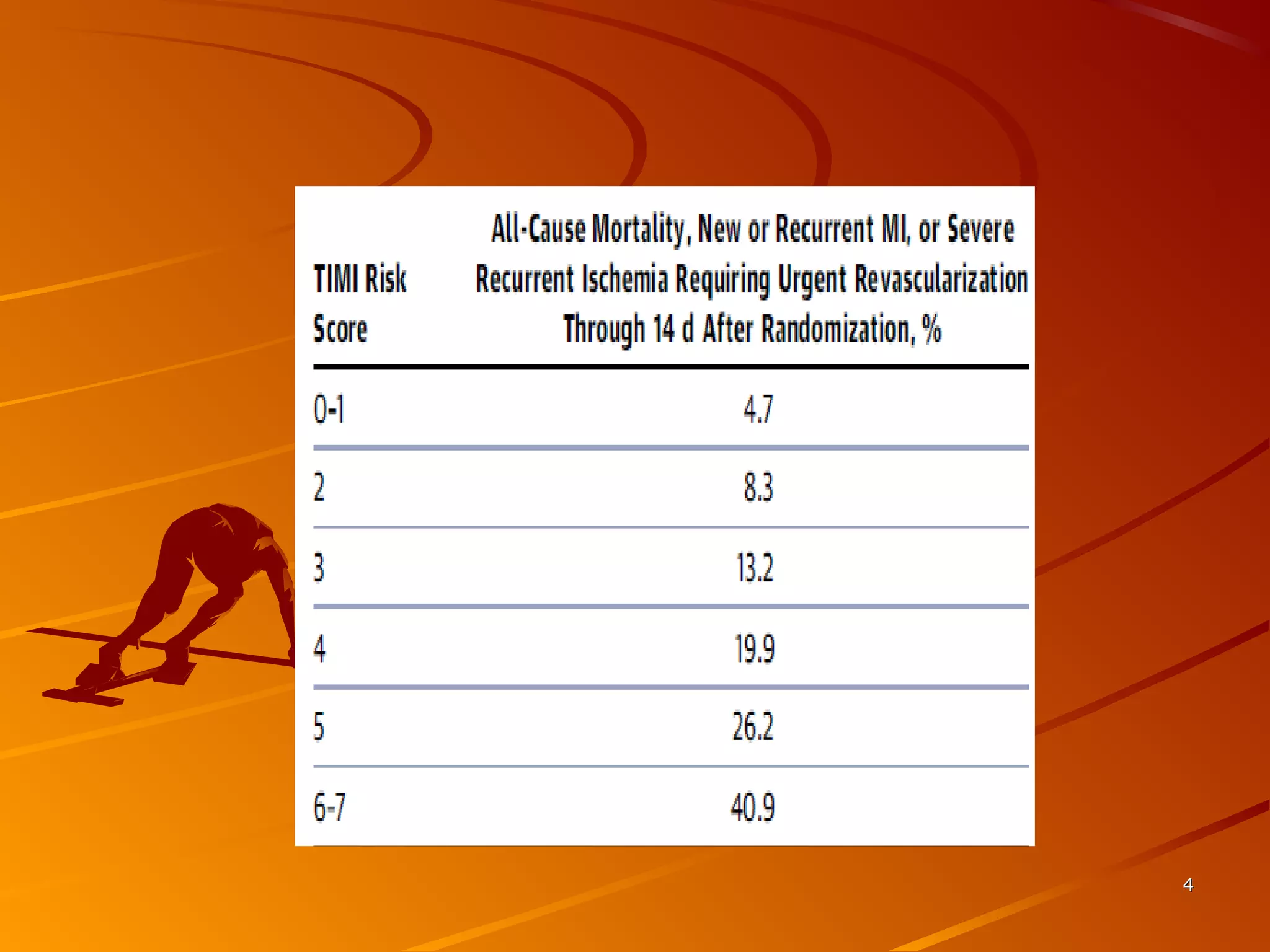
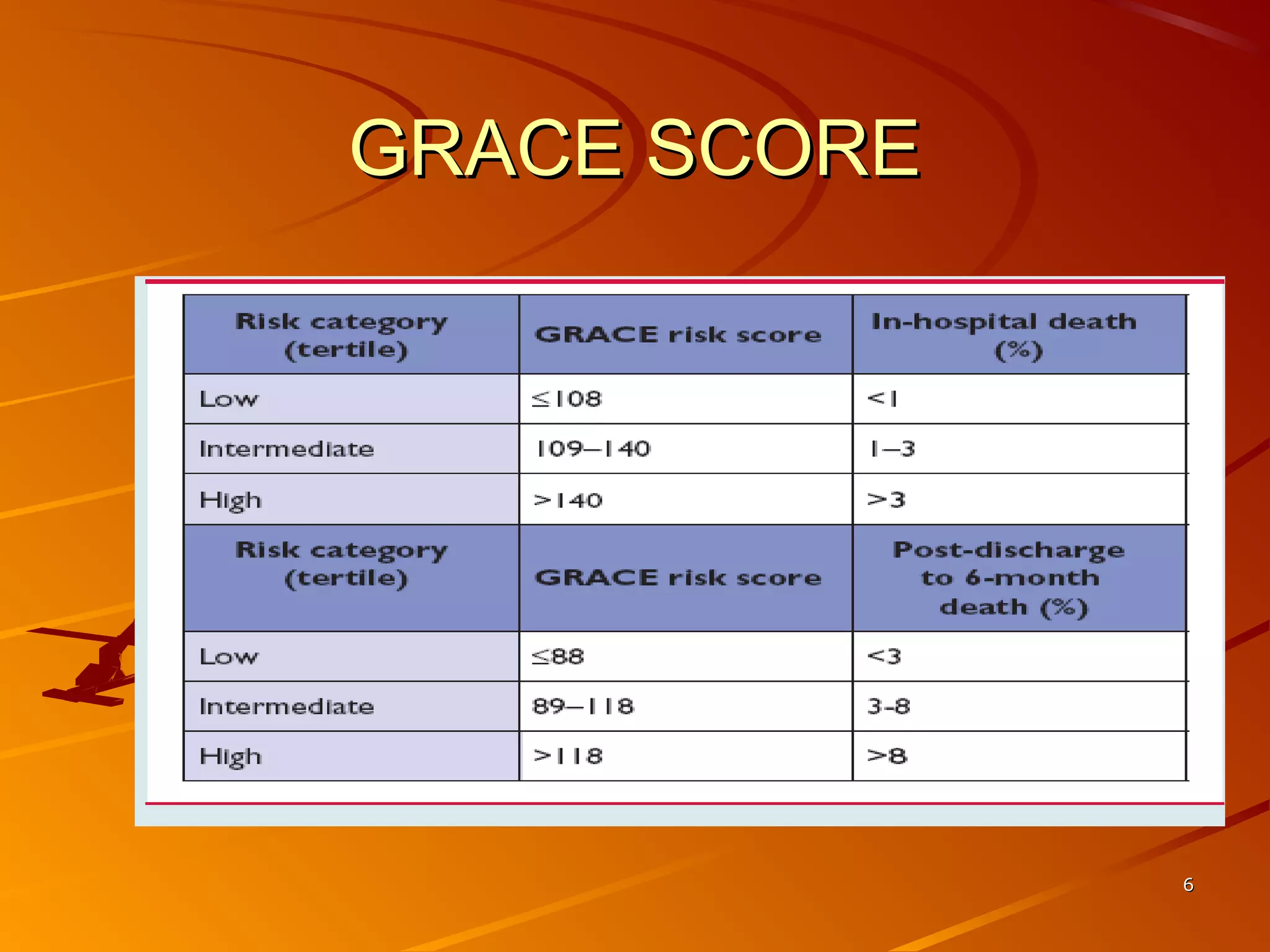
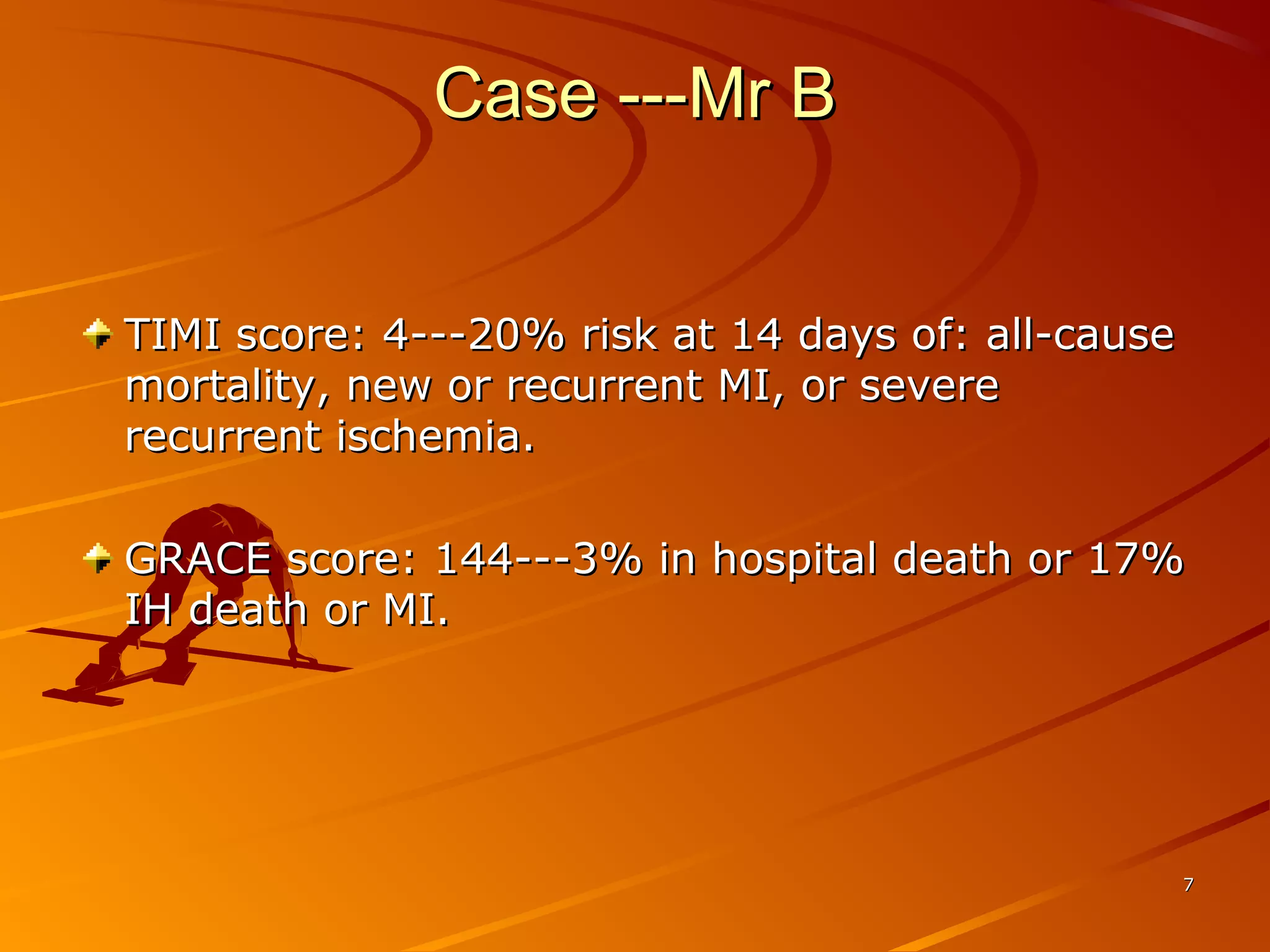
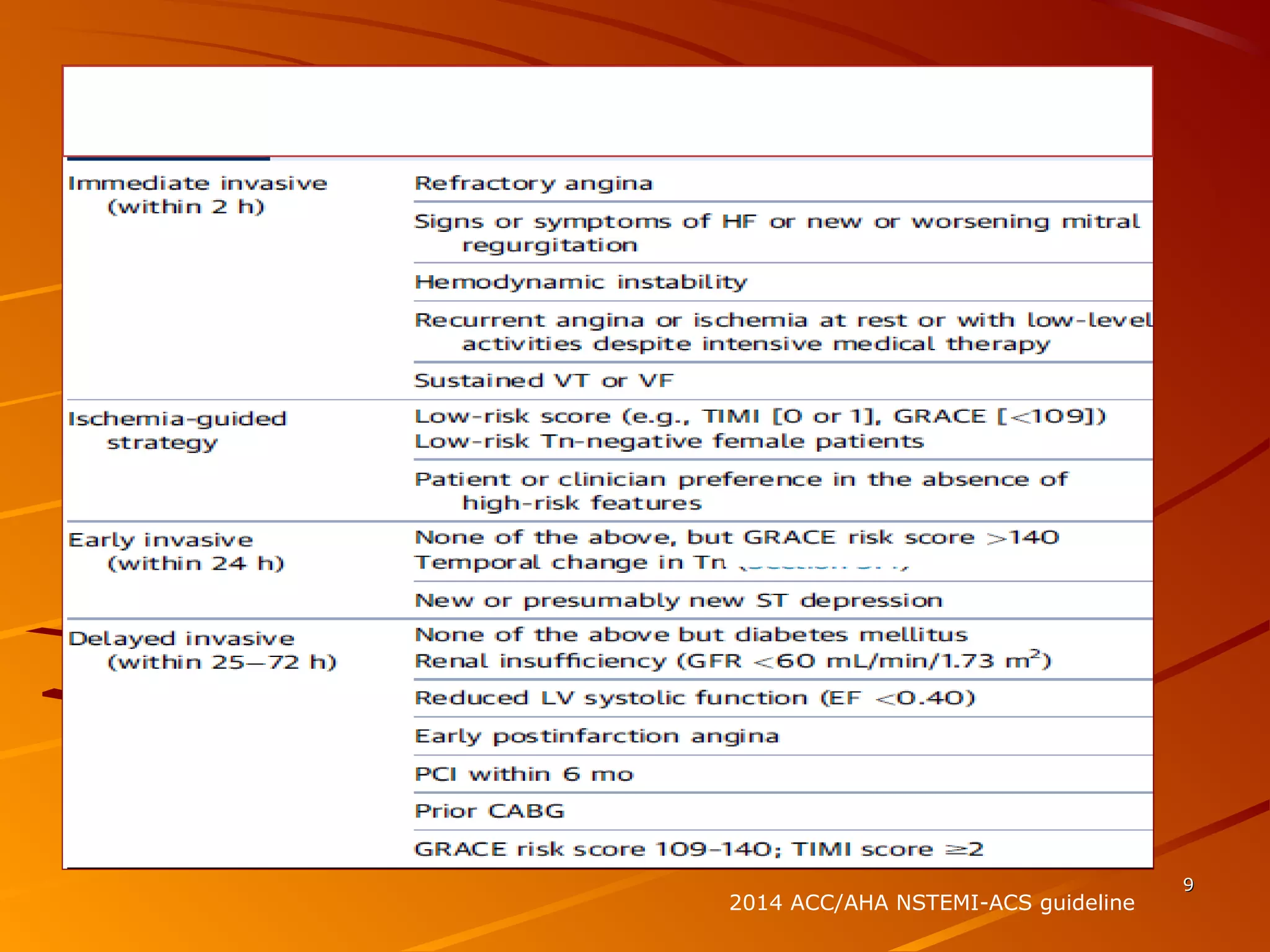
