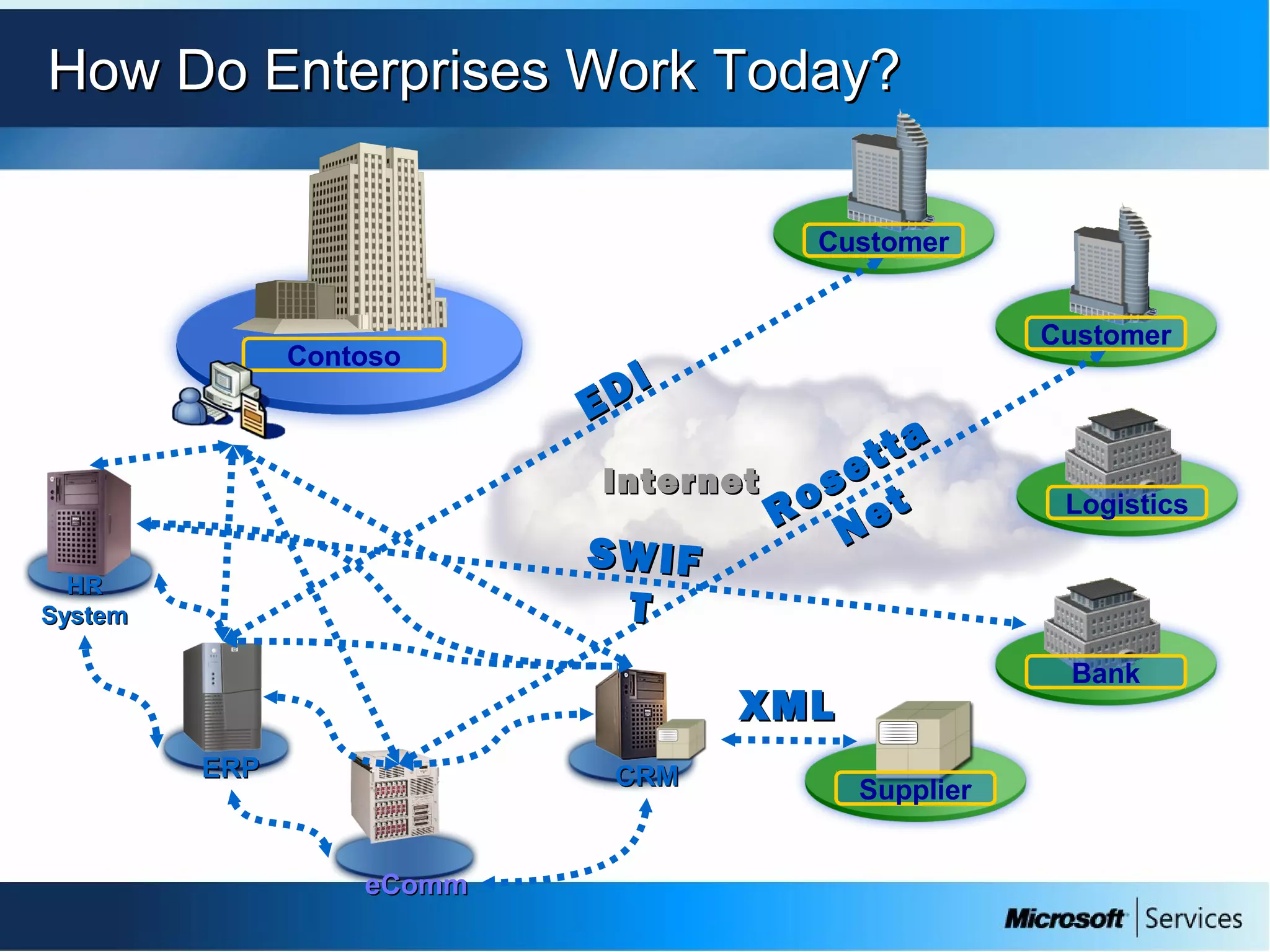
