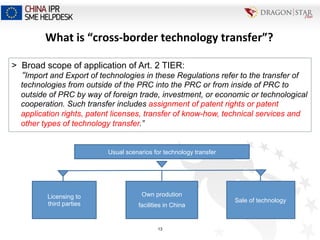
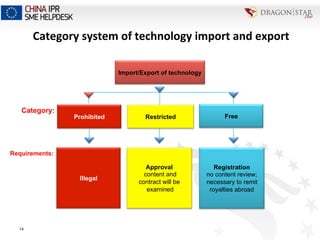
The document discusses intellectual property (IP) implications and legal considerations for conducting research and development (R&D) activities in China. It provides an overview of the relevant legal framework in China, including the Patent Law, Contract Law, and Technology Import and Export Administration Regulations. It outlines important IP rights related to R&D in China and abroad, such as rights to inventions, patent applications, and granted patents. The presentation emphasizes that any transfer of patents or patent applications in China to foreigners requires approval from the State Intellectual Property Office of China.