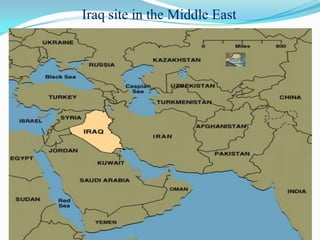
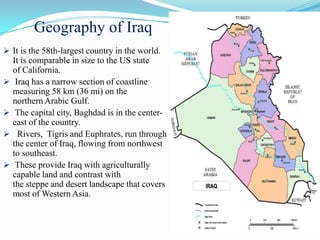
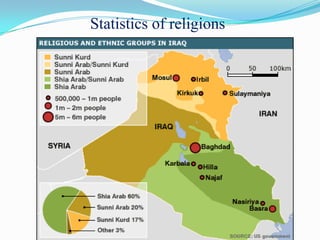
Iraq is a country located in Western Asia, bordered by Syria, Turkey, Iran, Jordan, Kuwait, and Saudi Arabia. It has a narrow coastal section on the Persian Gulf. The Tigris and Euphrates rivers run through central Iraq. Iraq has a long history as the site of many ancient civilizations, including the Sumerian, Babylonian, Assyrian, and Abbasid empires. Today, Iraq is a federal parliamentary republic with a majority Muslim population, most of whom are Shia or Sunni Muslims. Popular Iraqi cuisine includes dishes like biryani, dolma, and kebabs. Football is the most popular sport, and weddings are important social and cultural events