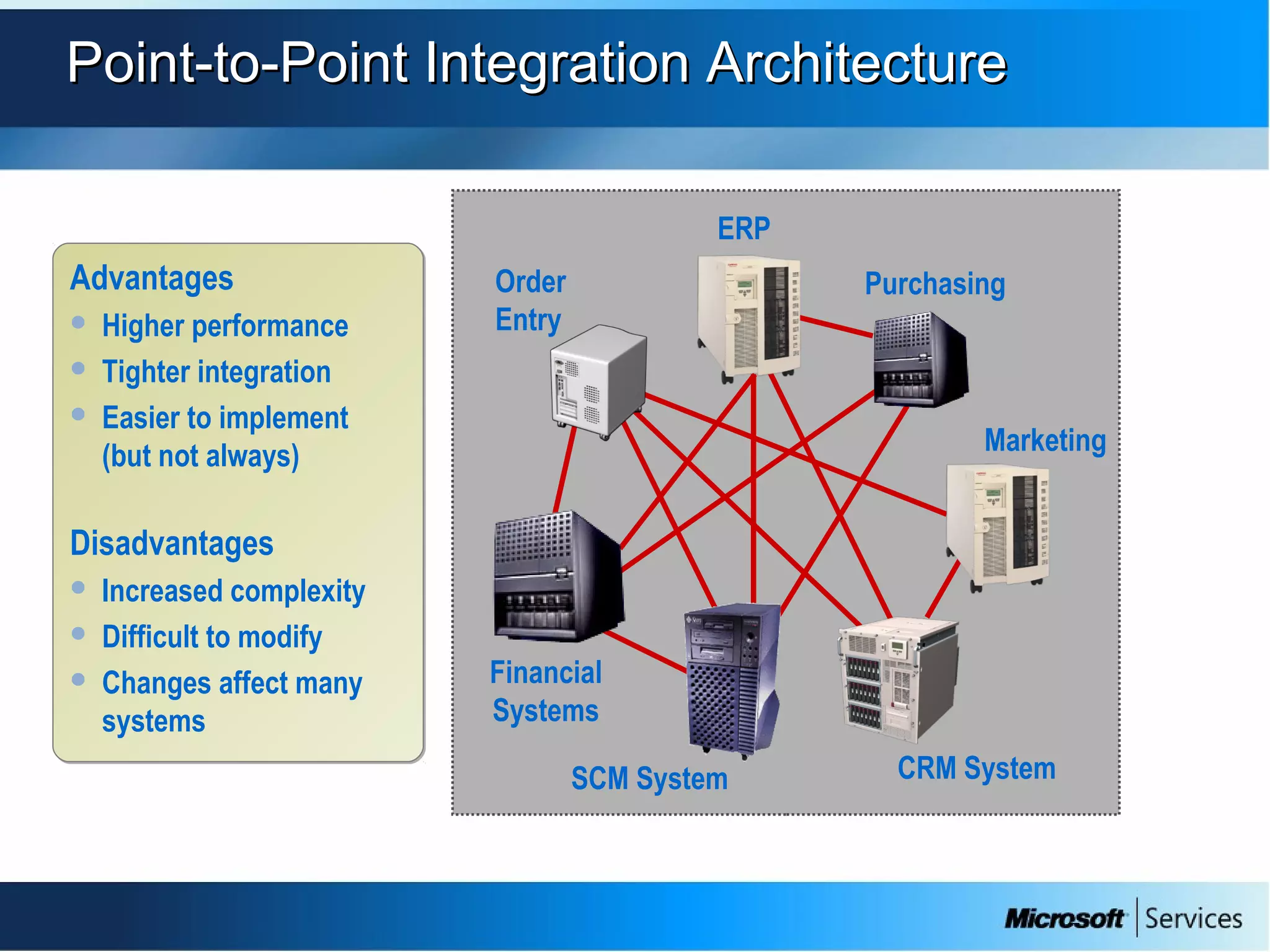
