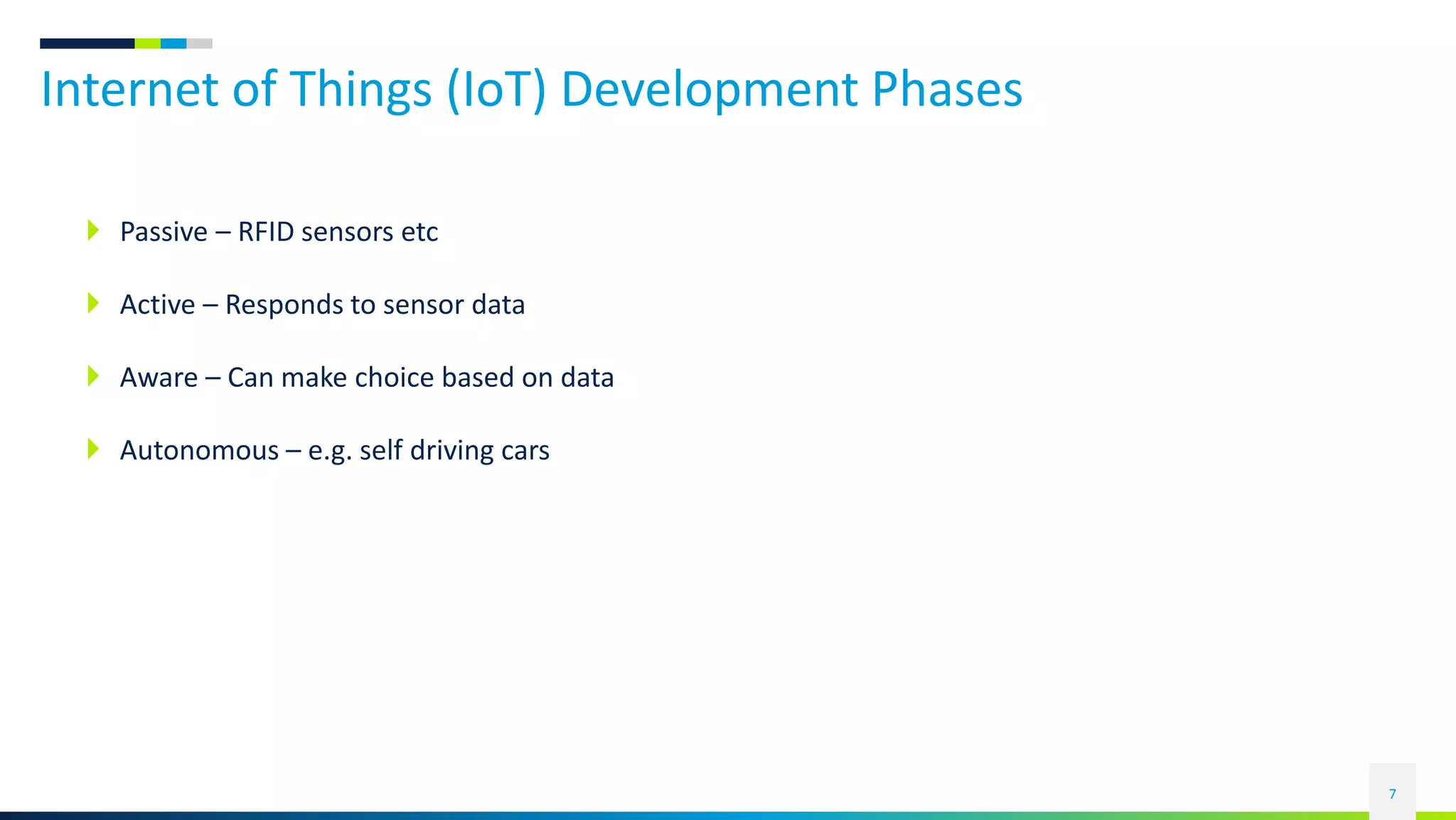
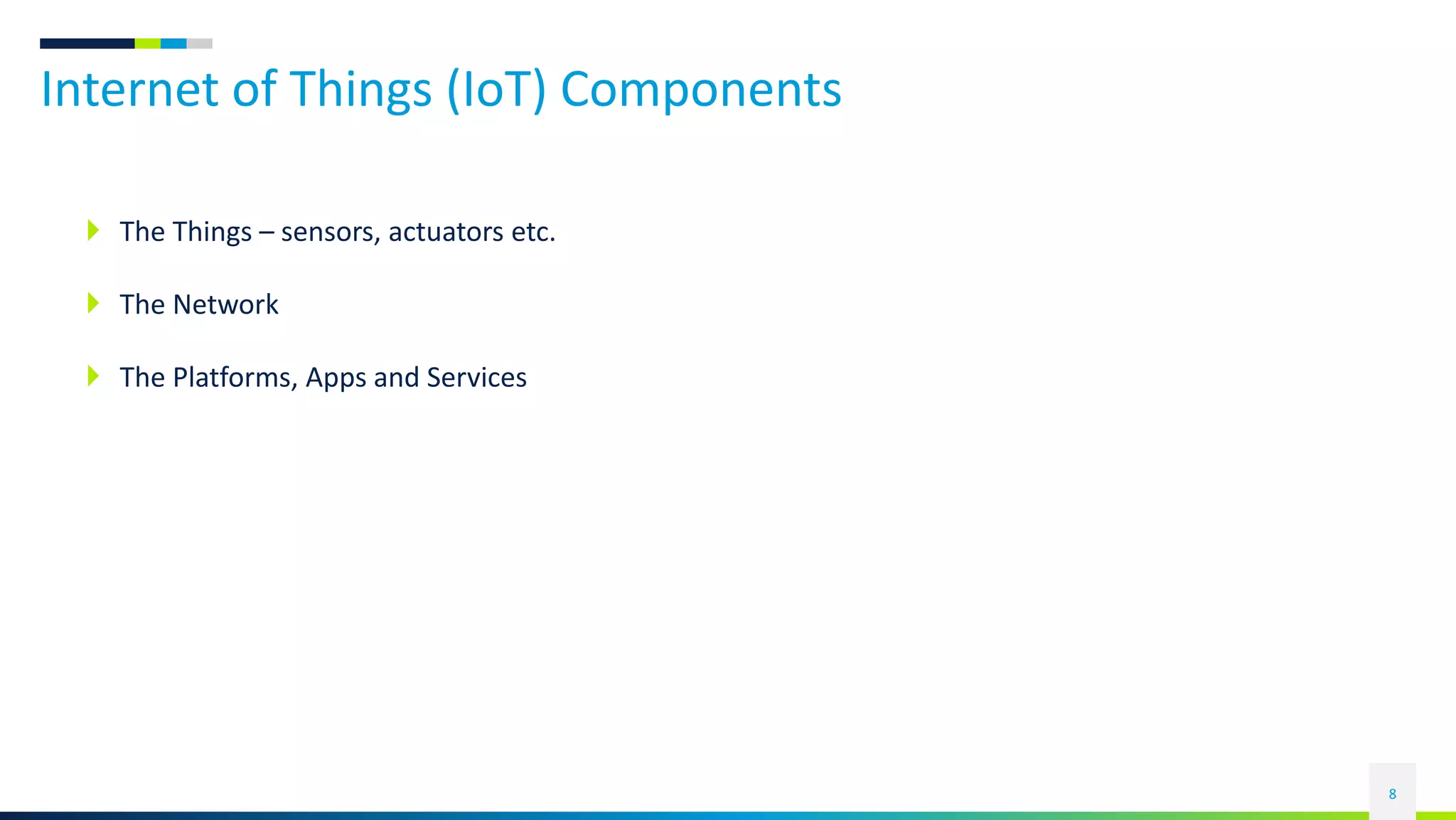
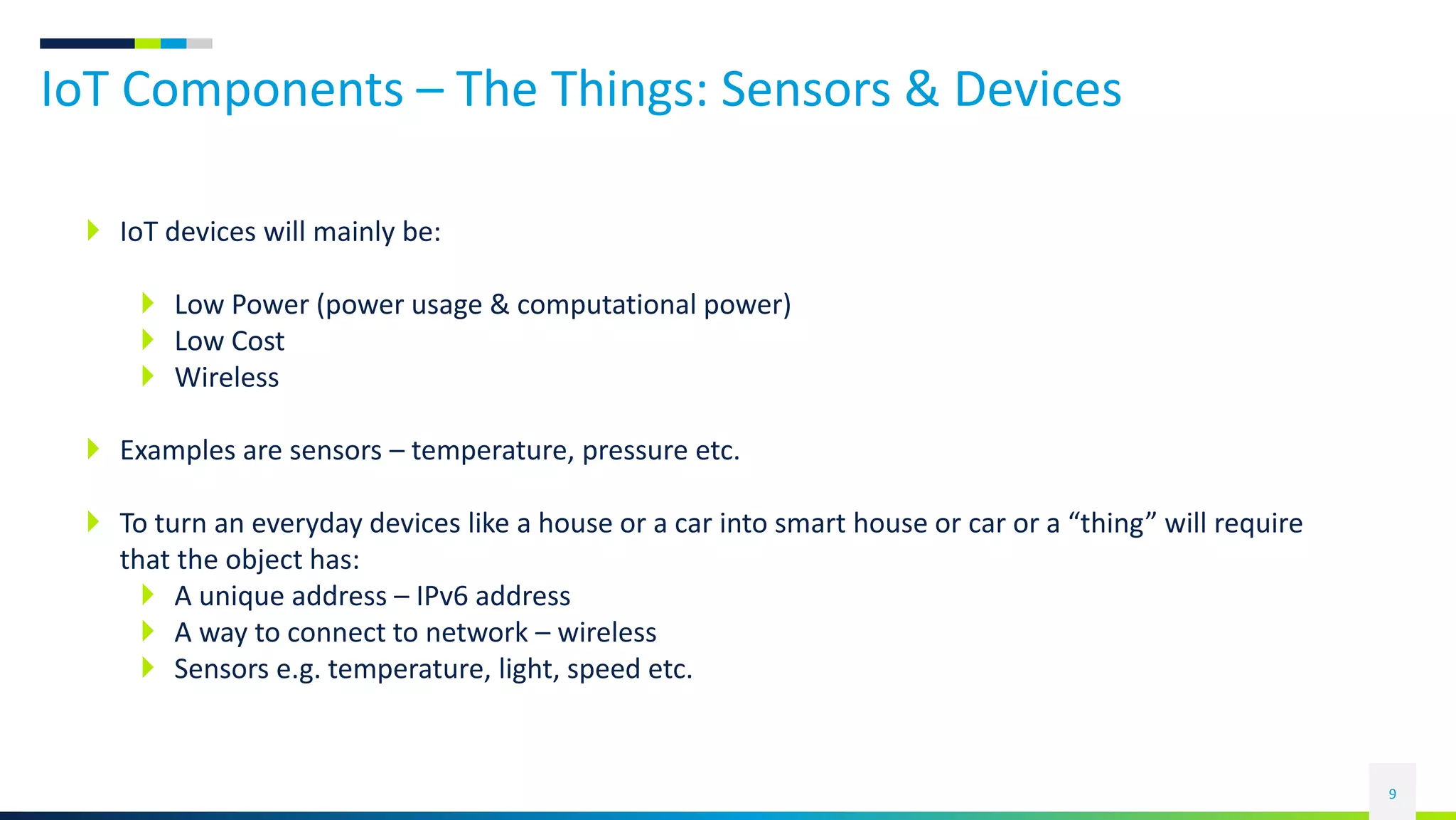
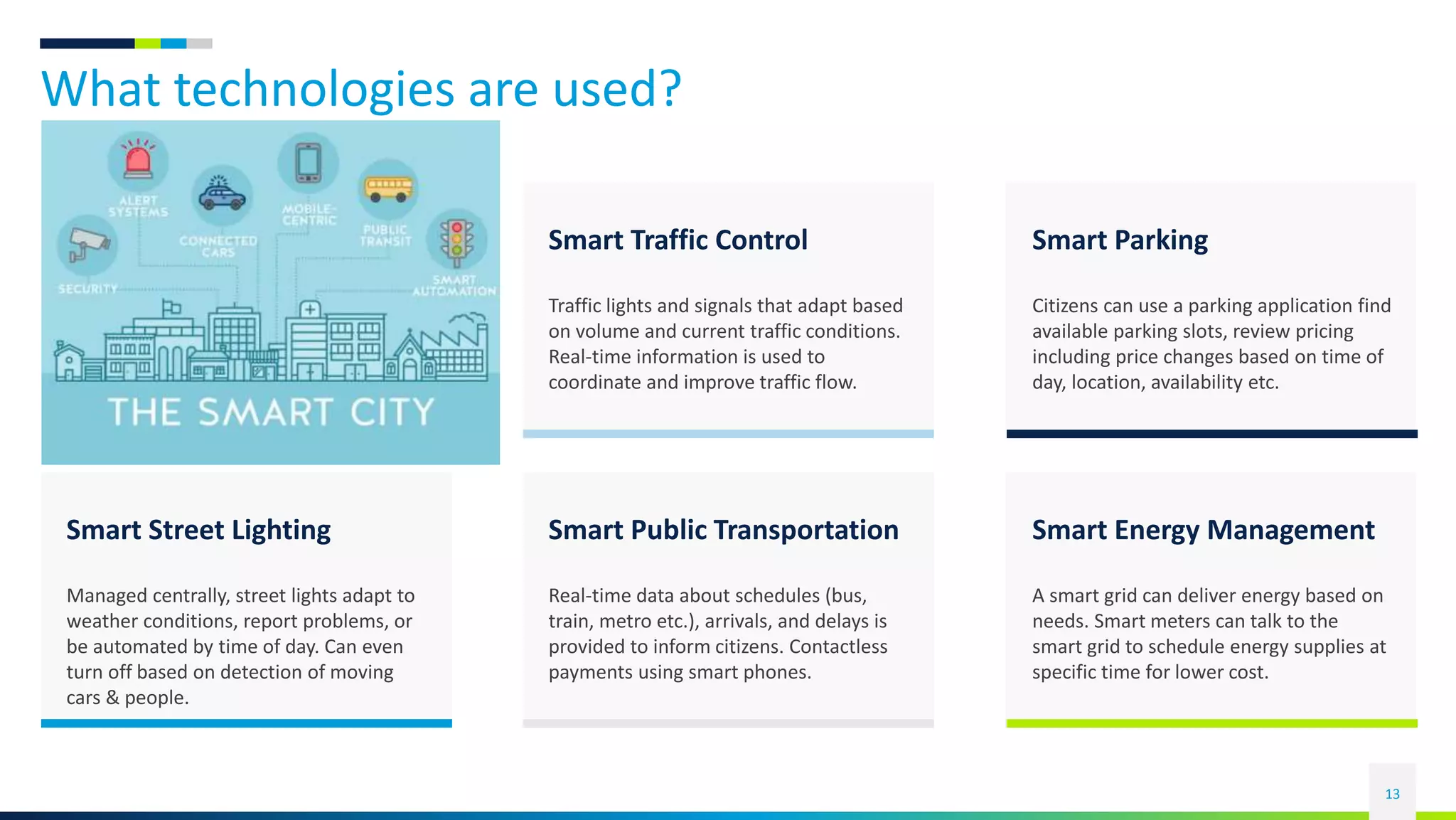
This document discusses the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart devices. It defines IoT as connecting everyday devices to the internet through sensors and software, allowing them to collect and share data. Common IoT sectors include the home, healthcare, factories, and cities. IoT development involves devices becoming more passive, active, aware, and autonomous over time. Key IoT components are things like sensors, networks that connect devices, and platforms that analyze data from devices. An example of a smart city application is given, outlining technologies used for traffic control, parking, transportation, energy, lighting, water management, waste handling, and security.