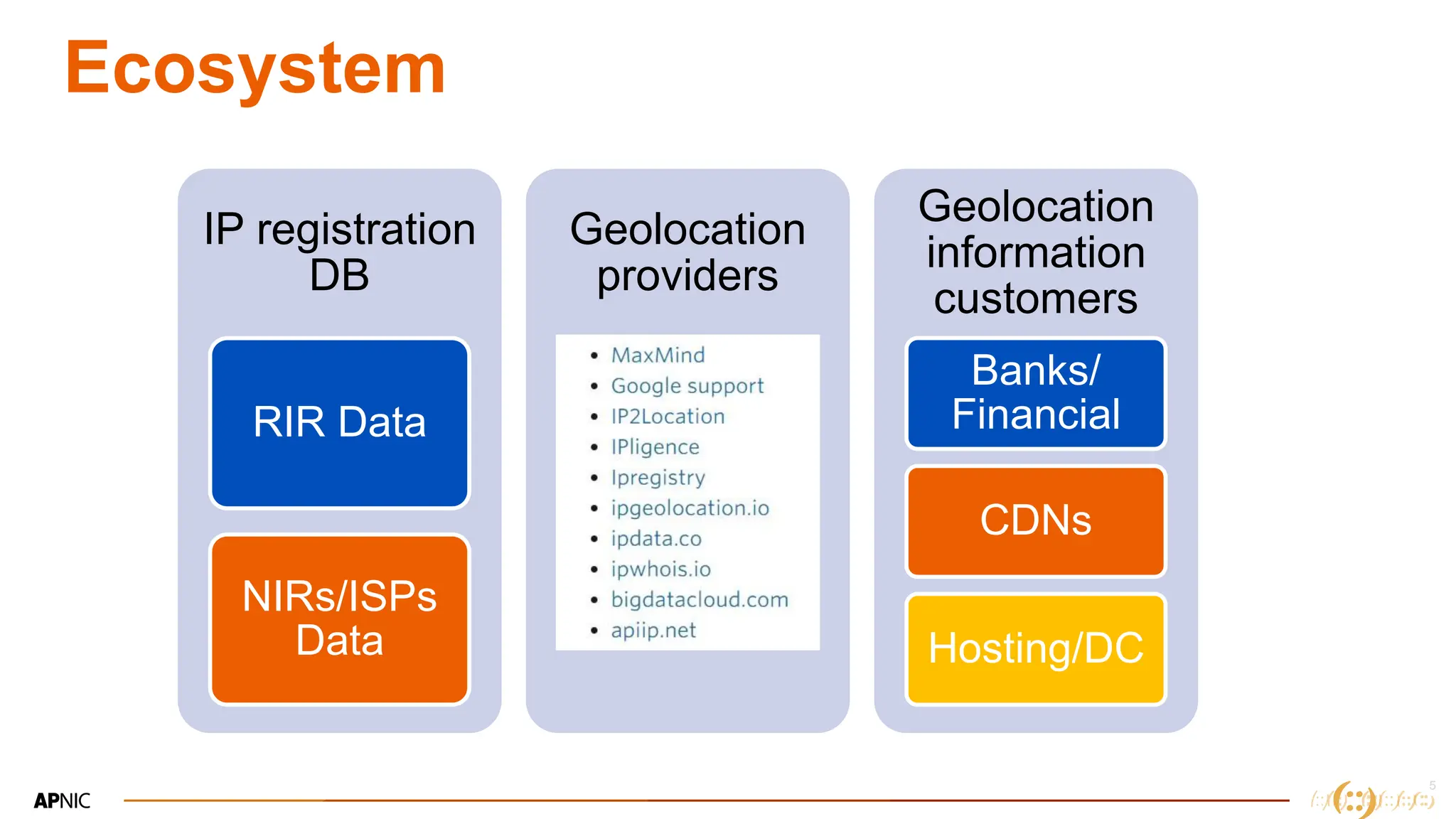
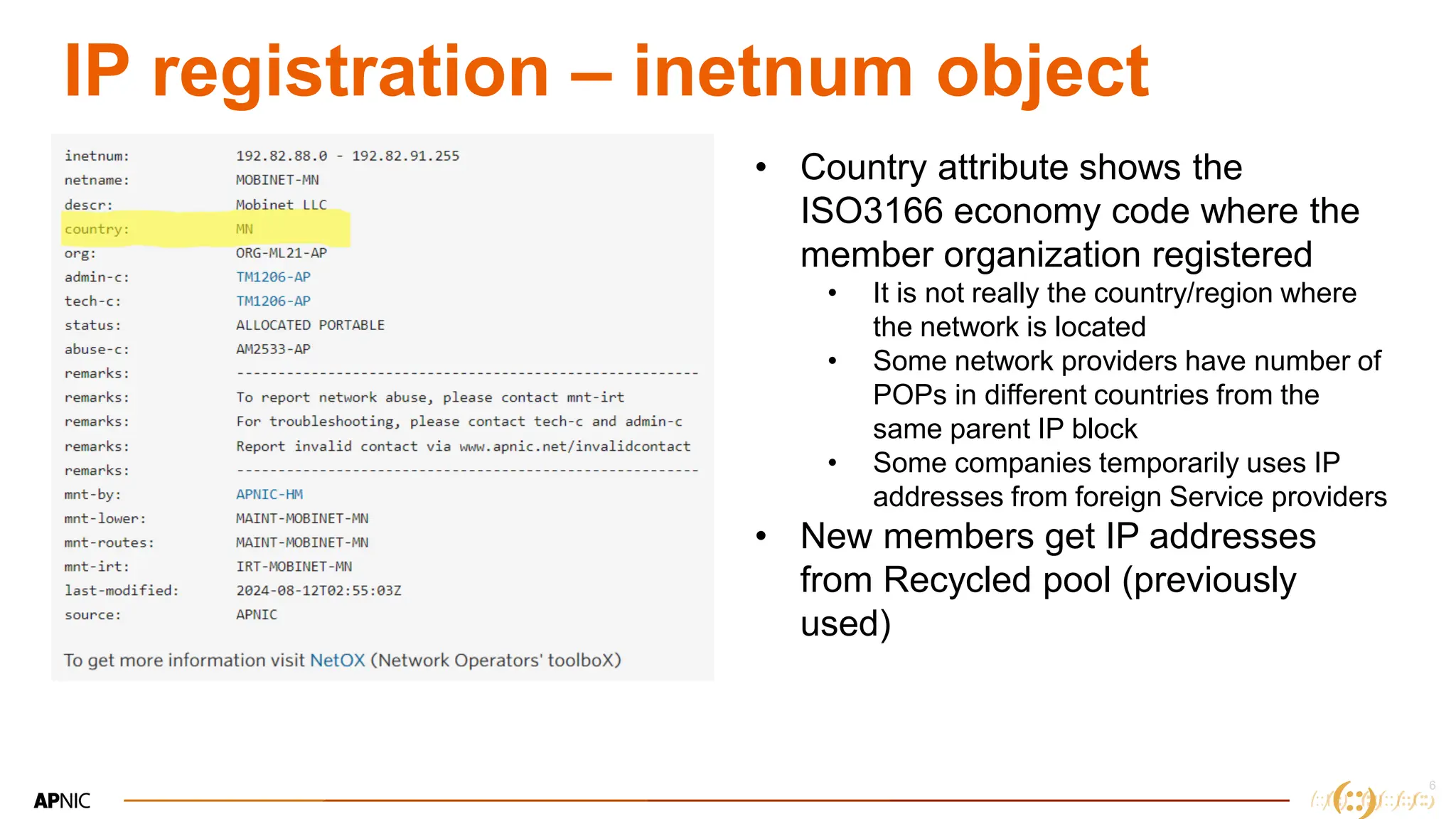
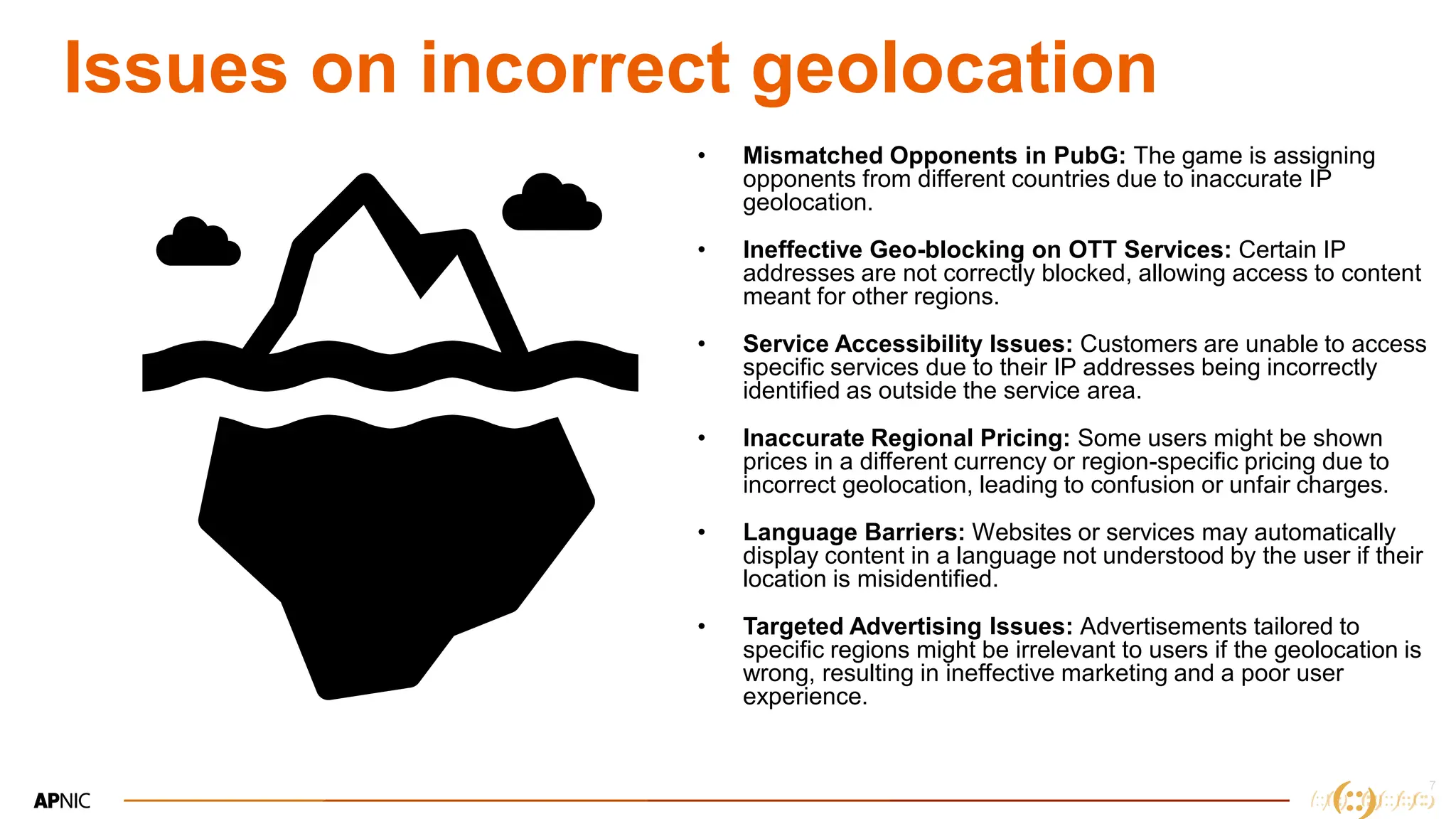