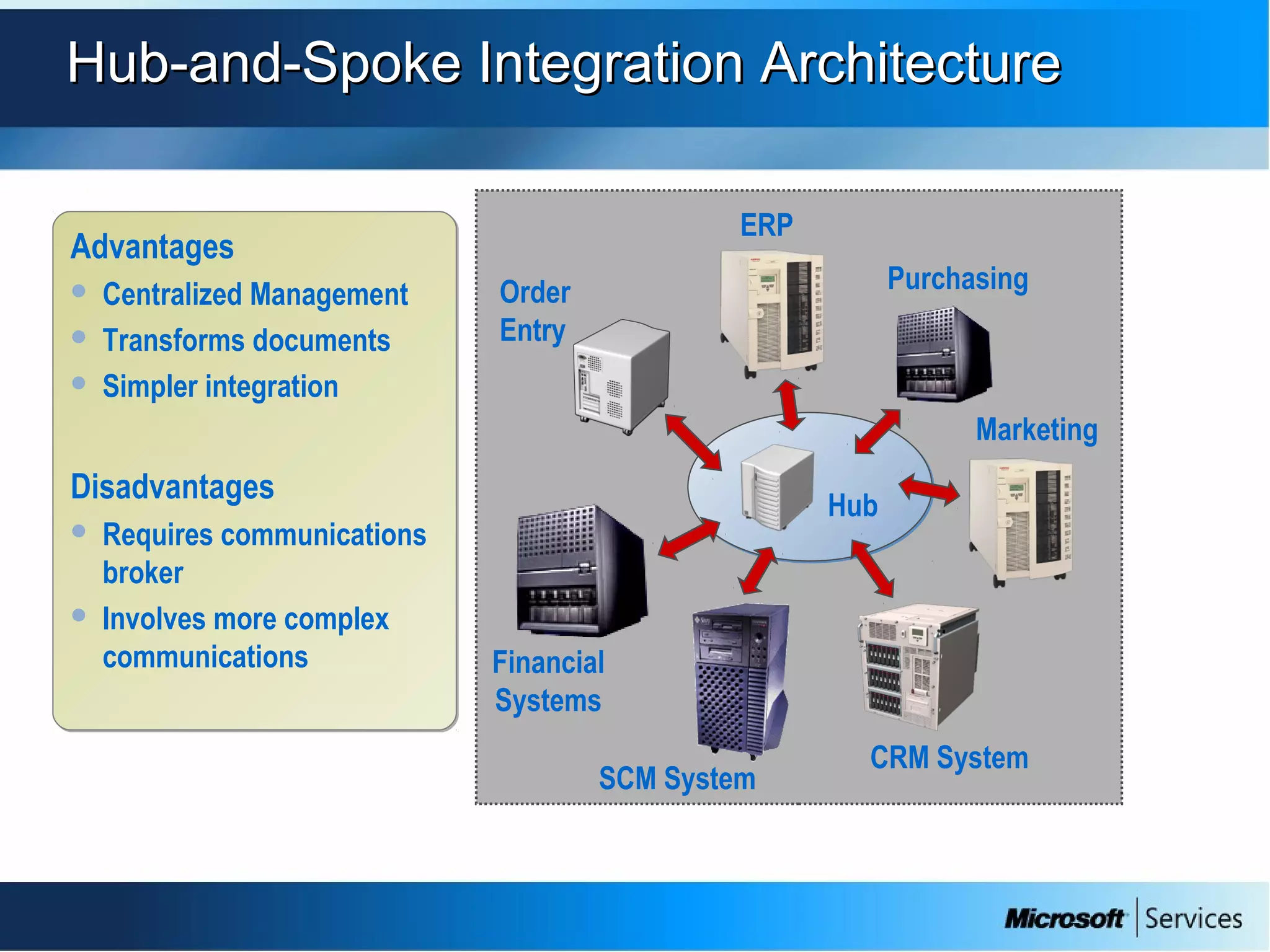
