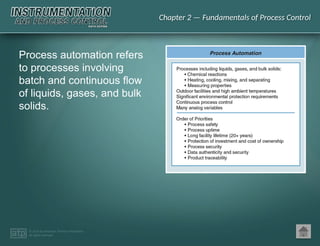
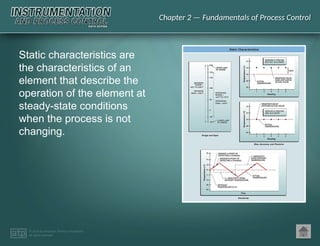
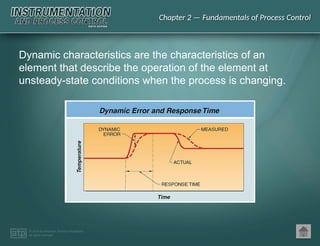
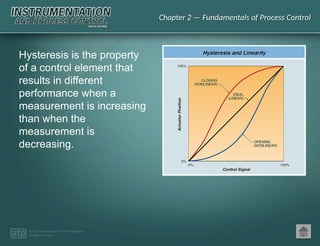
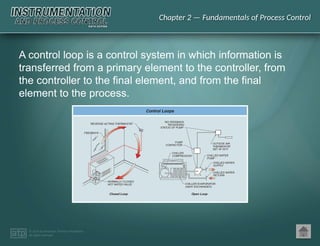
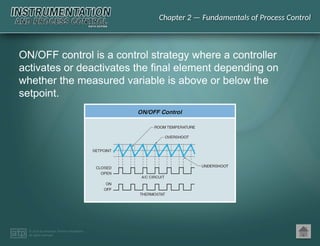
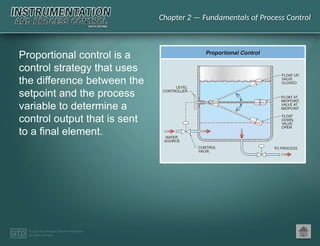
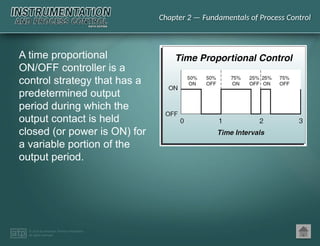
The document discusses basic and premium PowerPoint presentations for instrumentation process and control education, providing essential instructional content and options for instructors. It covers topics in process control, including automation, control elements, control loops, and various control strategies. Key concepts such as static and dynamic characteristics, hysteresis, and different control strategies like on/off and proportional control are also presented.