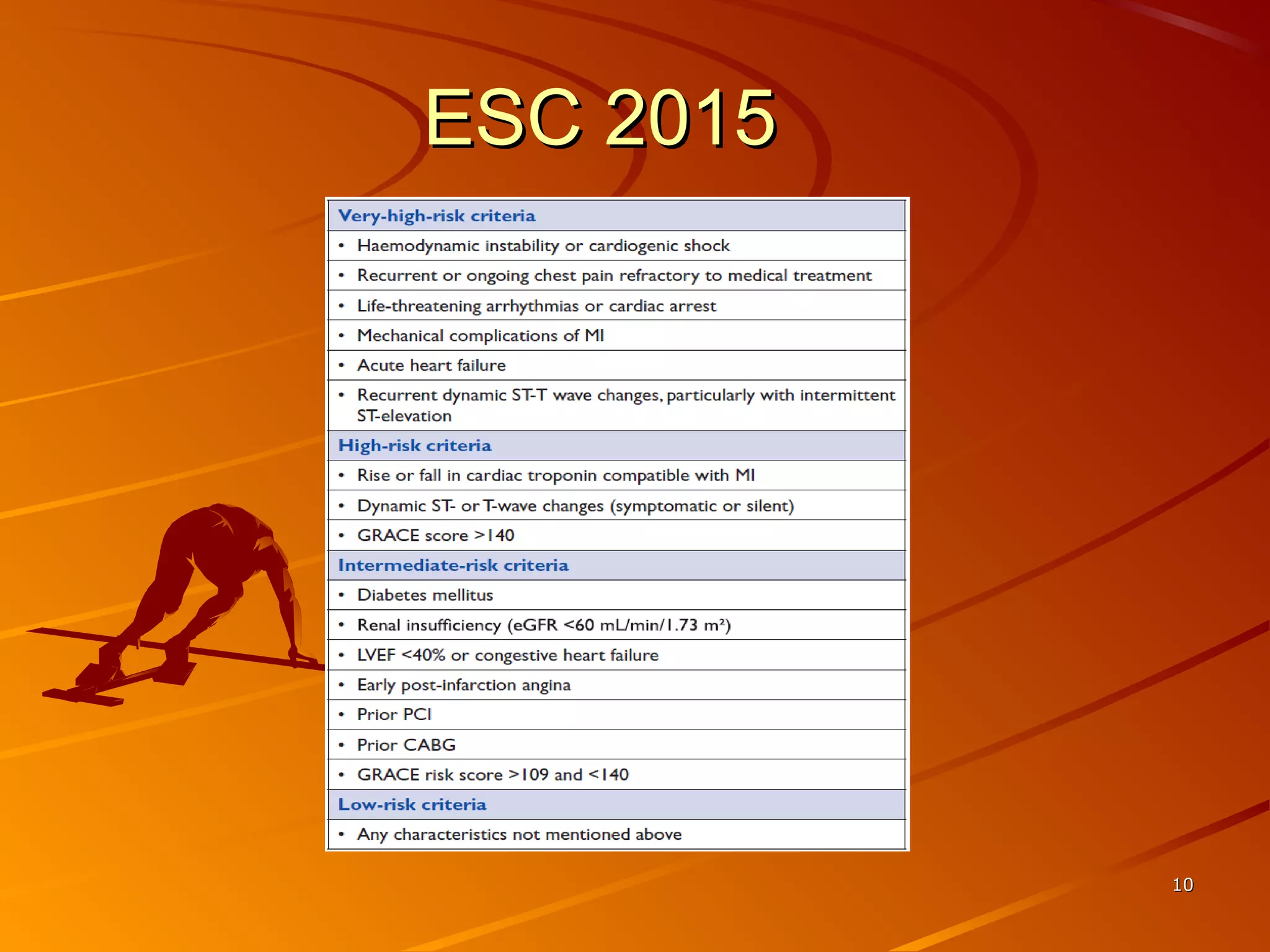
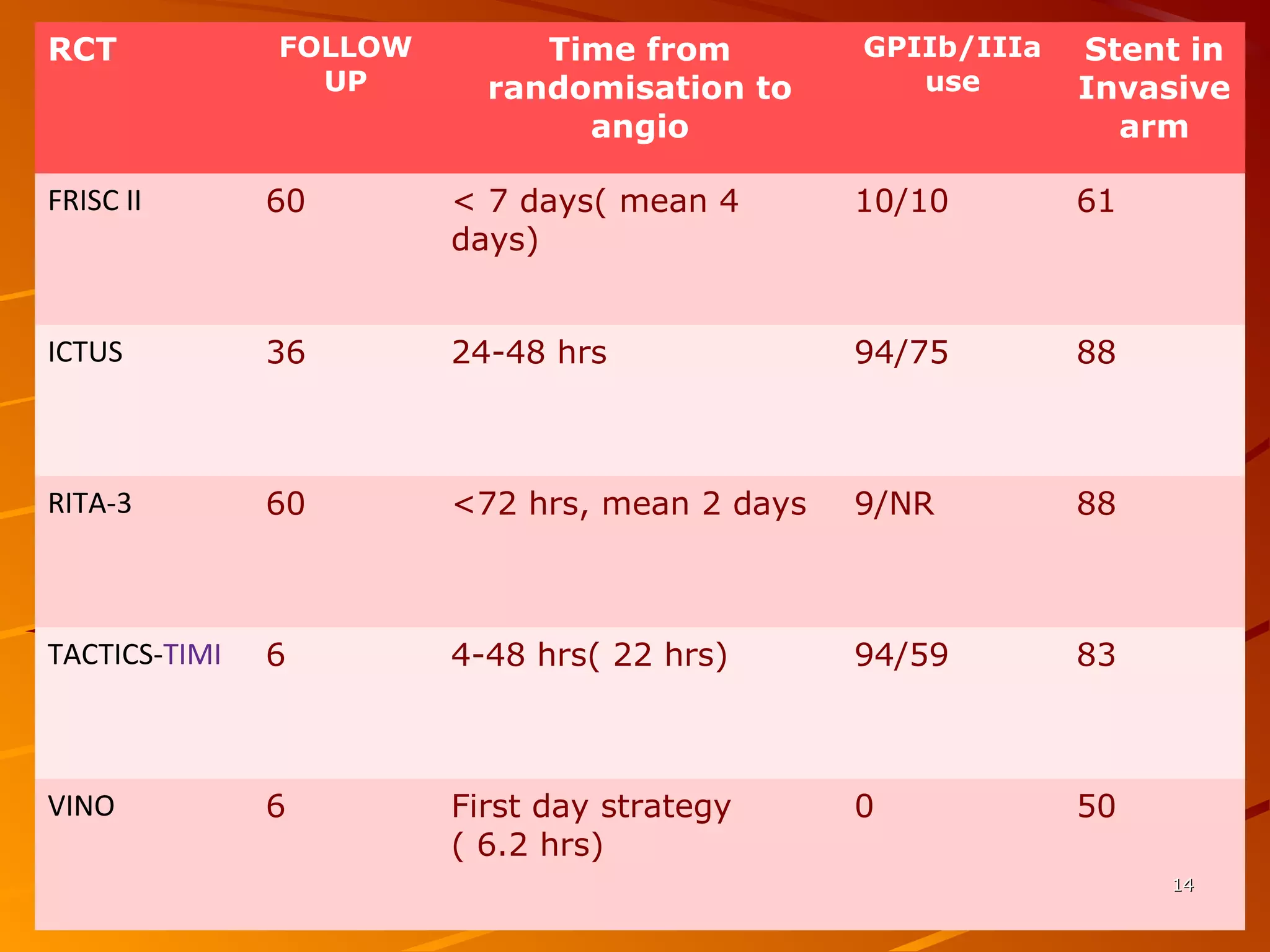
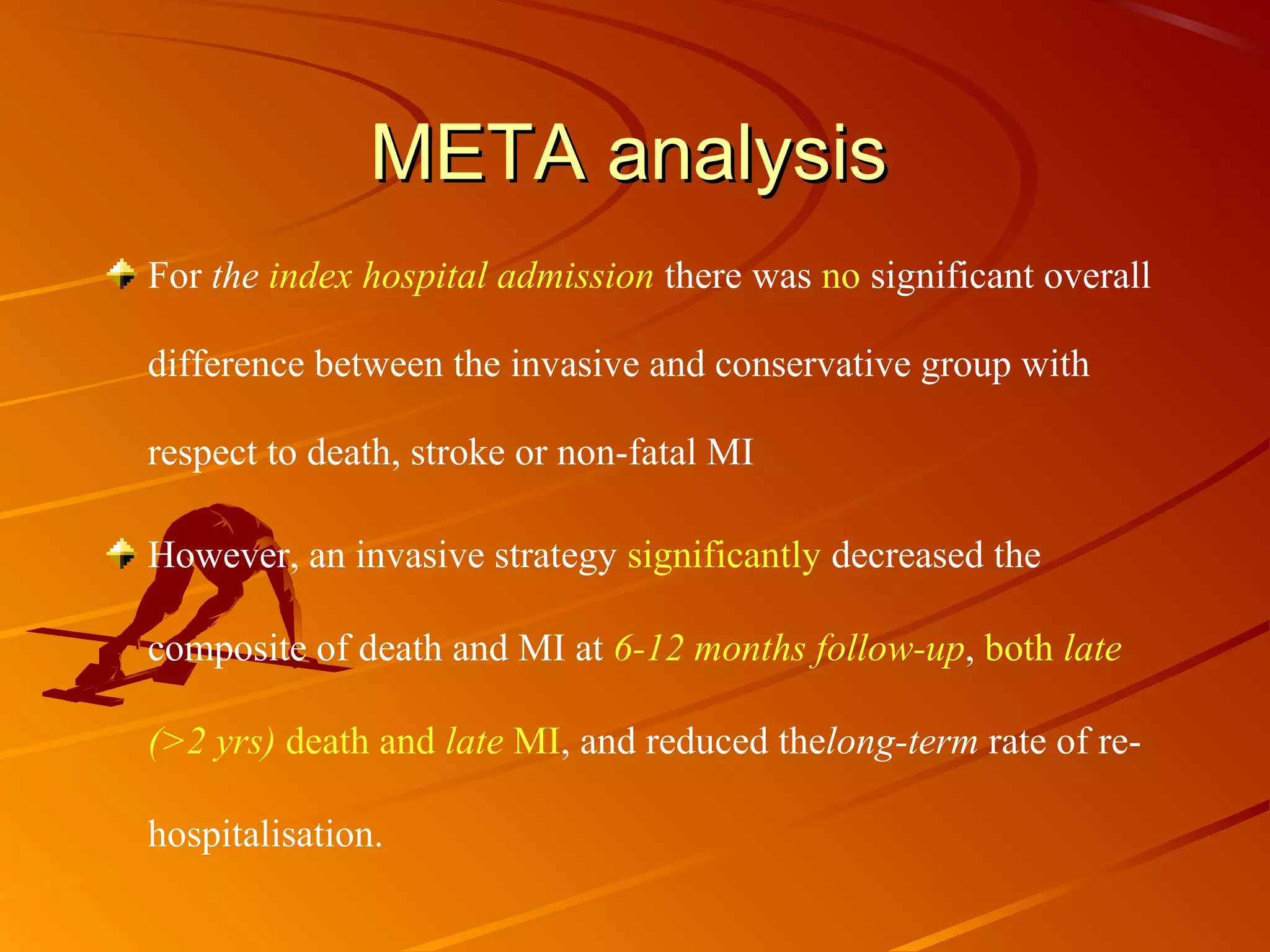
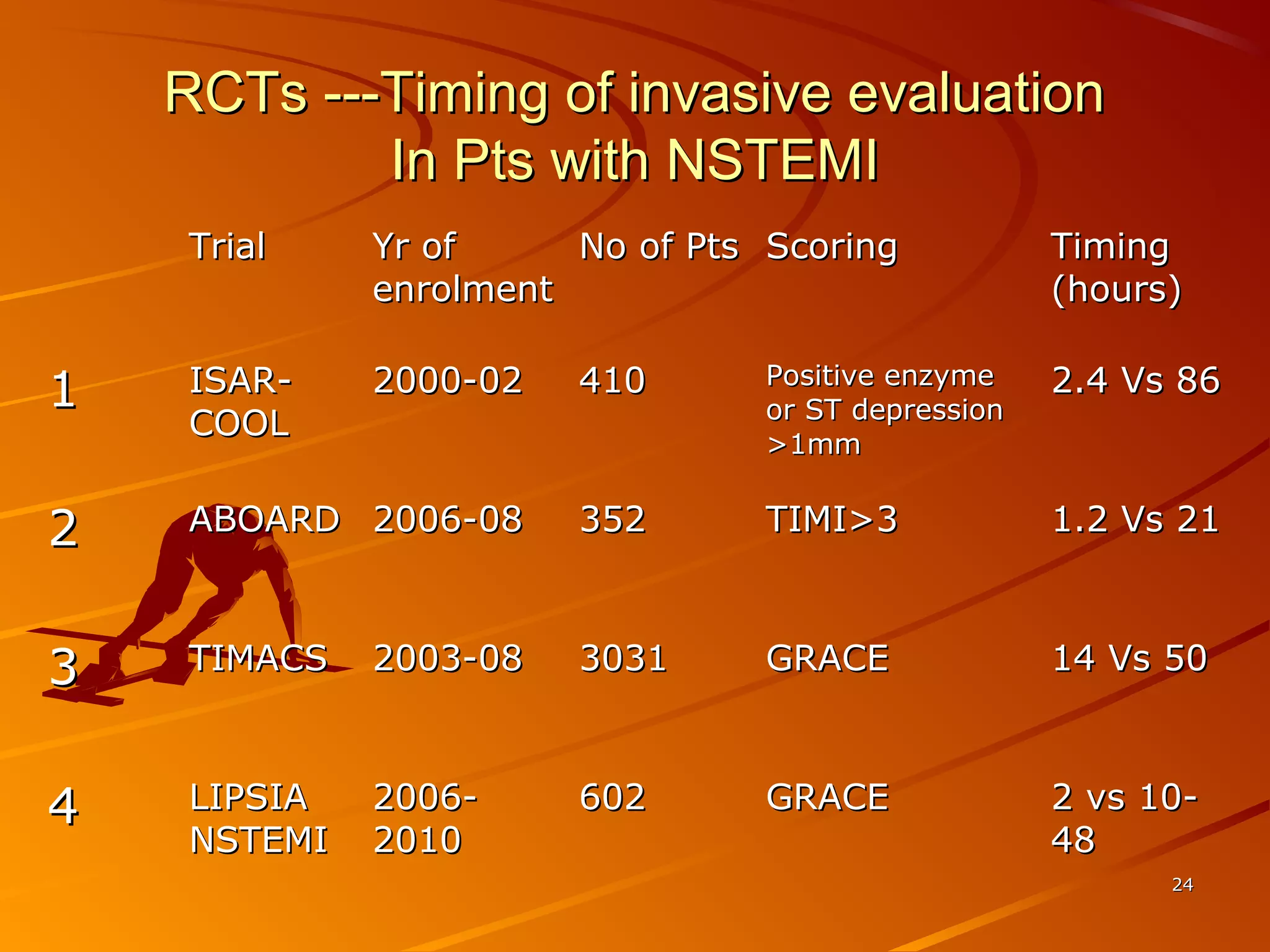