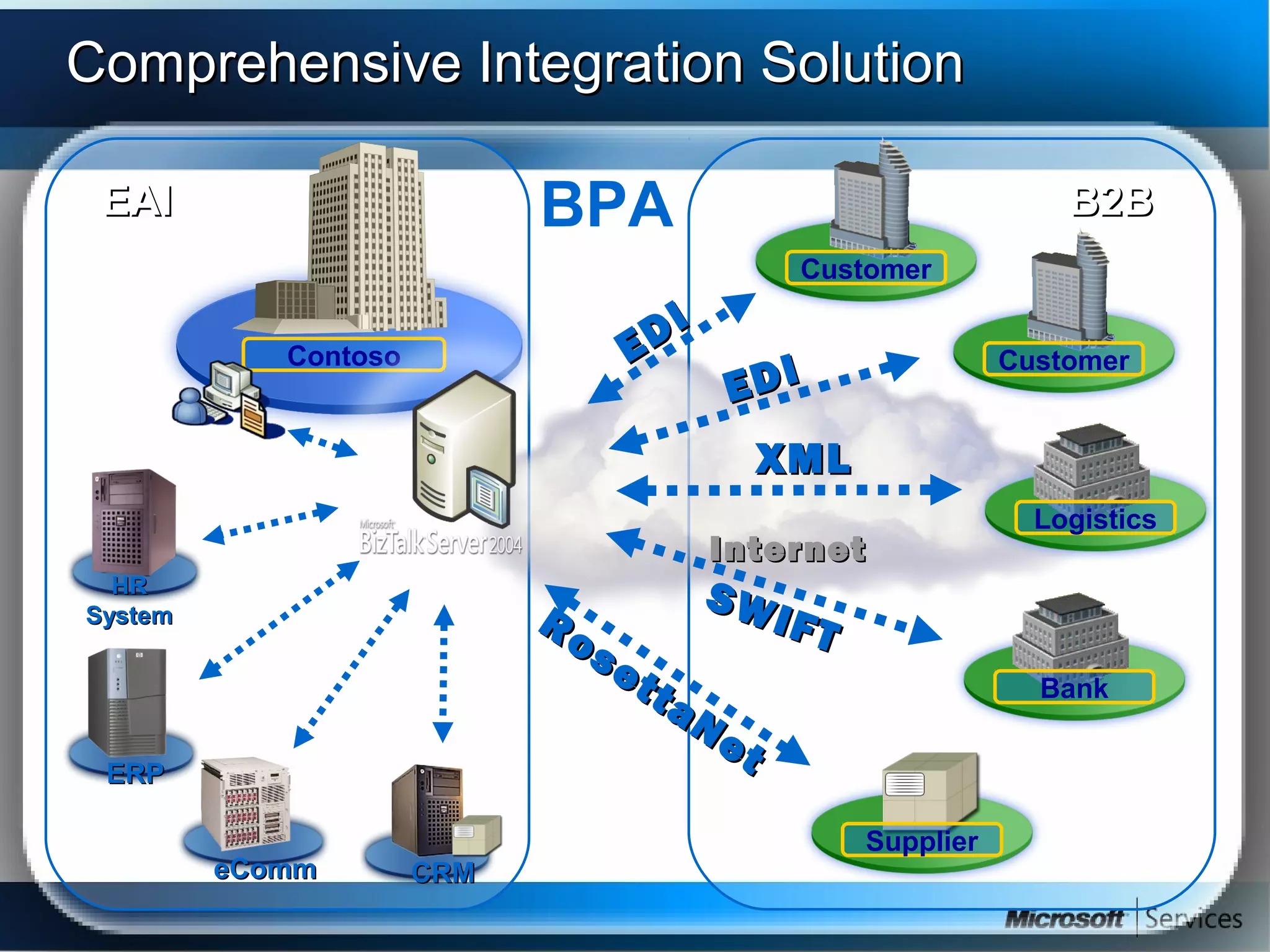
