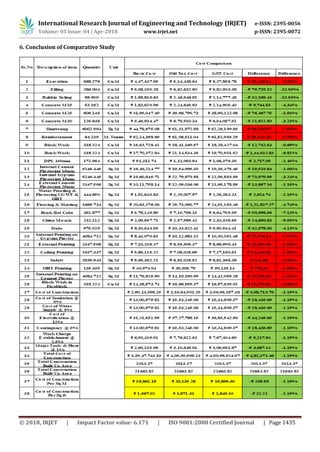
The document analyzes the impact of Goods and Services Tax (GST) implementation on the construction industry in India. It summarizes the methodology used, which involved studying an existing construction project in detail to compare the pre-GST and post-GST costs. The analysis found that material tax rates changed for many items, with some increasing slightly and others decreasing significantly up to 22%. Labor rates also increased by 3% under GST. Despite this, the overall project cost was found to decrease by up to 1.2% after accounting for GST, and with input tax credit the savings could be even greater. Therefore, the study concludes that GST has had a positive effect on costs in the construction sector.


![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 05 Issue: 04 | Apr-2018 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2018, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 6.171 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 1436
It can be easily observed from the above calculations that
even though ITC is not taken in consideration, there has
been a considerable reduction of up to 1.2% of the Project
Cost by application of GST. If the ITC studies are taken in
consideration, then this cost will reduce even more &
hence, it can be said that it is a good effect of GST on
construction industry. It is also seen that only the Labour
Contracts are at total loss which is to be paid attention by
the contractors bidding for labour contract.
7. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This work has been performed in Thakur College
of Engineering, Mumbai, India. The authors of this paper
thanks Prof. Pratibha Singh, Prof. Chaitali Mehta and Prof.
Swapnil Raut for the helpful discussions & guide us in
analysis while carrying out this work.
8. REFERENCES
[1] GST: An economic overview: Challenges and Impact
Ahead IRJET Vol 4 Issue 4 Apr-17.
[2] GST- A Game Changer in Indian Tax Structure IOSR
JBM
[3] Planning, Scheduling and tracking of residential
project using primavera IJARCSMS Vol 3 Issue 5 May-
15.
[4] A Benefit Study of Petroleum Inclusion in GST Bill St.
Joseph’s College of Commerce Bangalore.
[5] An overview of GST – Reduction of Tax Burden St.
Joseph’s College of Commerce Bangalore.
[6] First Discussion Paper on GST in India Empowered
Committee of State Finance, New Delhi.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v5i4322-190223083436/85/IRJET-Building-Construction-Before-After-GST-5-320.jpg)