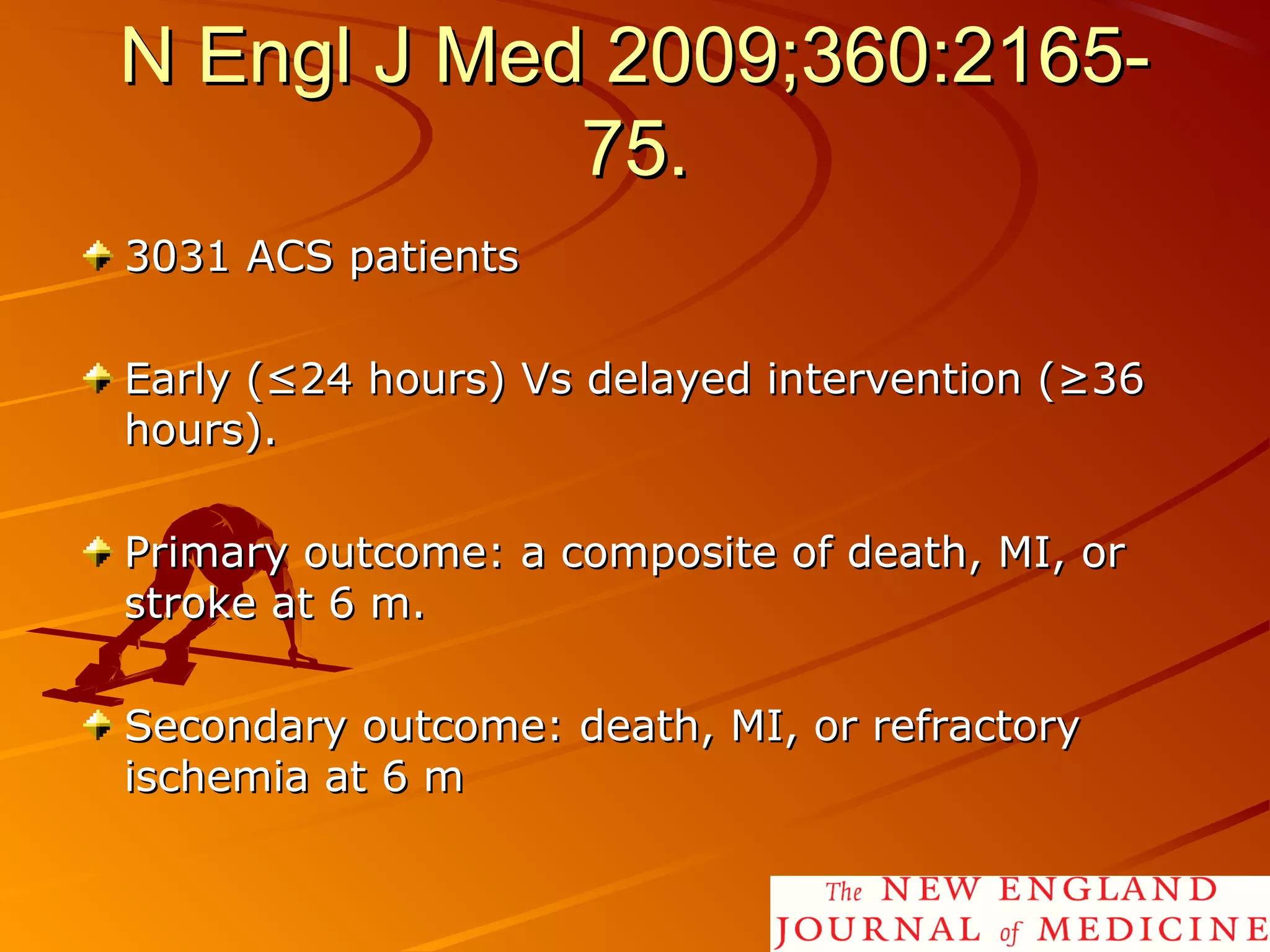
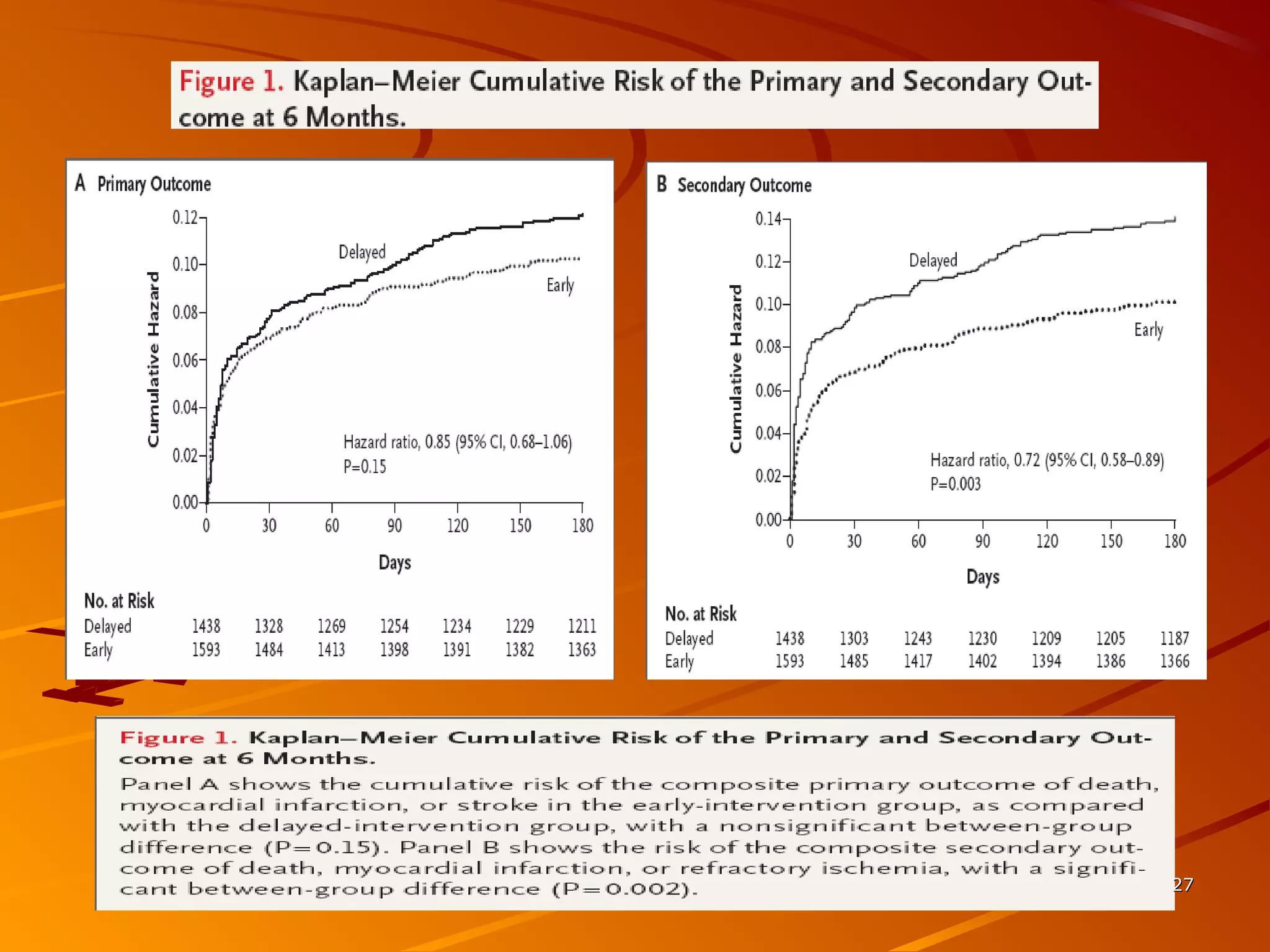
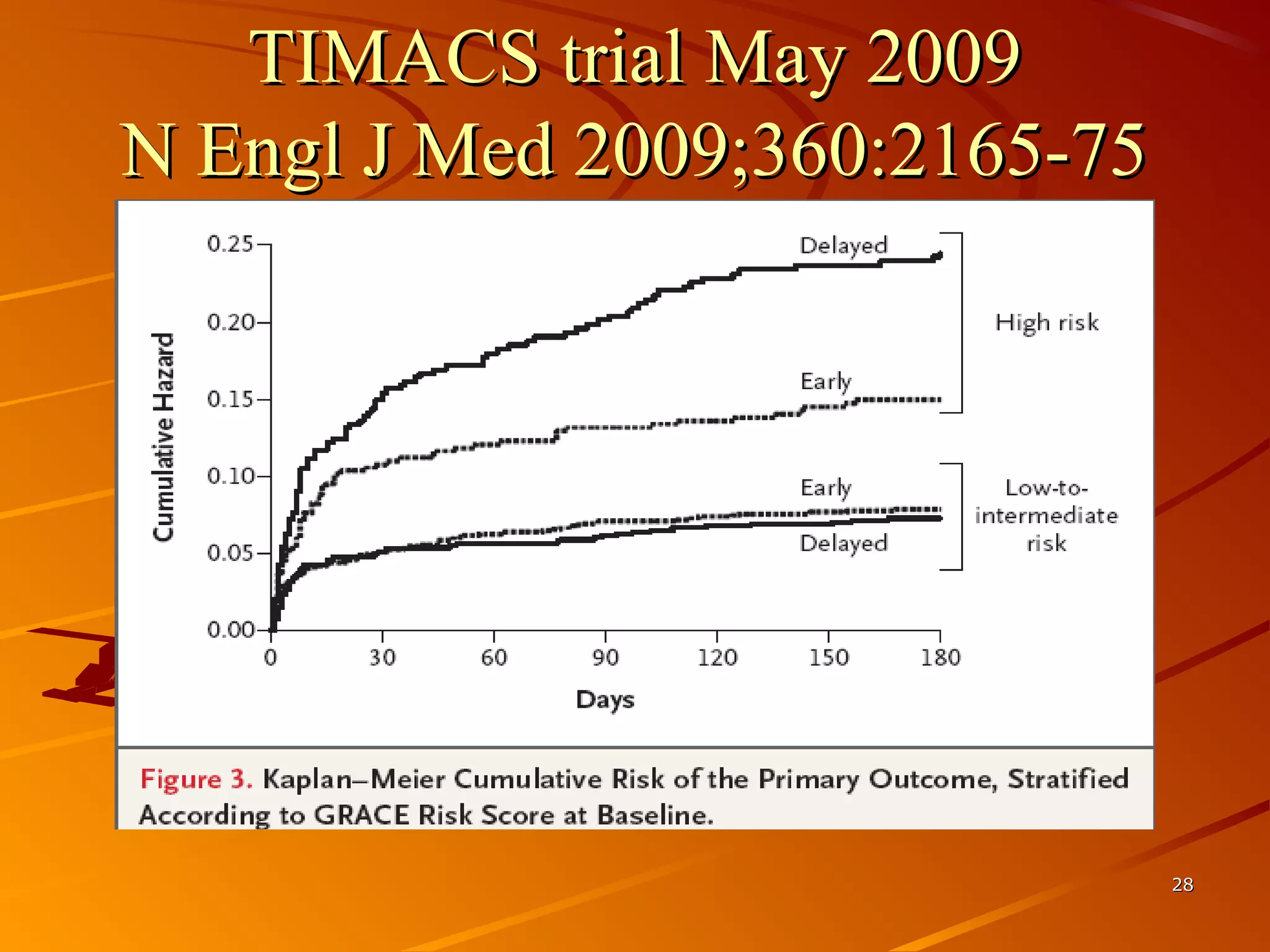
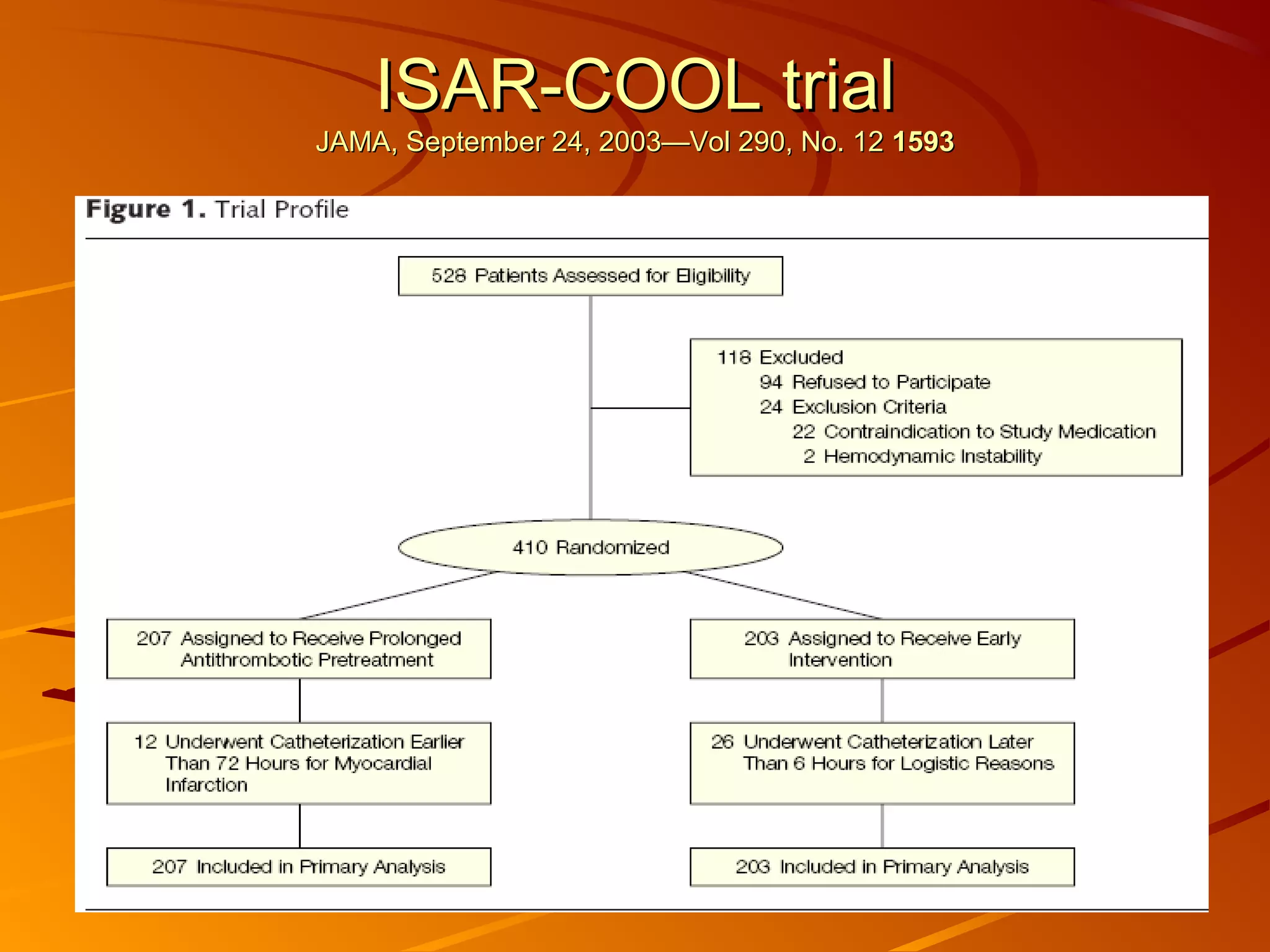
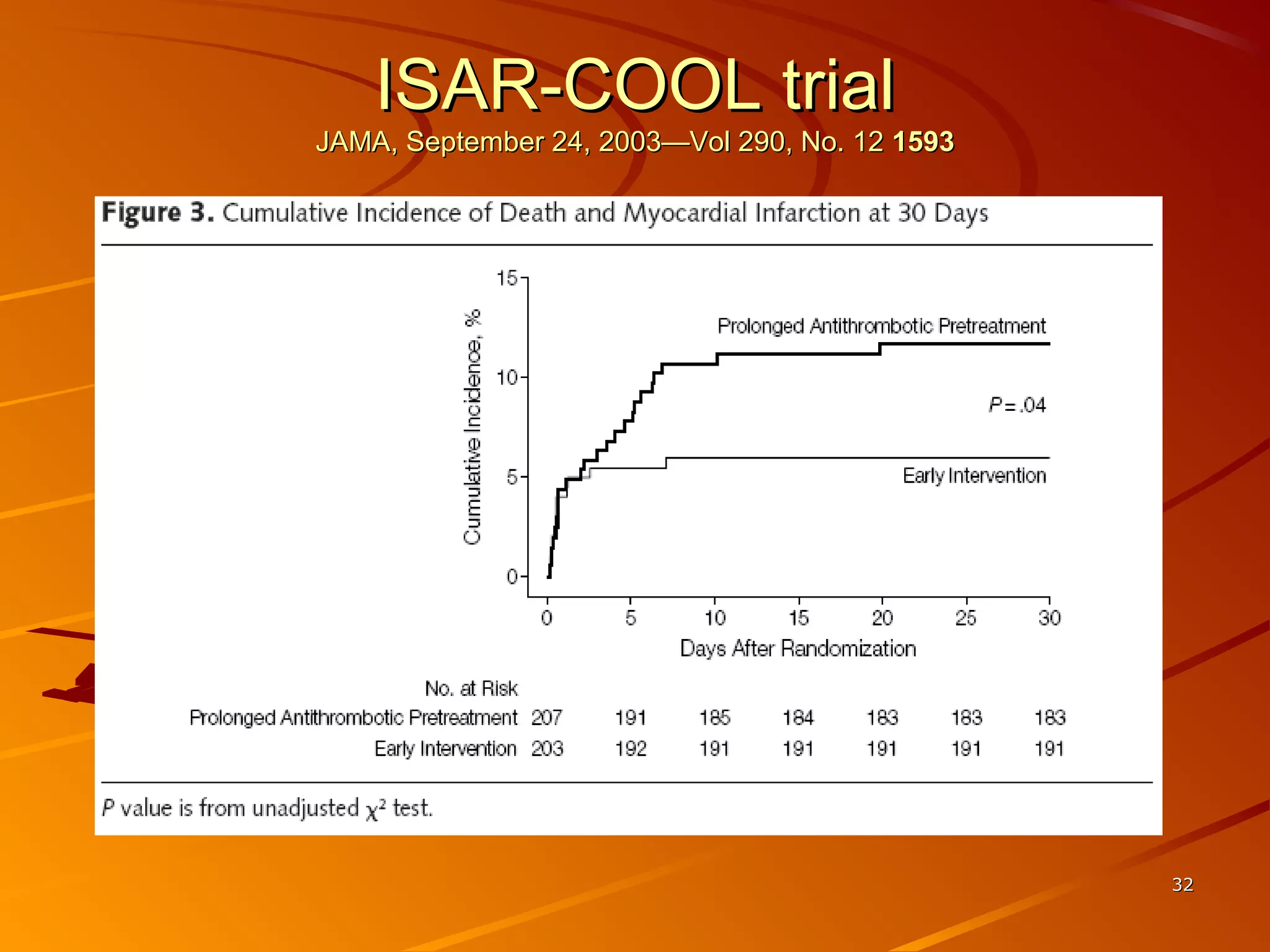