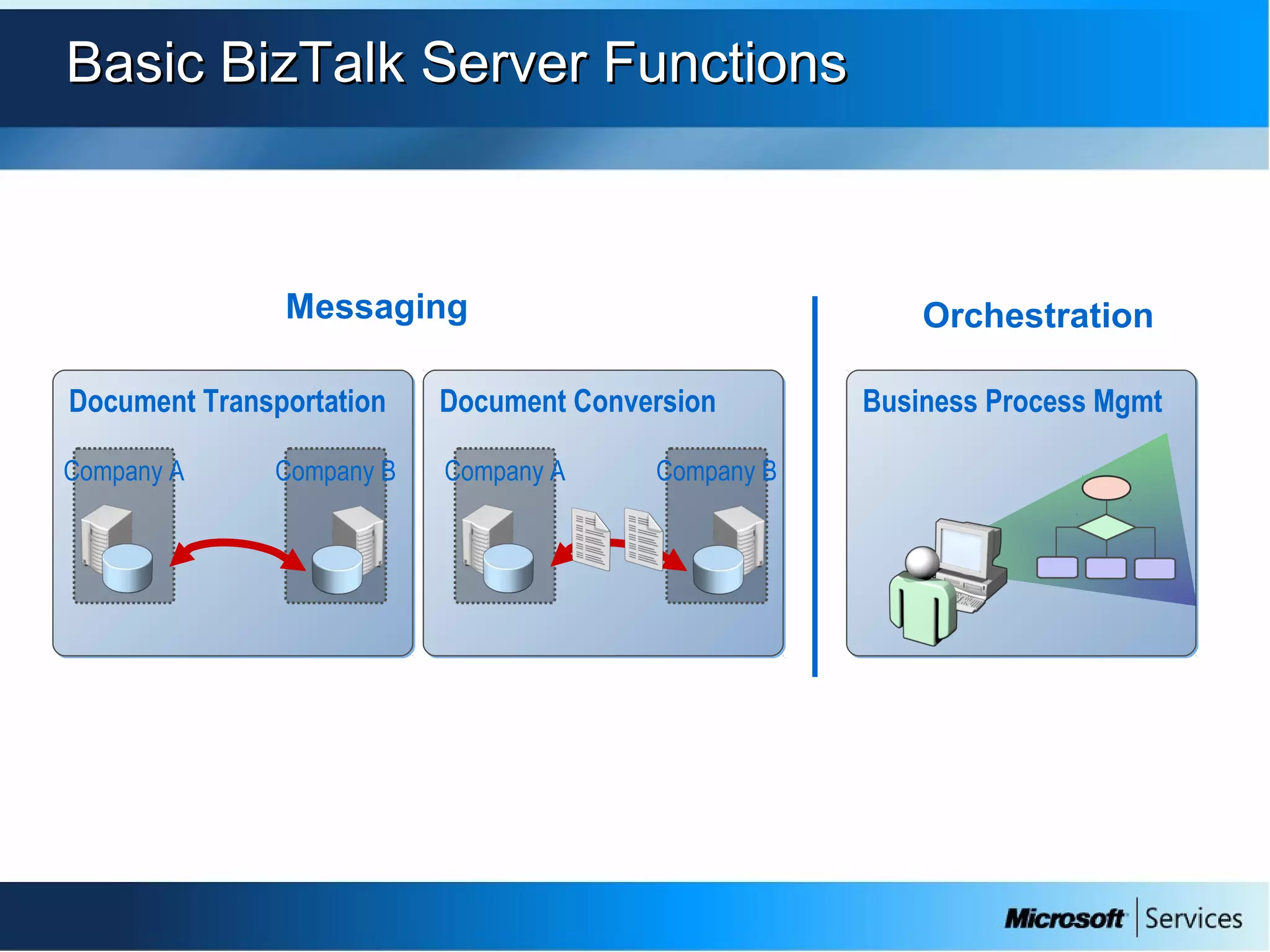
