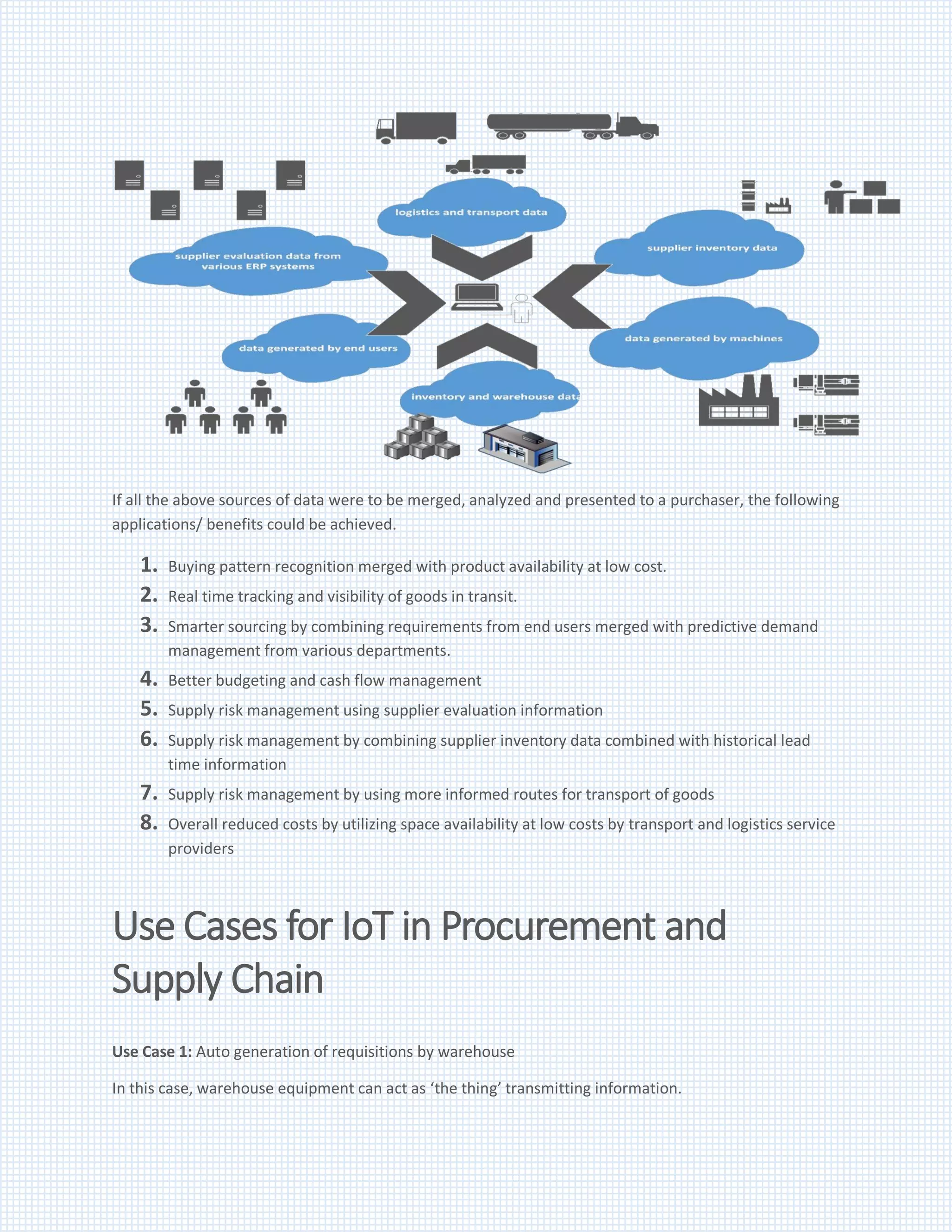
IoT refers to connecting physical devices to the internet and to each other to generate and share data. This data can provide insights to improve procurement and supply chain management. Specifically, IoT data from internal sources like warehouses and machines and external sources like suppliers can be used to better manage risks, reduce costs, improve processes, make effective decisions, conduct spend analysis and forecasting, and enhance supplier management. Examples of potential benefits include automatically generating requisitions based on warehouse inventory levels and improving subcontracting processes through real-time tracking of parts and quality checks. The key is identifying meaningful ways to leverage relevant IoT data sources for specific organizational needs.