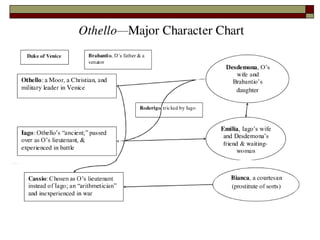
William Shakespeare wrote Othello in 1604. It is a tragedy about the downfall of Othello, a Moorish general in the Venetian army, whose jealousy is manipulated by his ensign Iago. Iago convinces Othello that his wife Desdemona has been unfaithful with his lieutenant Cassio, which leads Othello to murder Desdemona in a fit of jealous rage. The document provides context on Shakespeare, key terminology used in Othello like verse, meter, and tragedy, as well as themes and characters in the play.