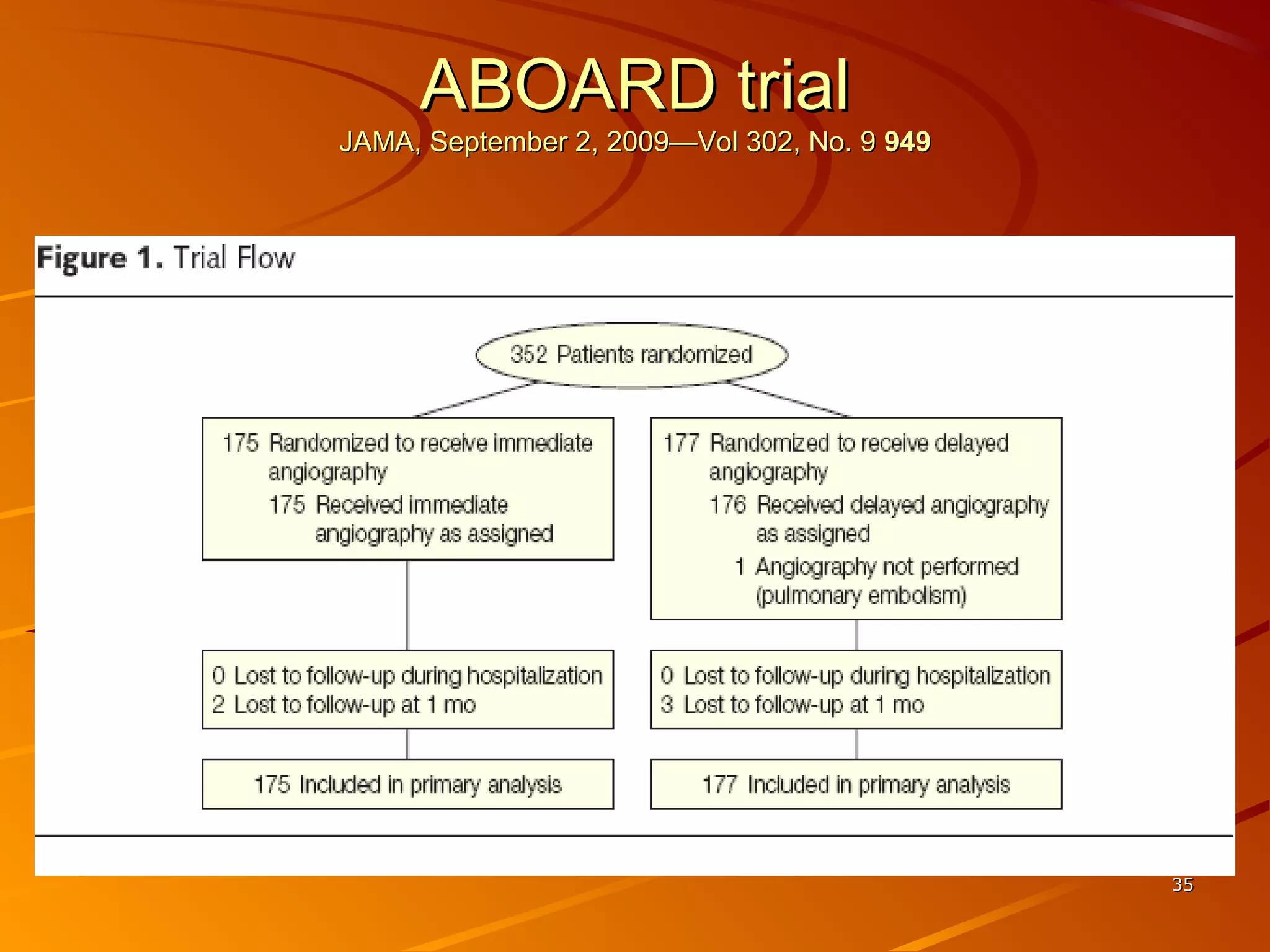
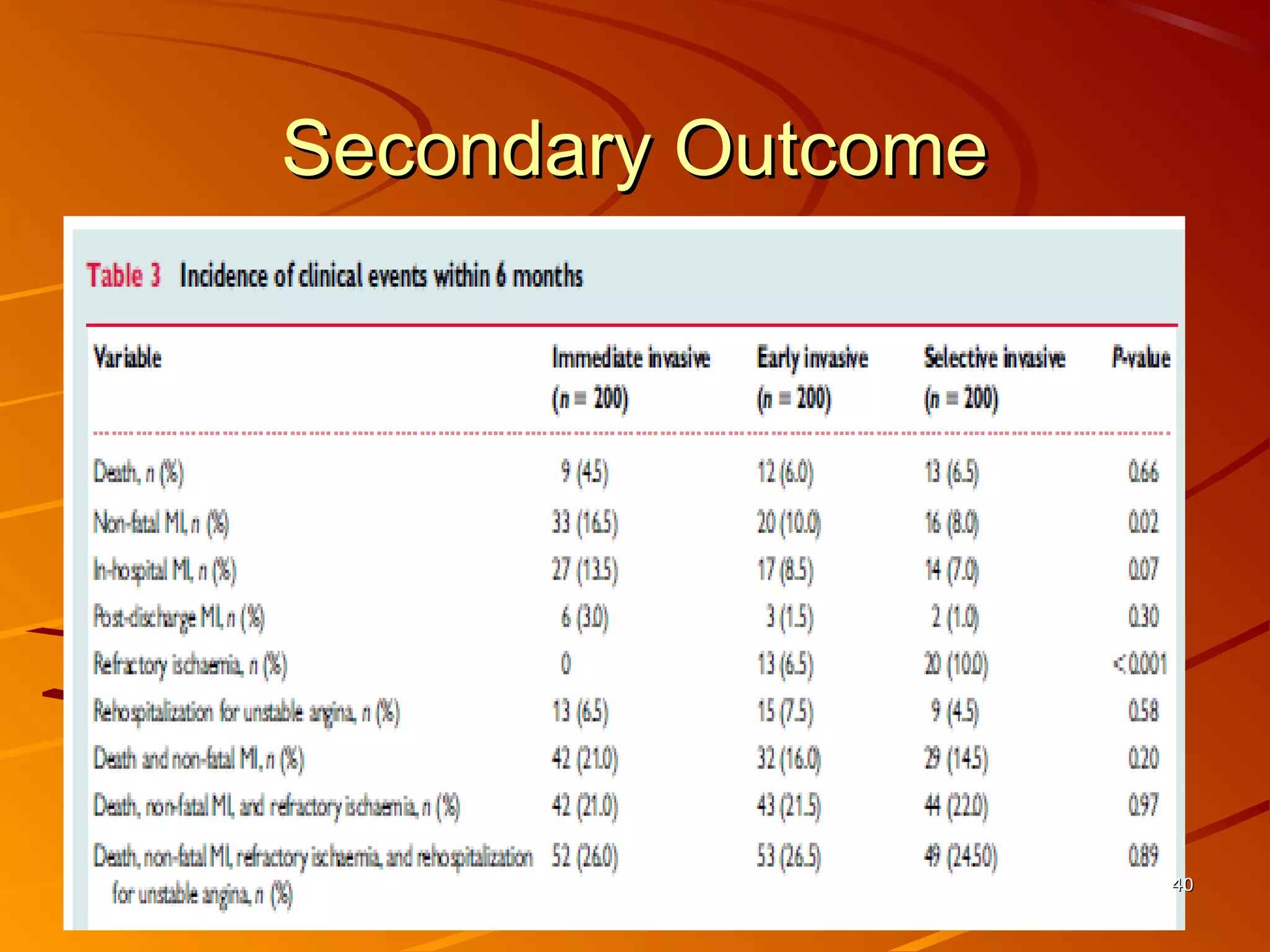
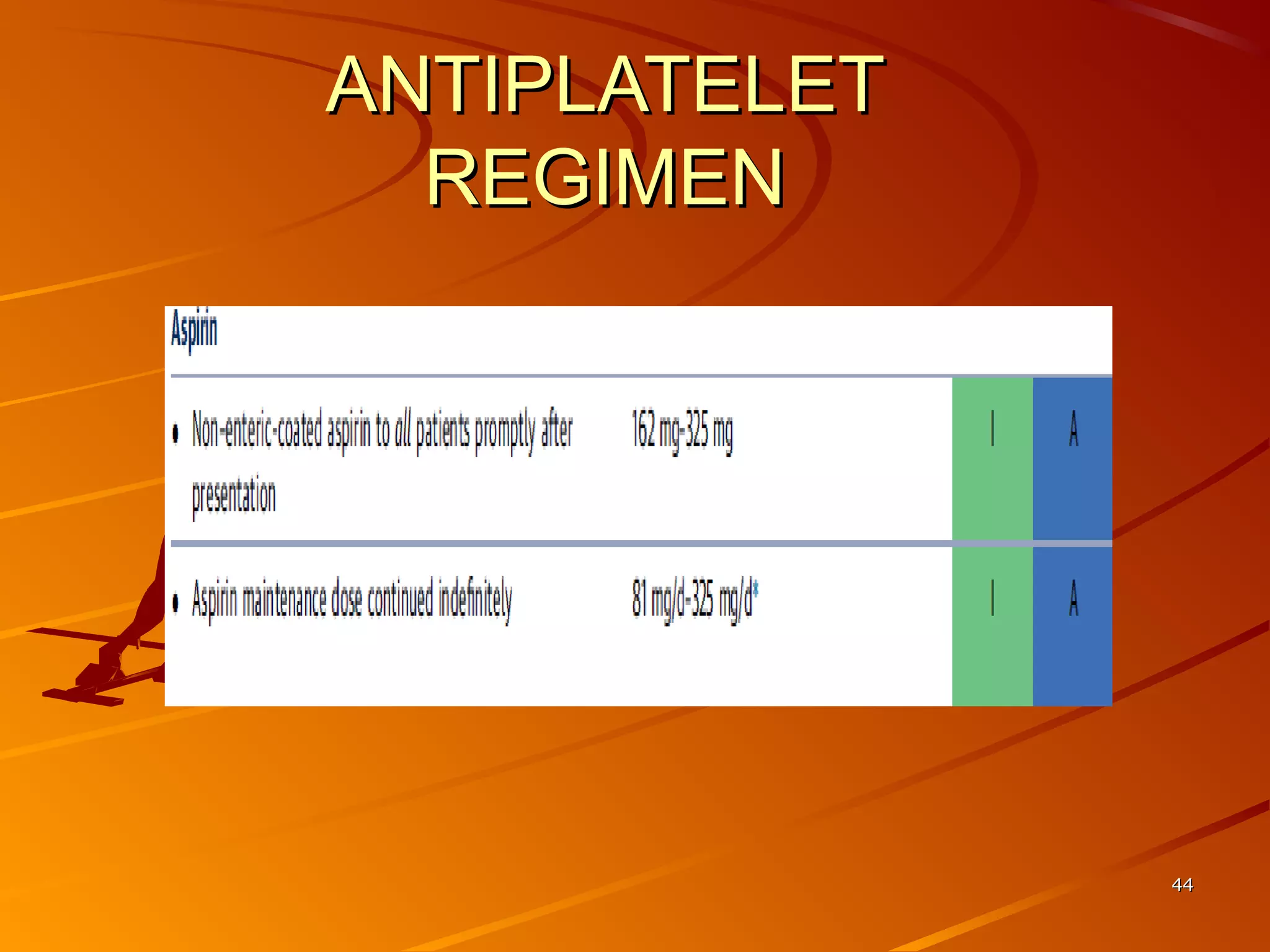
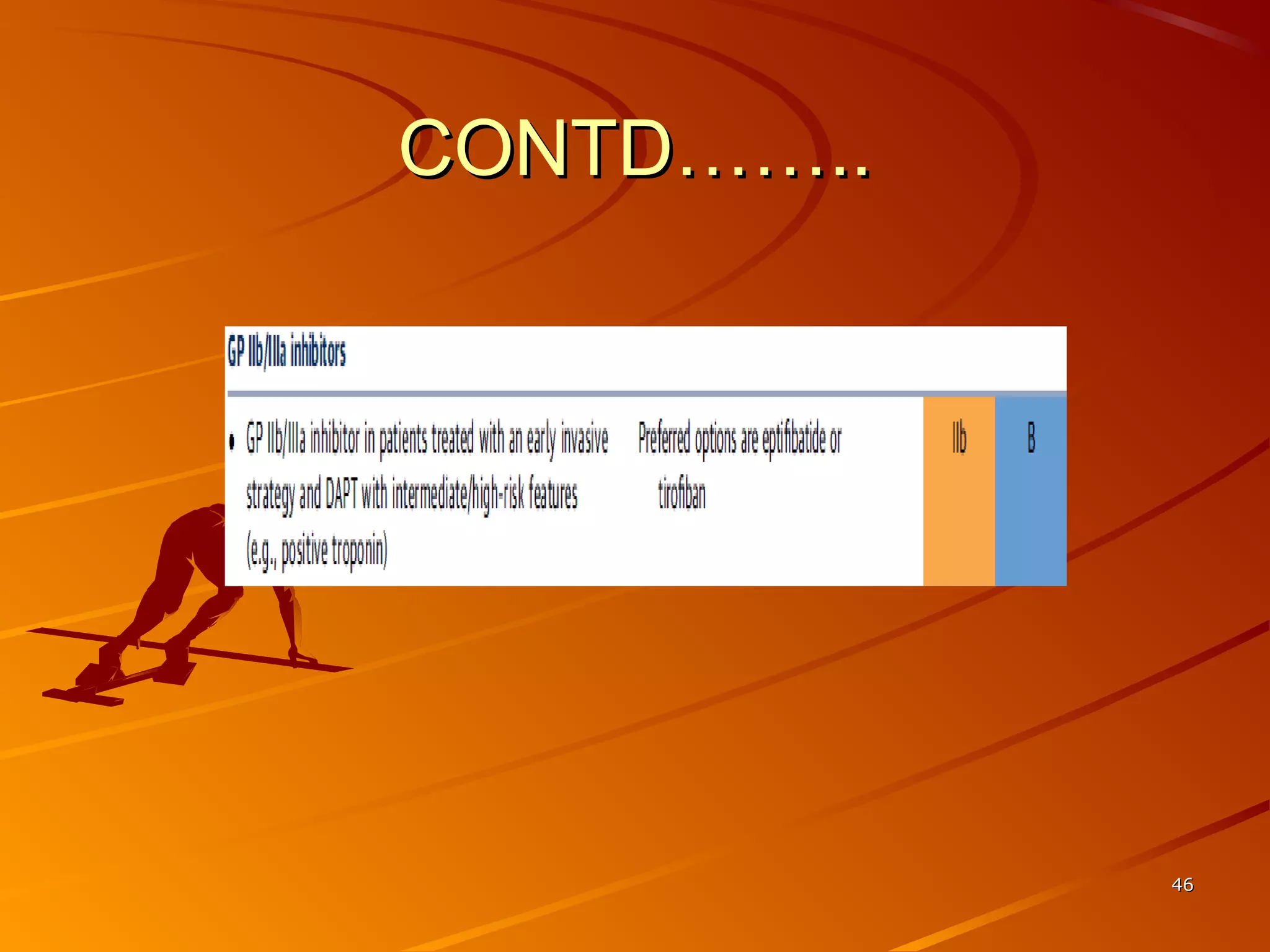