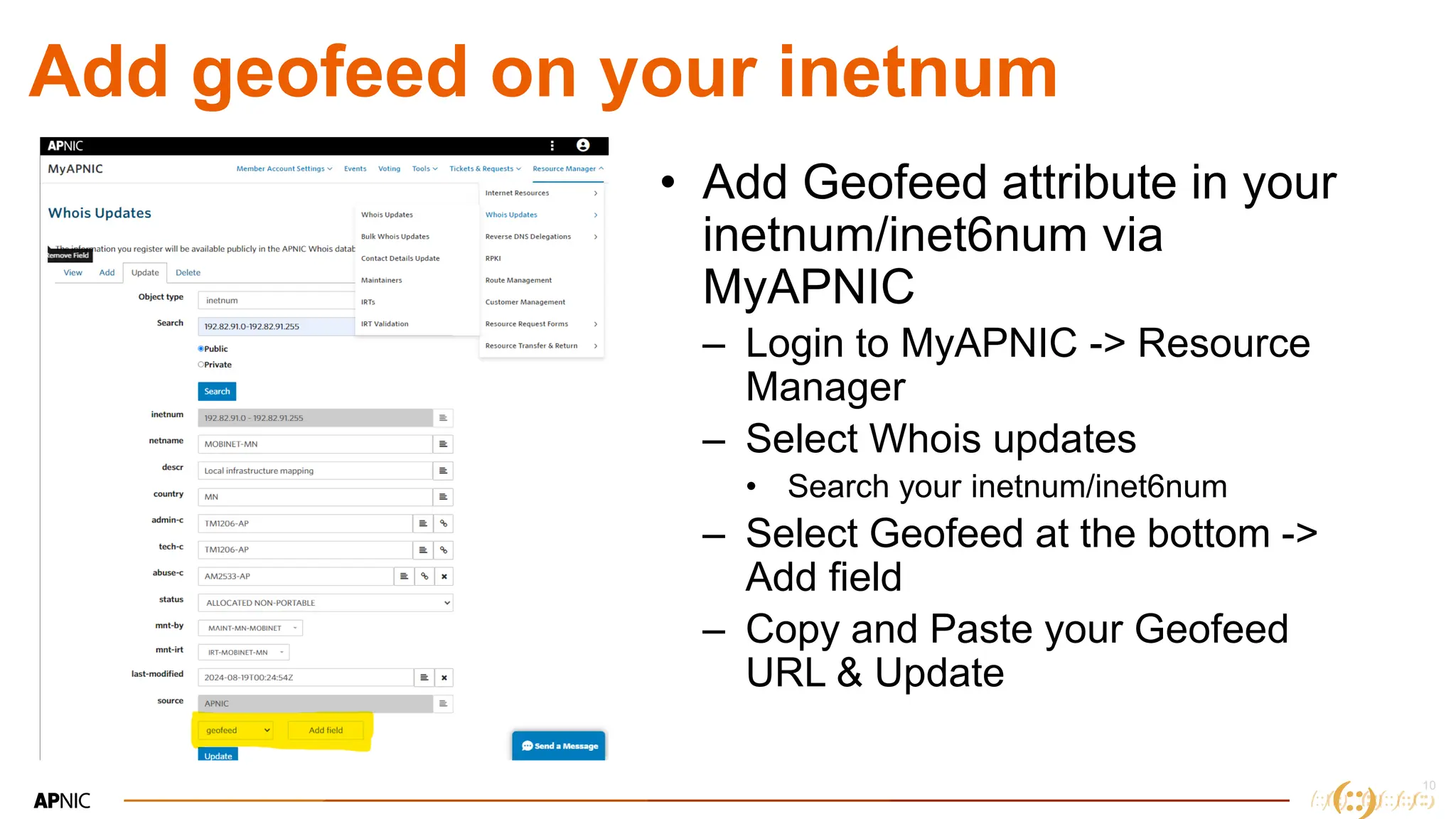
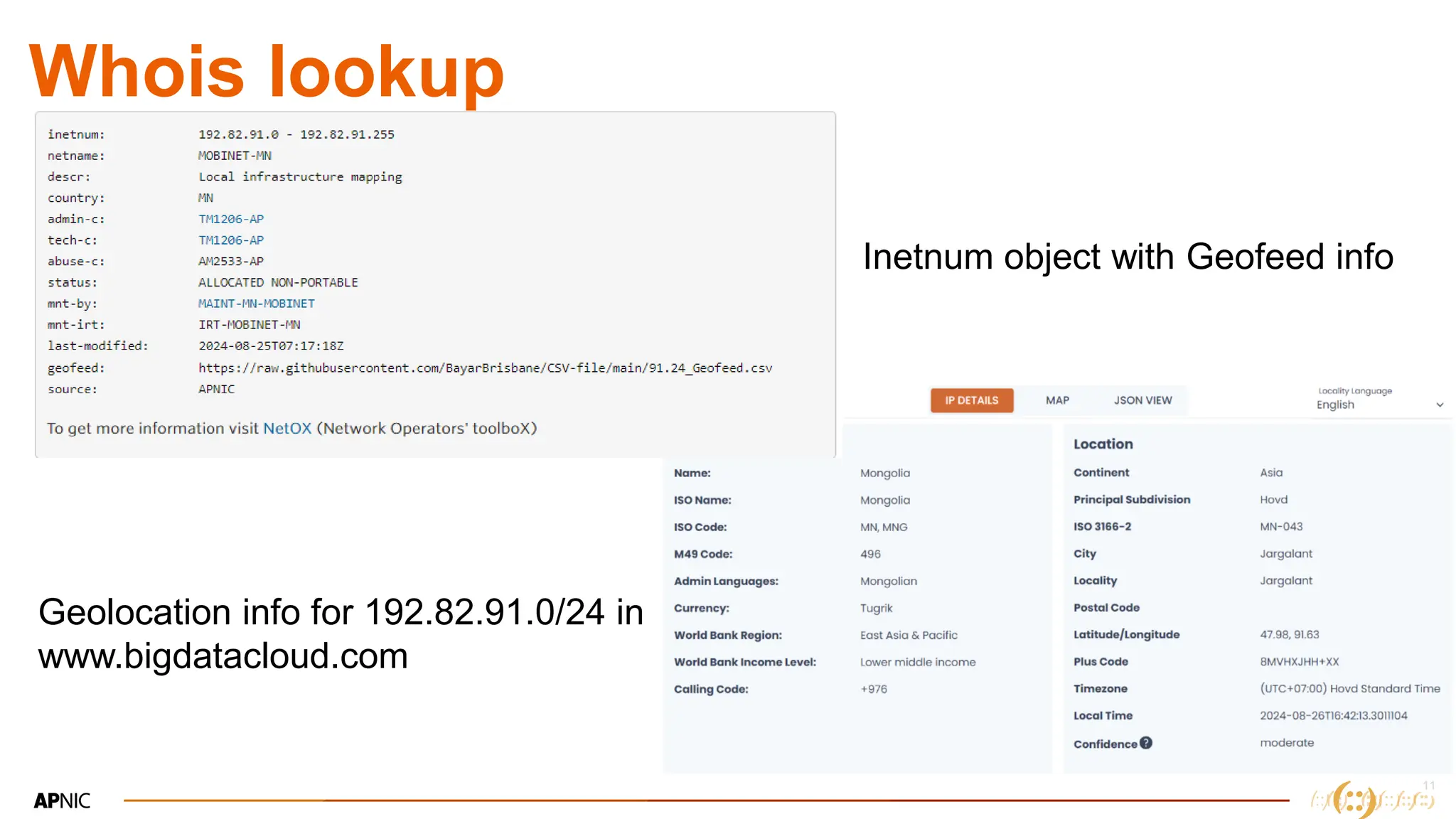
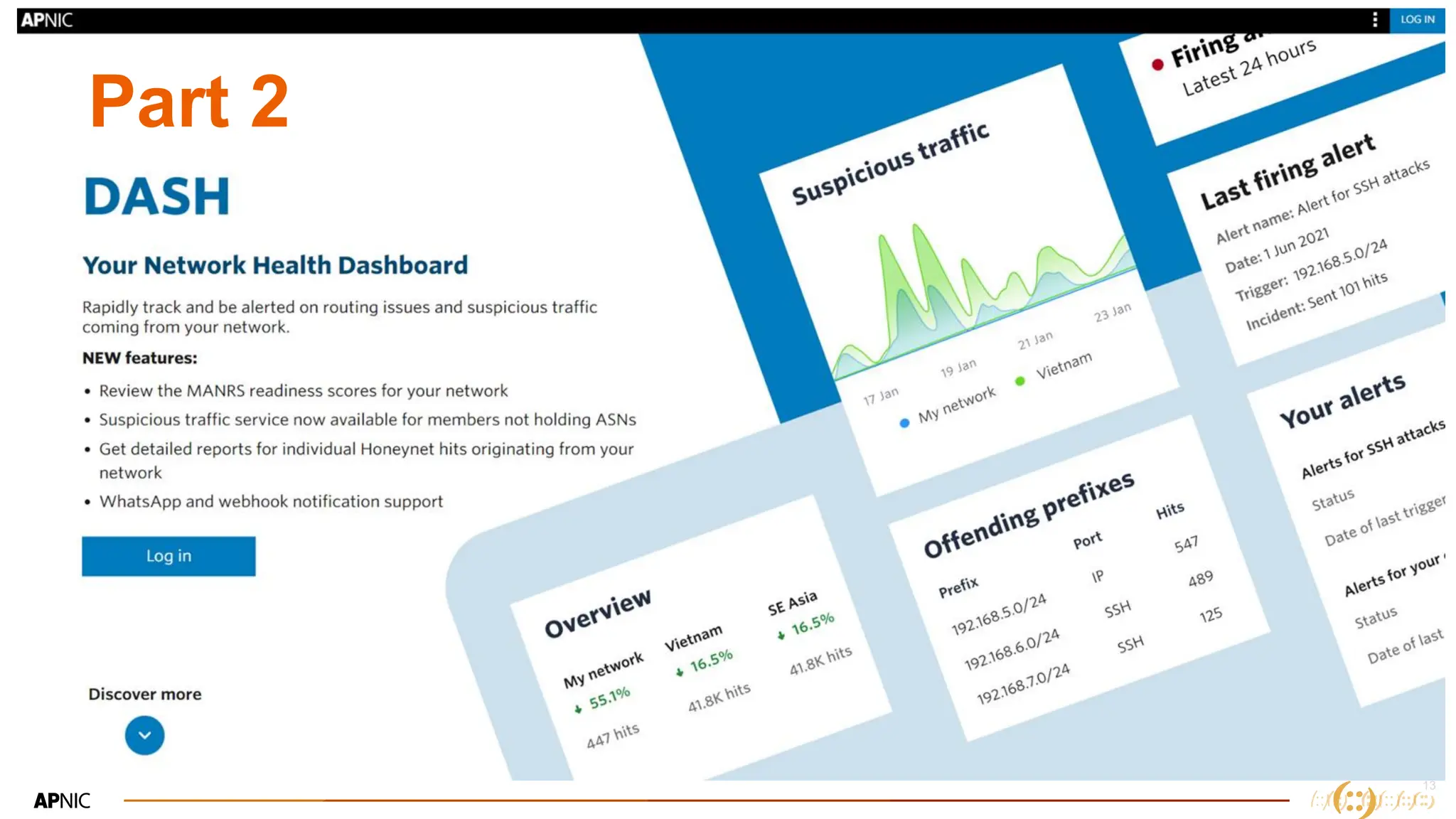
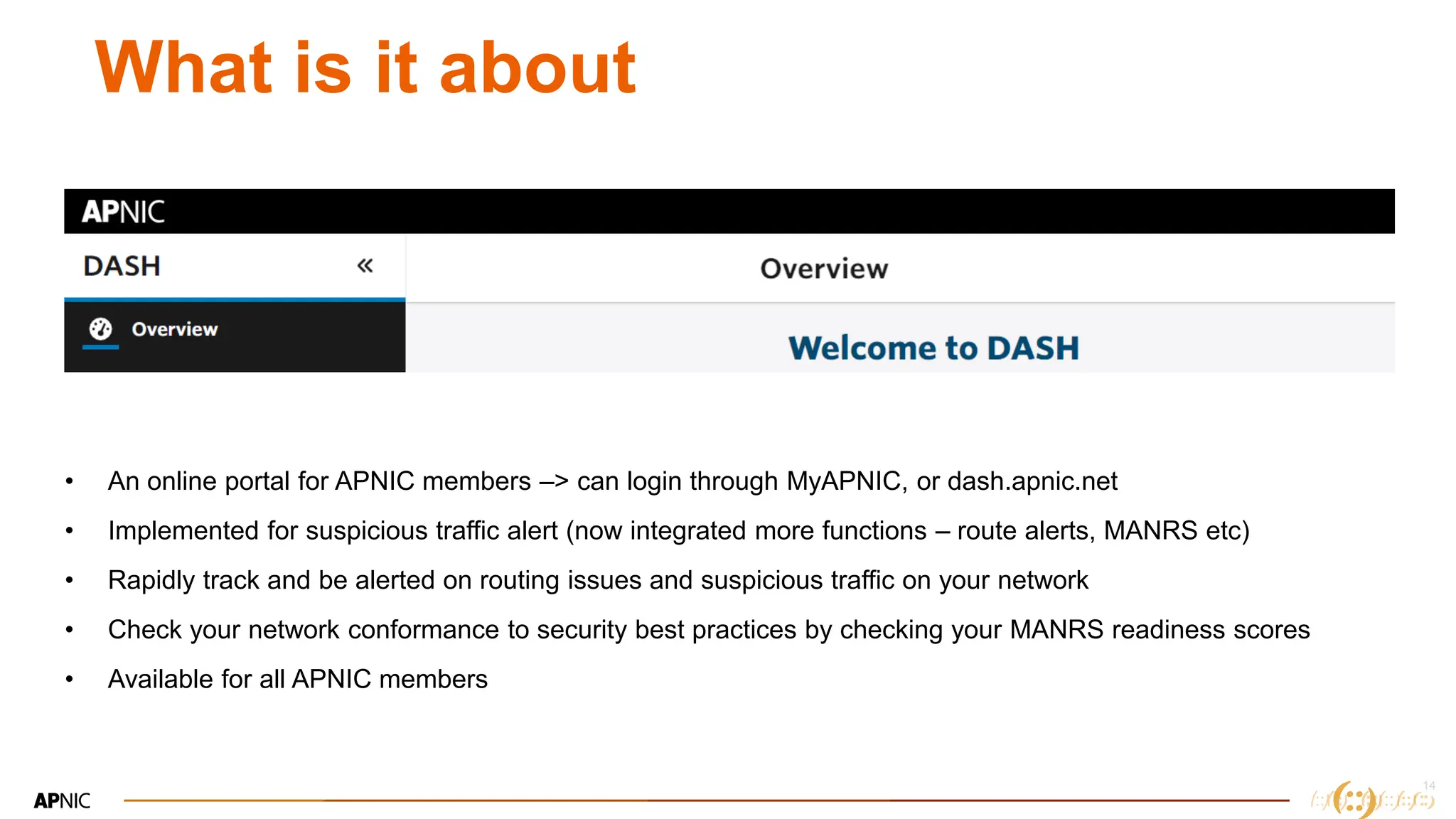
