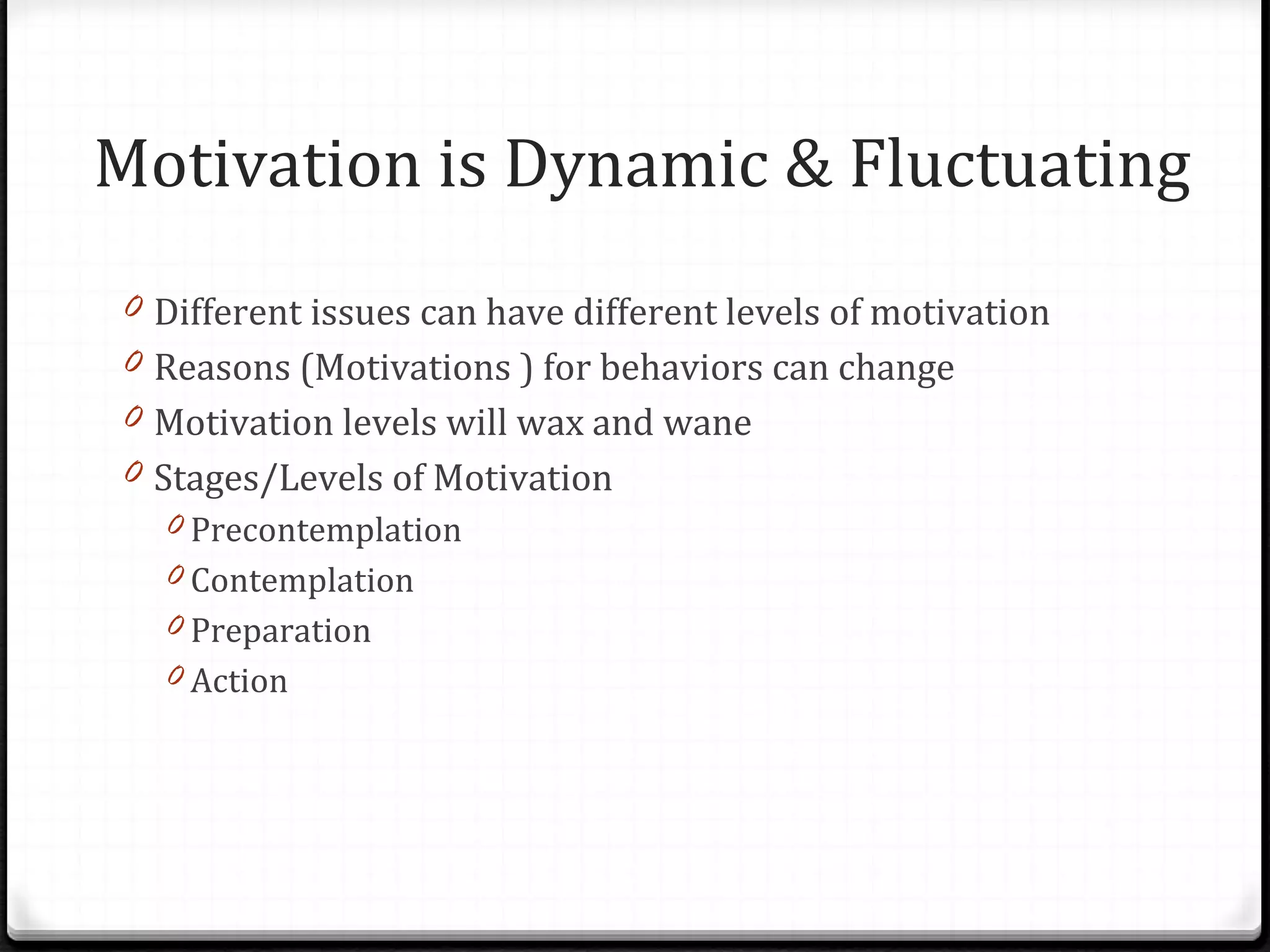
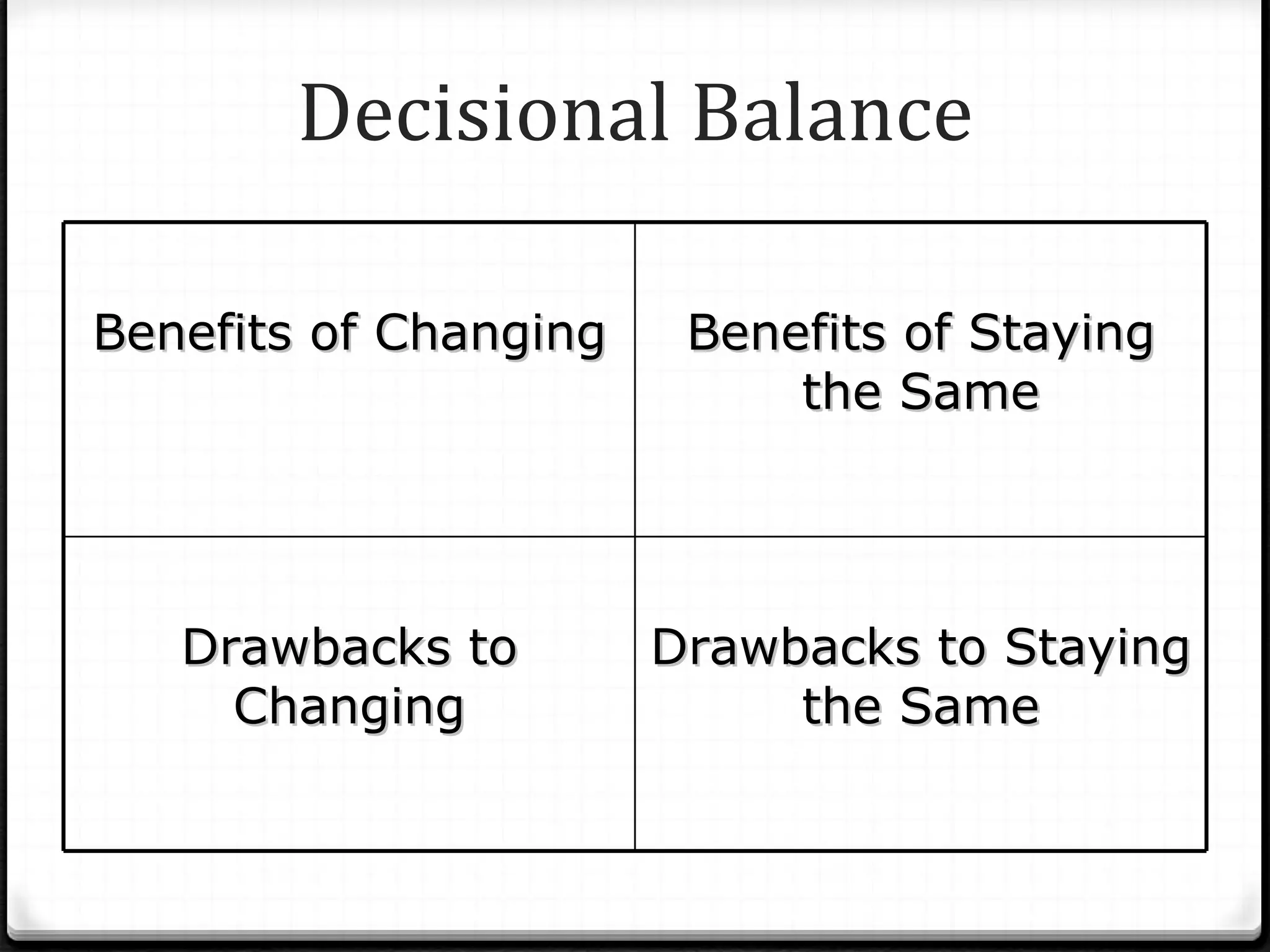
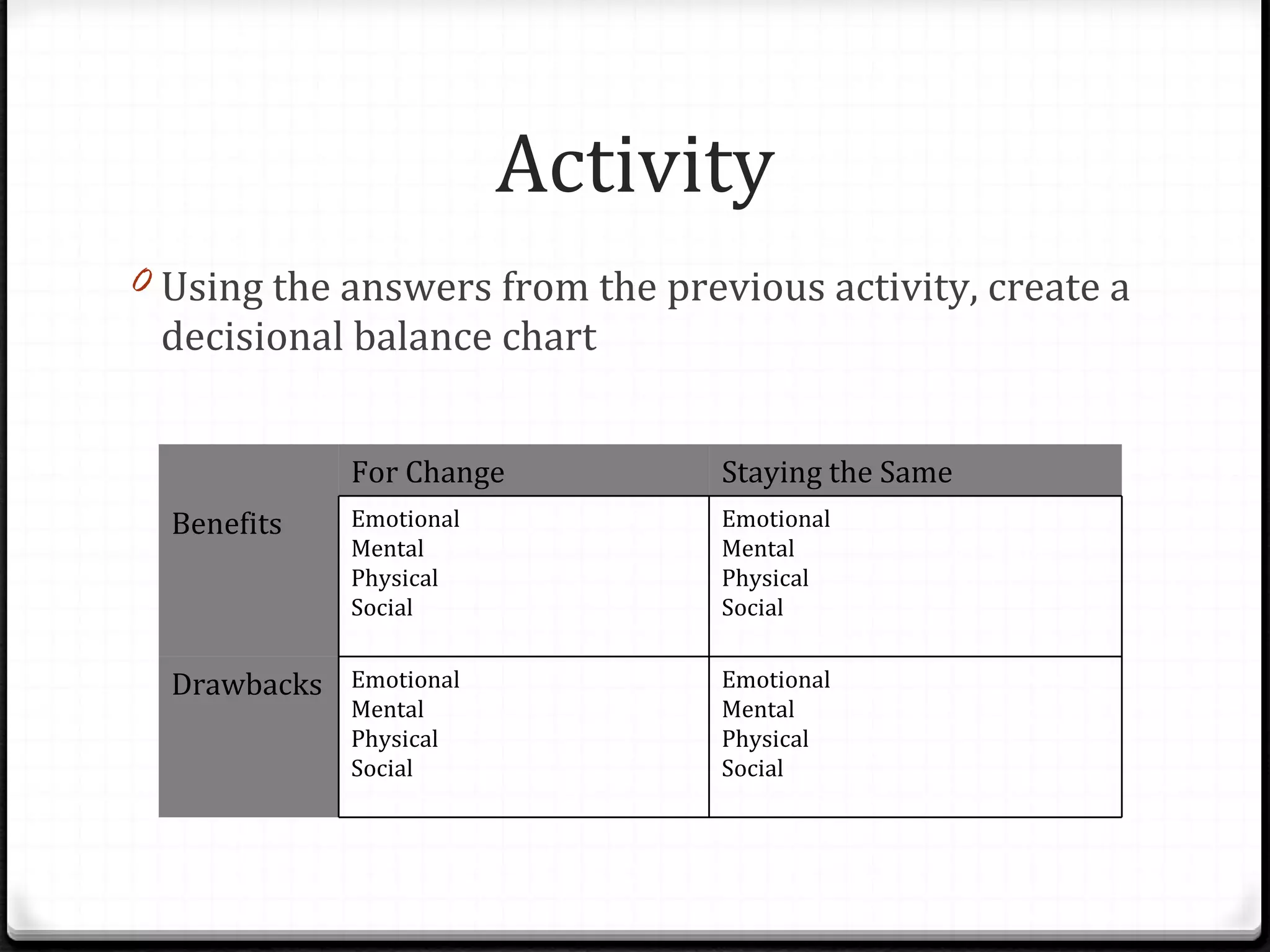
The document provides guidance on developing goals and increasing motivation to achieve them. It discusses defining motivation and its relationship to goal setting. Key aspects of motivation include commitment, control, and challenge. Motivation is multidimensional, involving emotional, cognitive, physical and social factors. The document then outlines techniques for setting goals and increasing motivation, including identifying reasons for change, developing a decisional balance, addressing triggers, enhancing coping skills, and ensuring basic needs are met.