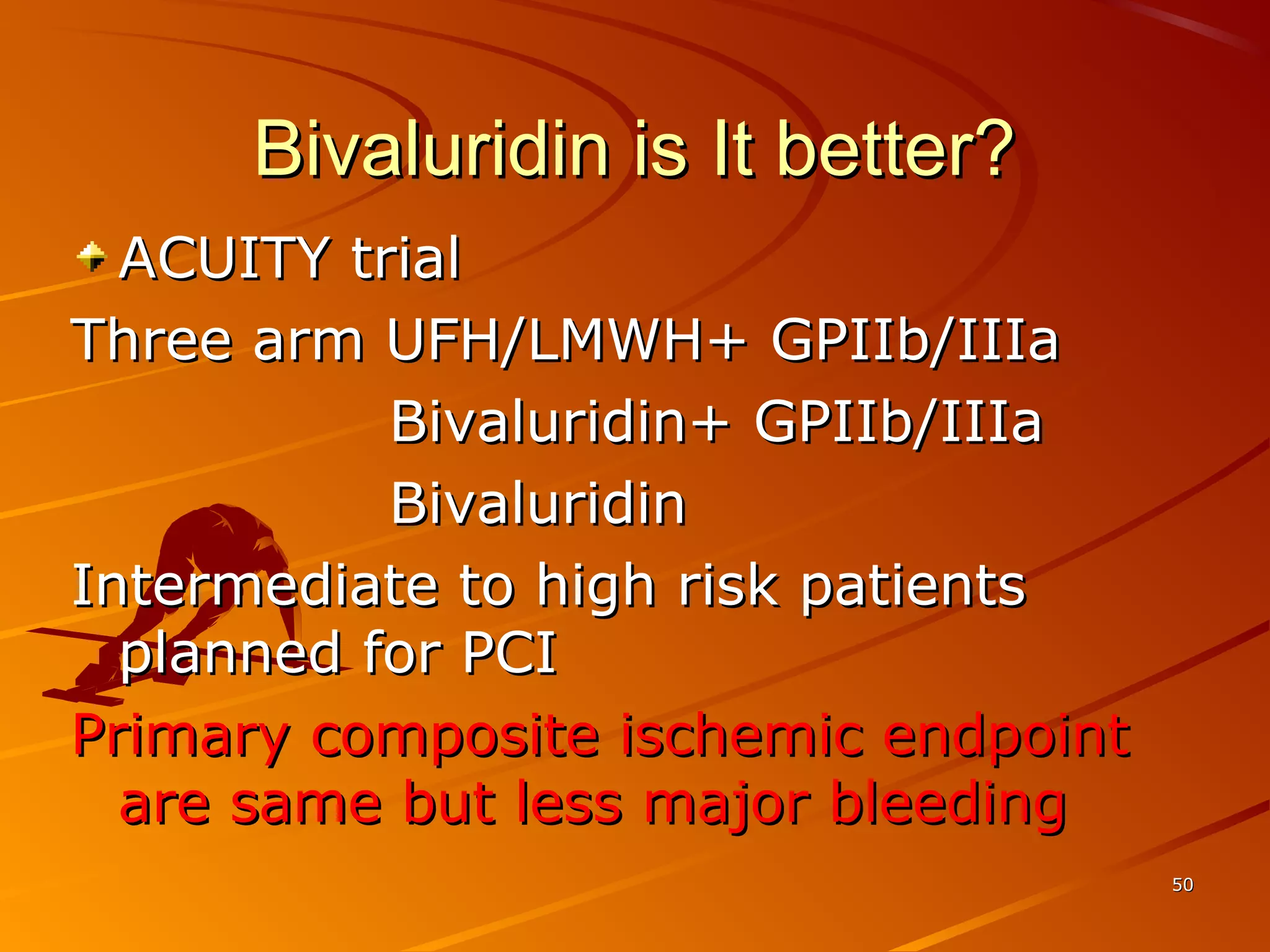
Mr. B is a 68-year-old man who presented with acute chest pain and was found to have ST depression on ECG and elevated troponin. His TIMI risk score was 4, indicating a 20% risk of adverse events in the next 14 days. His GRACE risk score was 144, indicating risks of 3% in-hospital death or 17% in-hospital death or MI. Guidelines recommend an invasive strategy for patients like Mr. B with NSTEMI based on randomized controlled trials showing reduced rates of death and MI compared to conservative management, especially in higher risk patients. Optimal timing of angiography is within 24 hours of presentation based on trials such as TIMACS and ISAR-CO