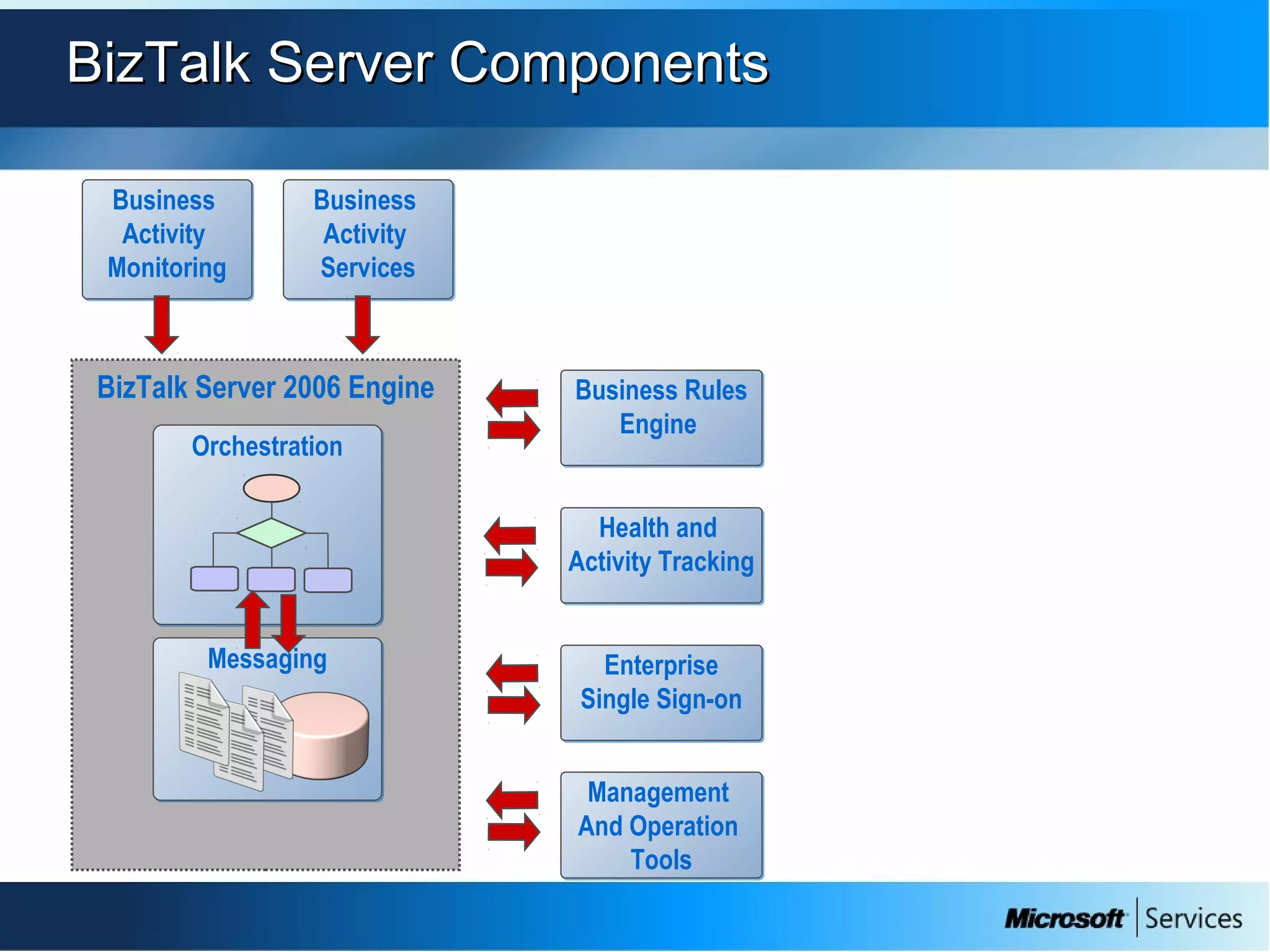