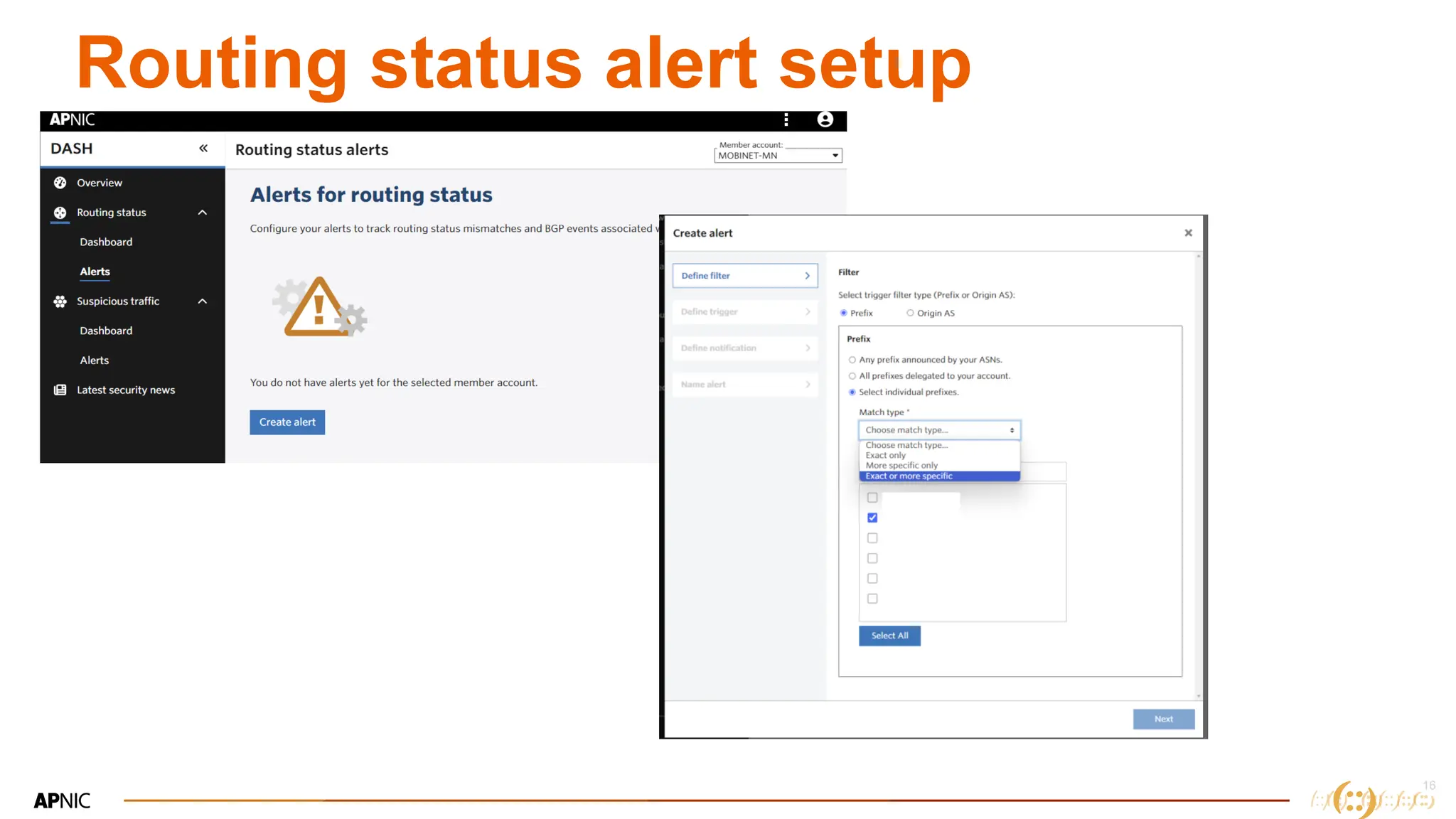
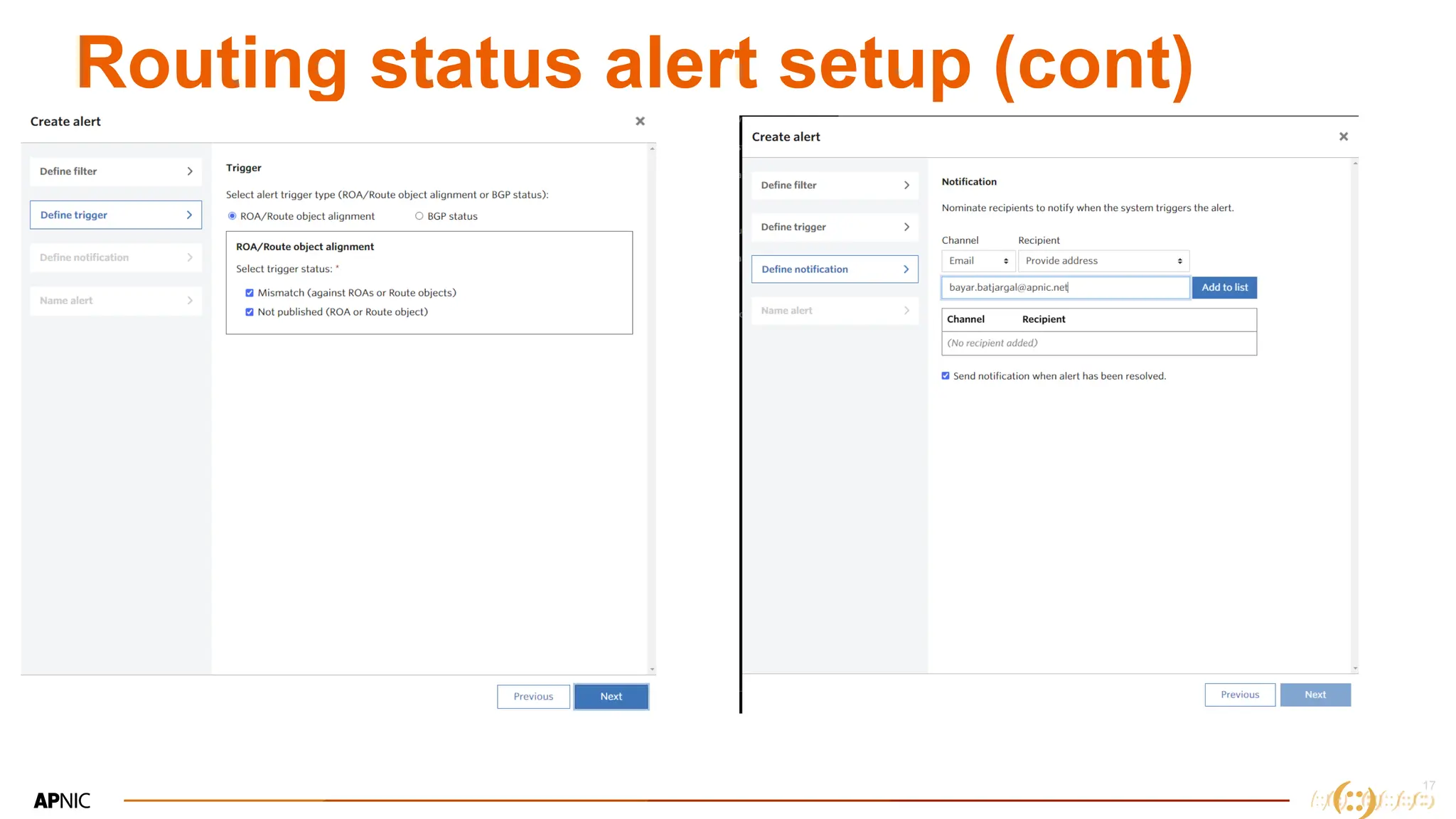
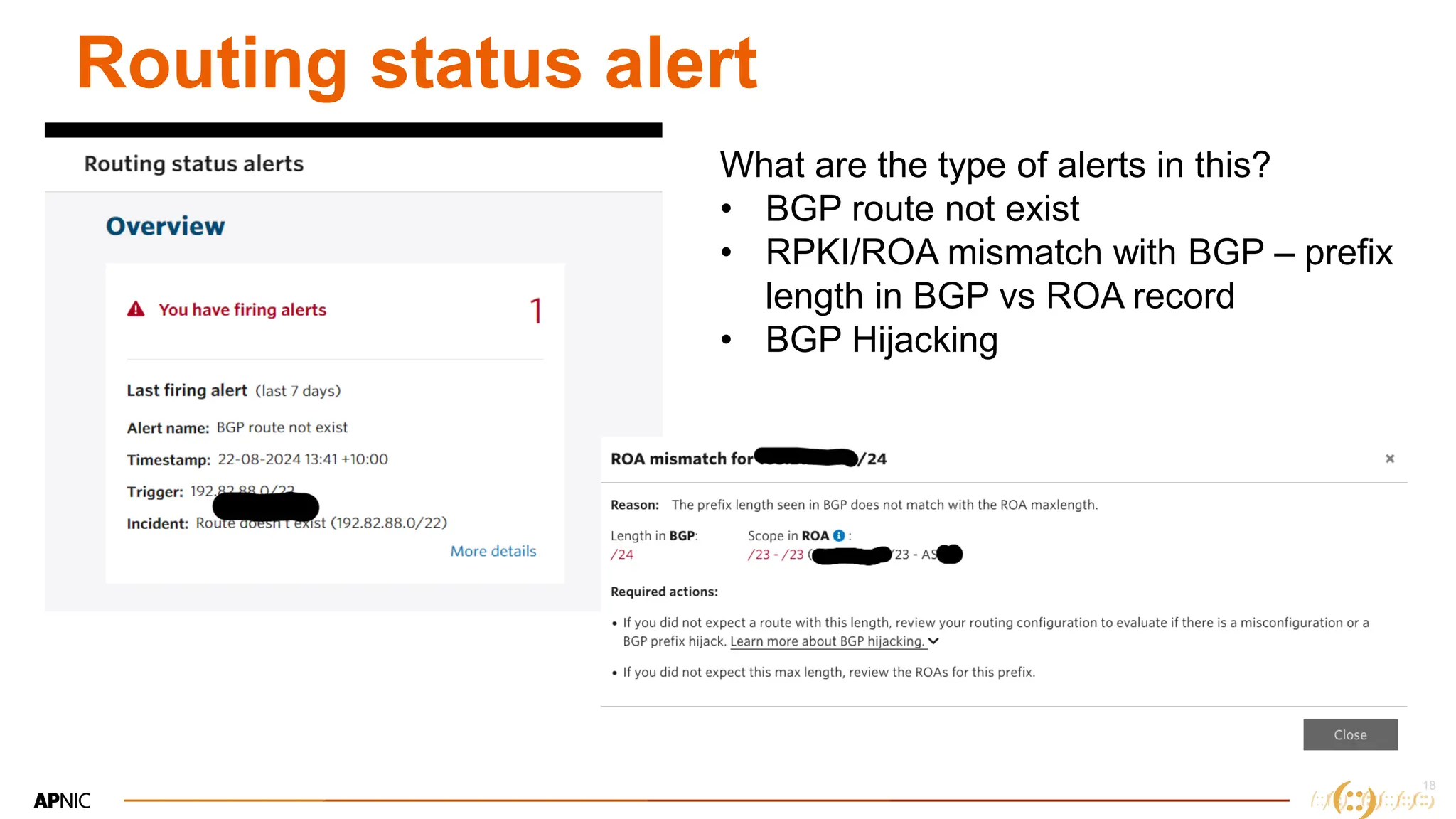
