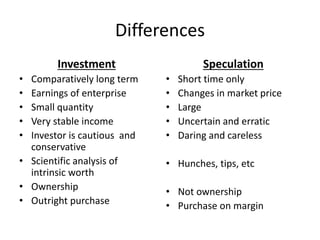
This document discusses different types of investments and financial instruments. It defines investment as purchasing an asset with the goal of generating future income or appreciation. Examples given include factories, education, and monetary assets. Speculation aims to profit from short-term price fluctuations rather than long-term growth. The document contrasts features of investments versus speculation. It also outlines the investment process, different types of financial instruments including money market instruments, treasury bills, certificates of deposit, commercial paper, repos, and call money markets.