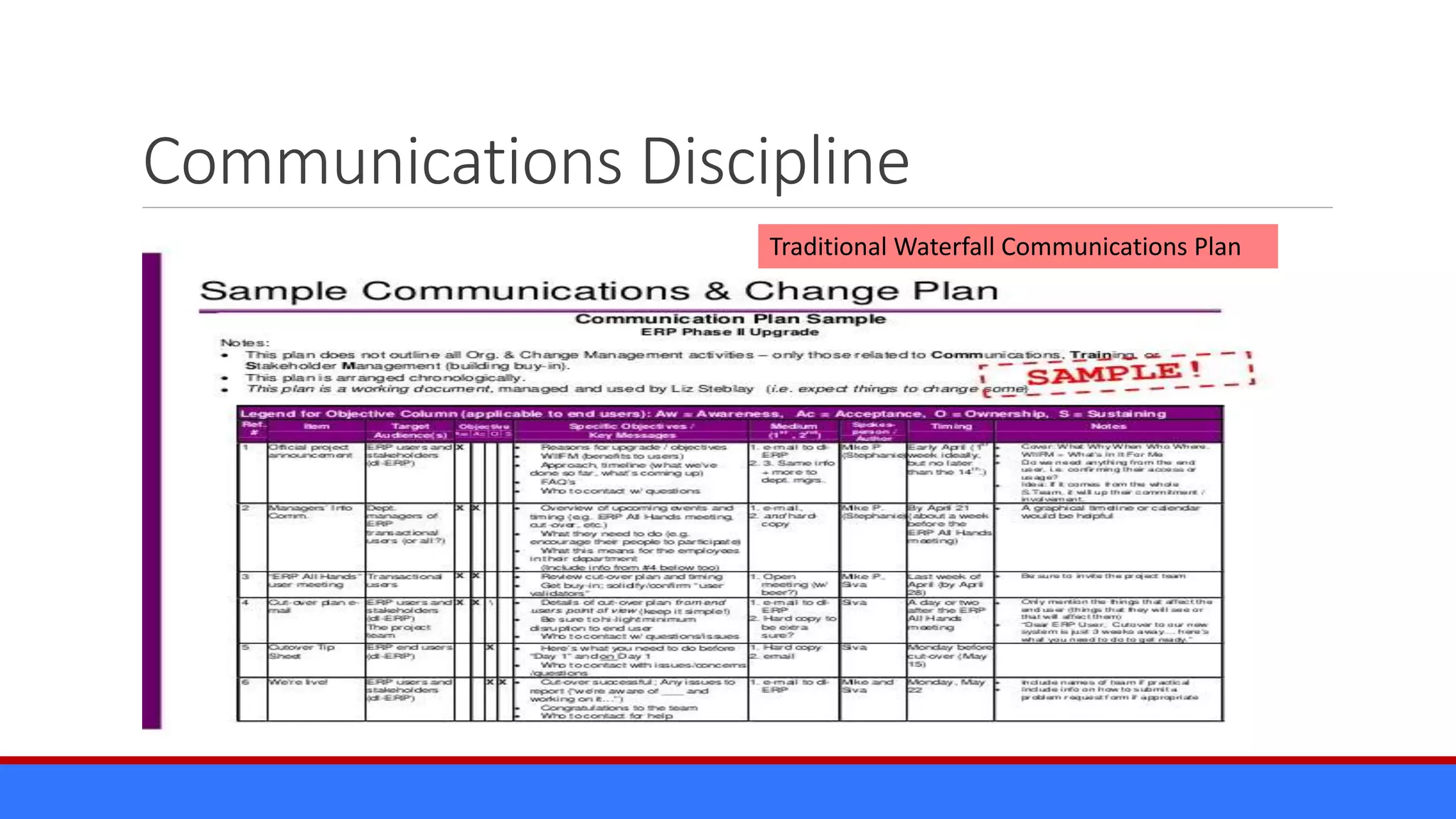
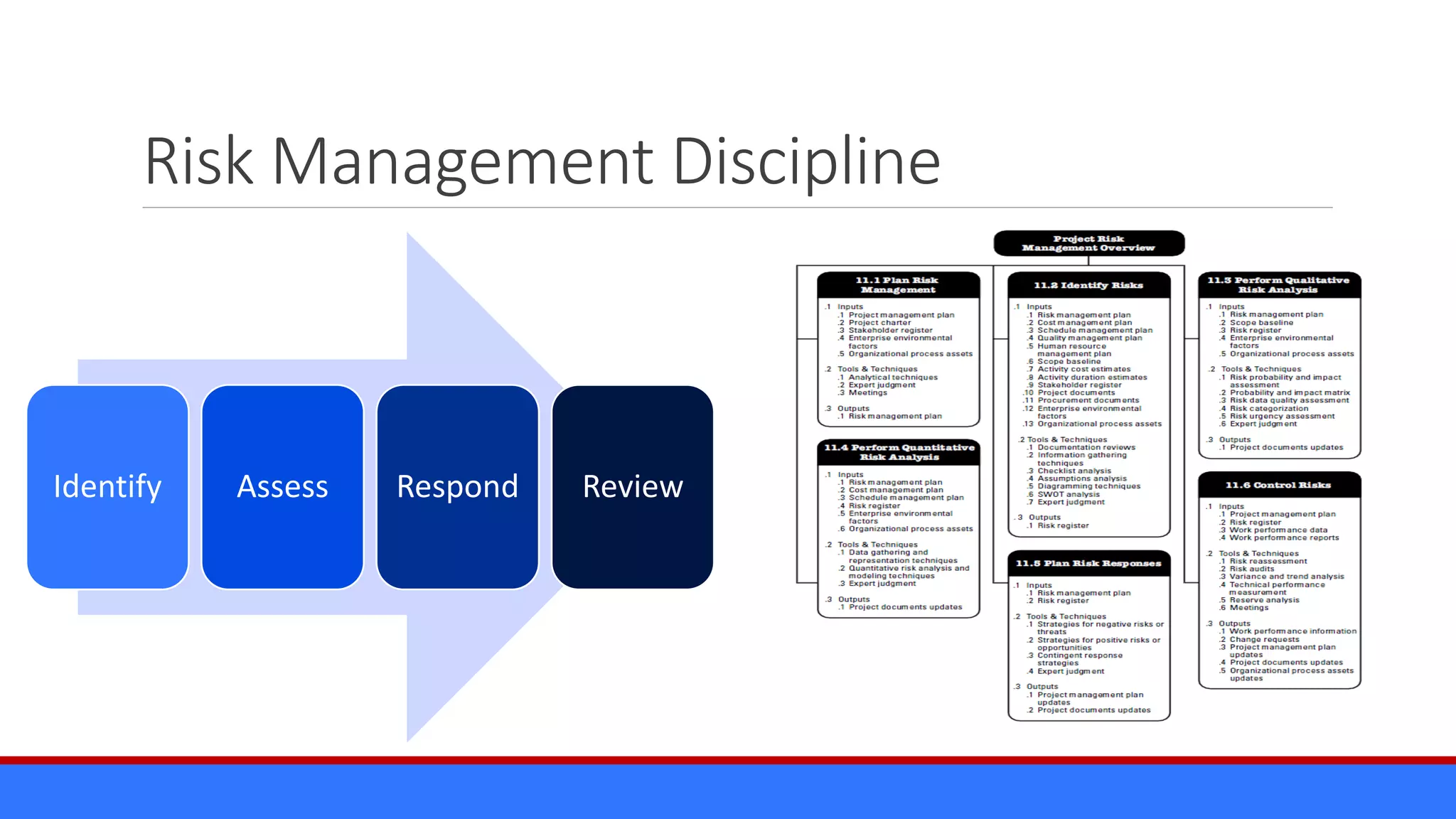
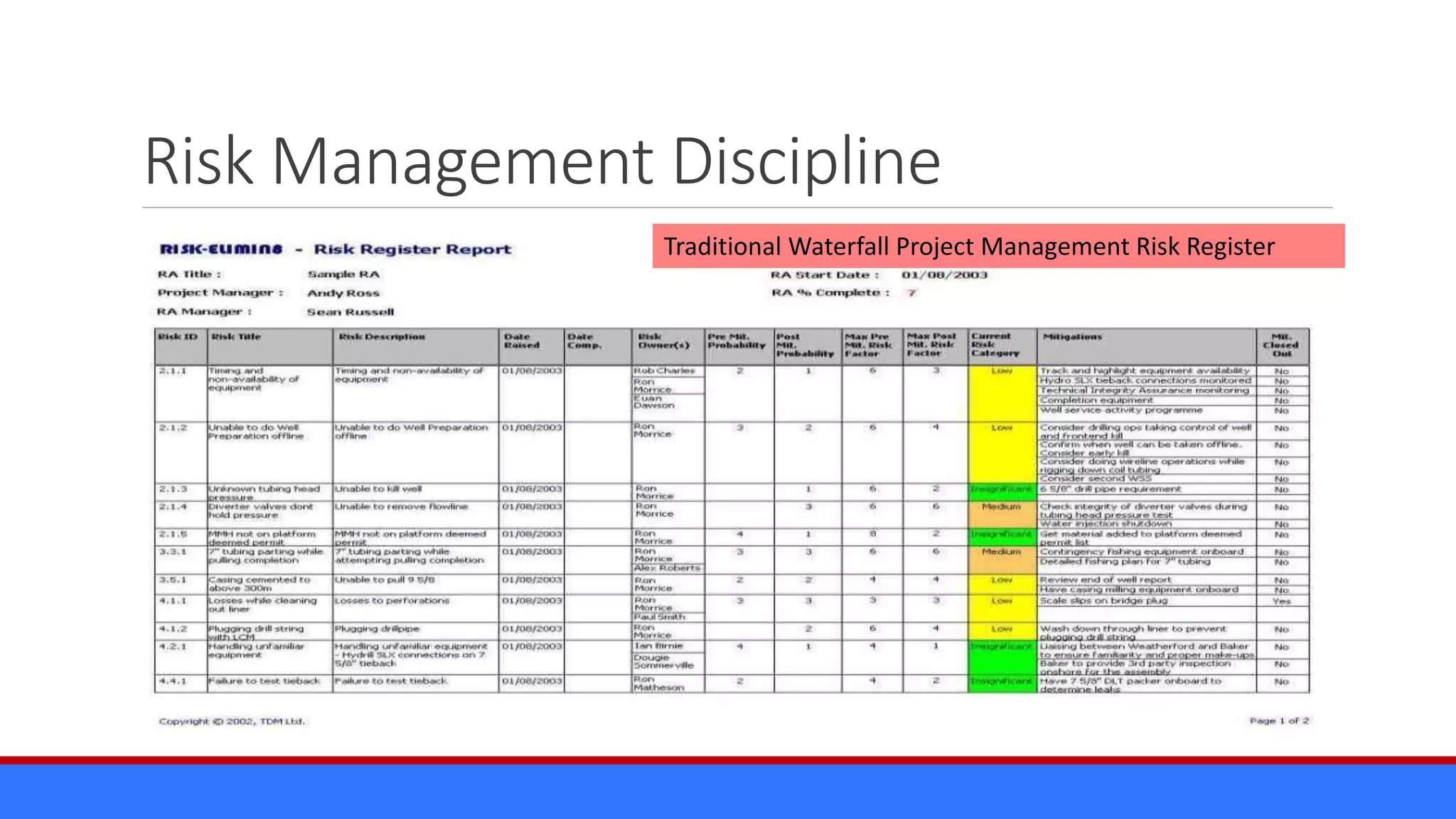
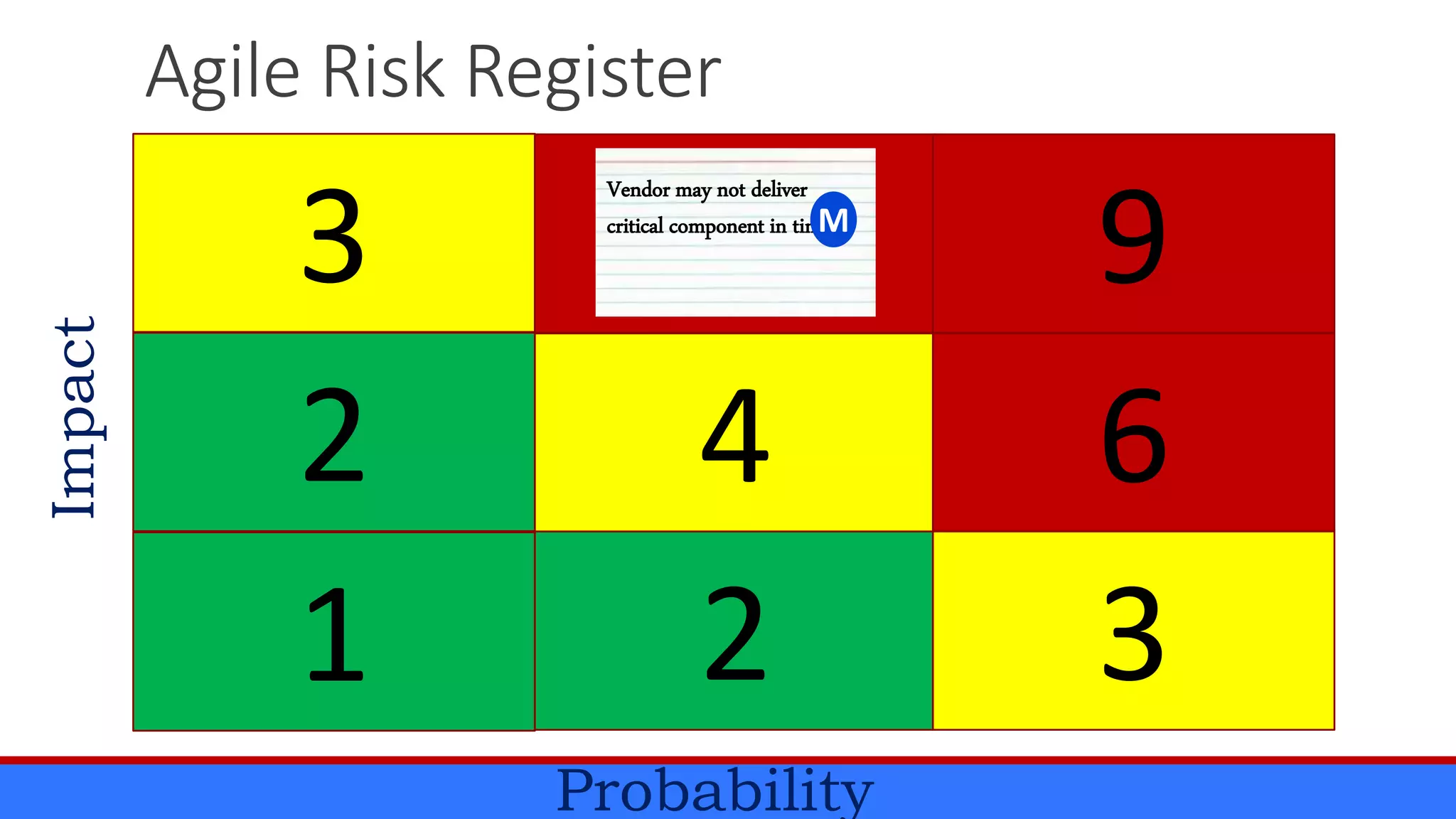
The document discusses the relevance of project management discipline in an agile environment, emphasizing its critical role in successful agile project execution. It outlines agile principles and methods, how they relate to traditional project management processes, and the importance of lean principles in enhancing project outcomes. Ultimately, it concludes that applying project management creatively within agile frameworks can lead to greater success in project execution and enterprise adoption.