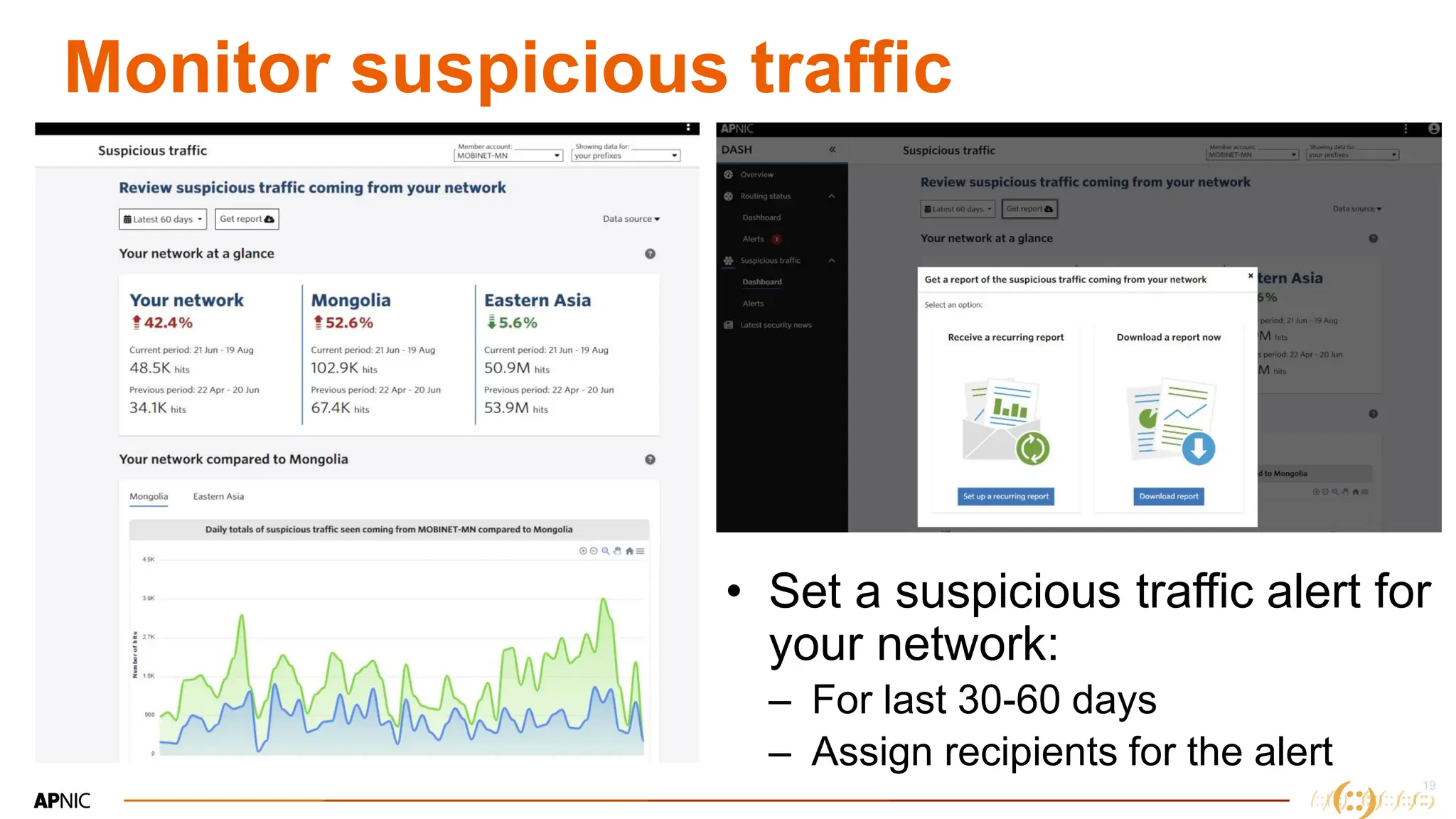
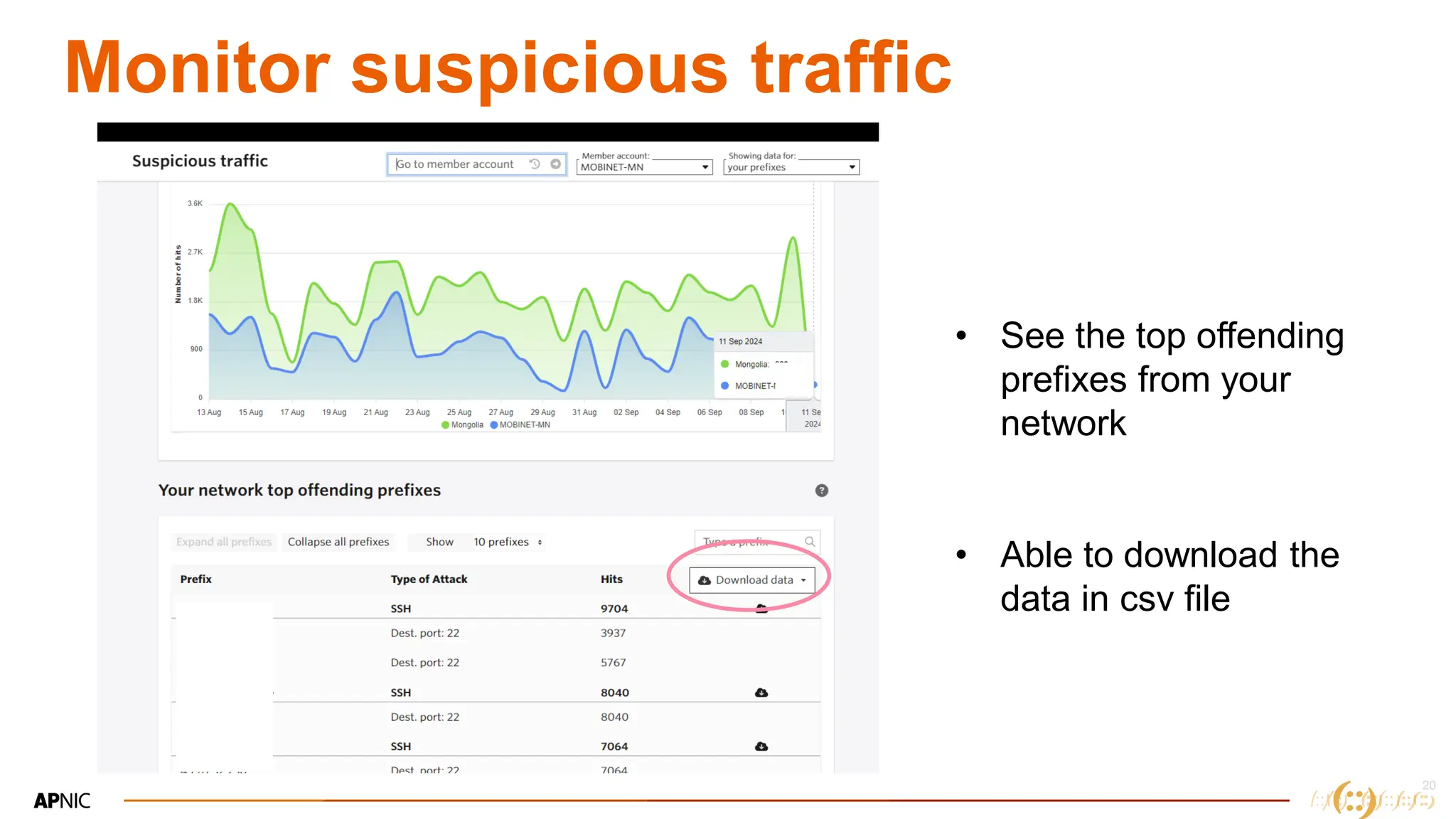
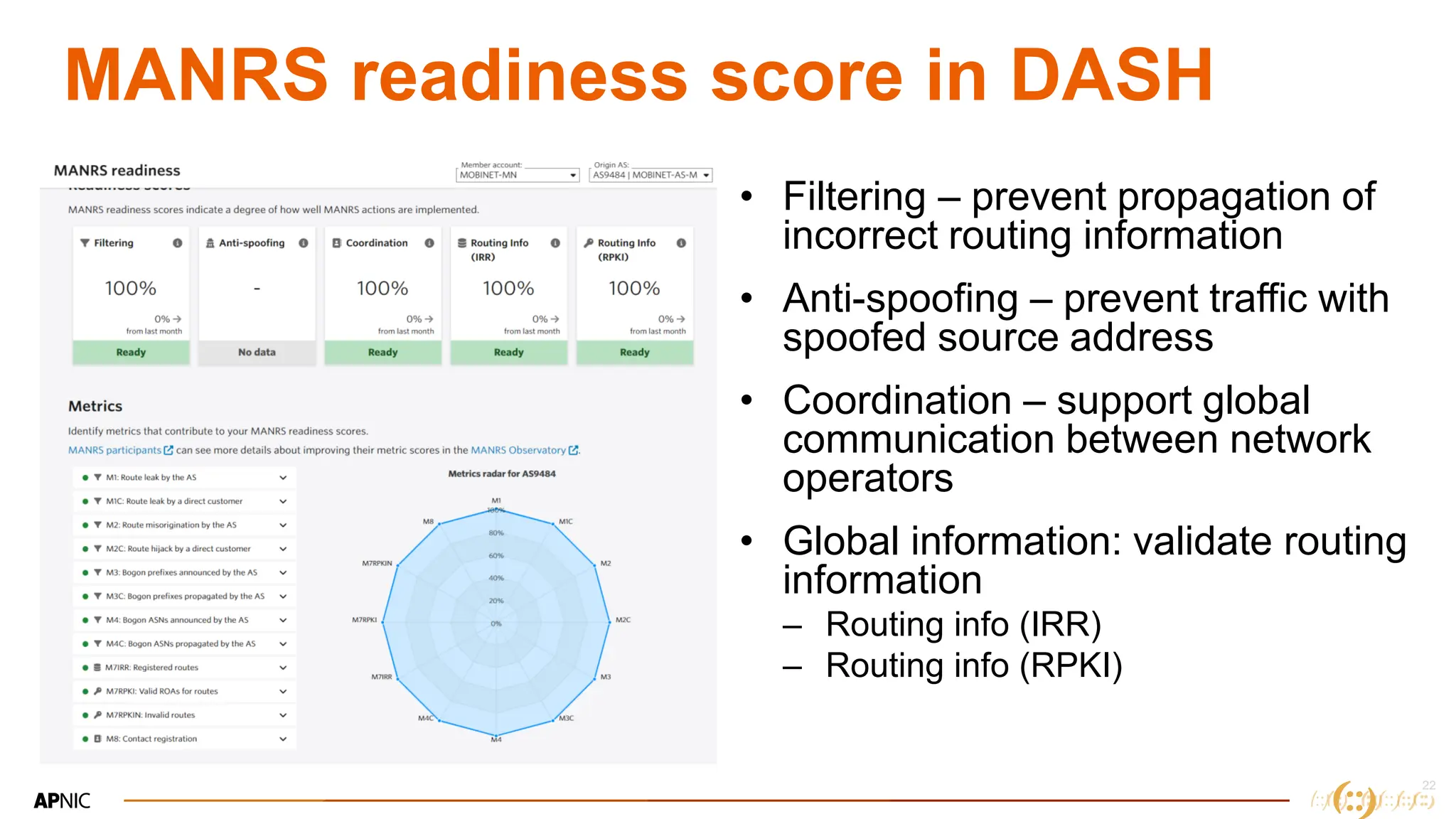
The document discusses IP geolocation, highlighting its importance for location-based services, legal compliance, and targeted advertising, while outlining issues with inaccurate geolocation that can affect online services and user experience. It also introduces the 'Dash' portal for APNIC members, which provides tools for monitoring suspicious traffic, routing issues, and compliance with security best practices. Additionally, the document covers the use of geofeeds to improve IP geolocation accuracy and the importance of adhering to routing security norms.