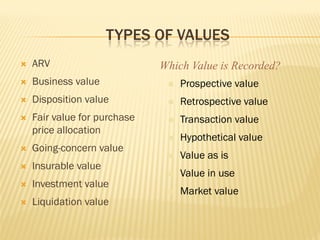
The document discusses the difference between price and value in real estate transactions. It notes that price is determined by a single buyer, while value is driven more broadly. It also notes that recorded purchase prices may not indicate true market value, as they can be influenced by factors like commissions, appraisals, and fraudulent valuations. Finally, it emphasizes understanding the various definitions of value and being aware of current market conditions to bridge the gap between price and recorded value.