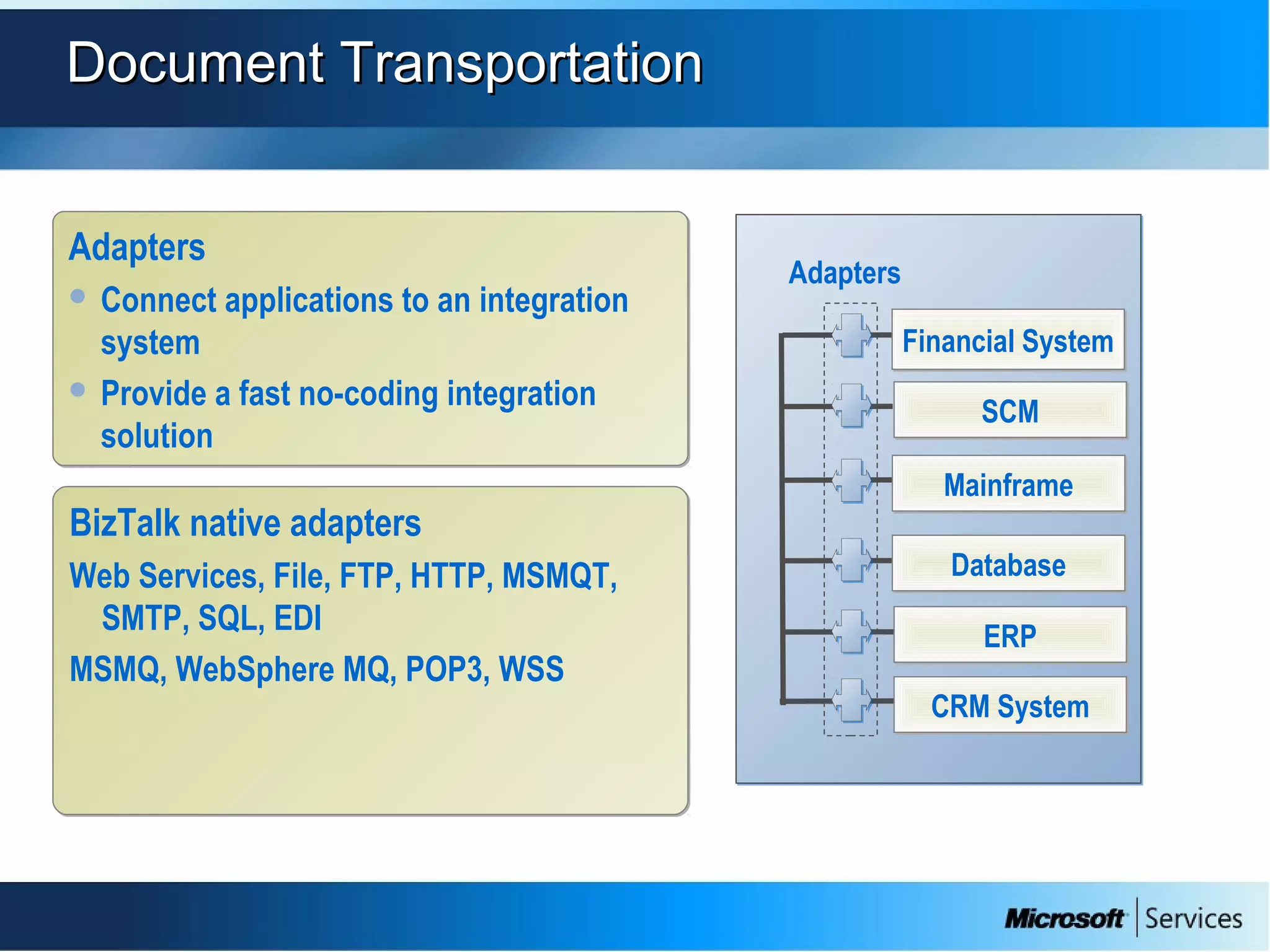
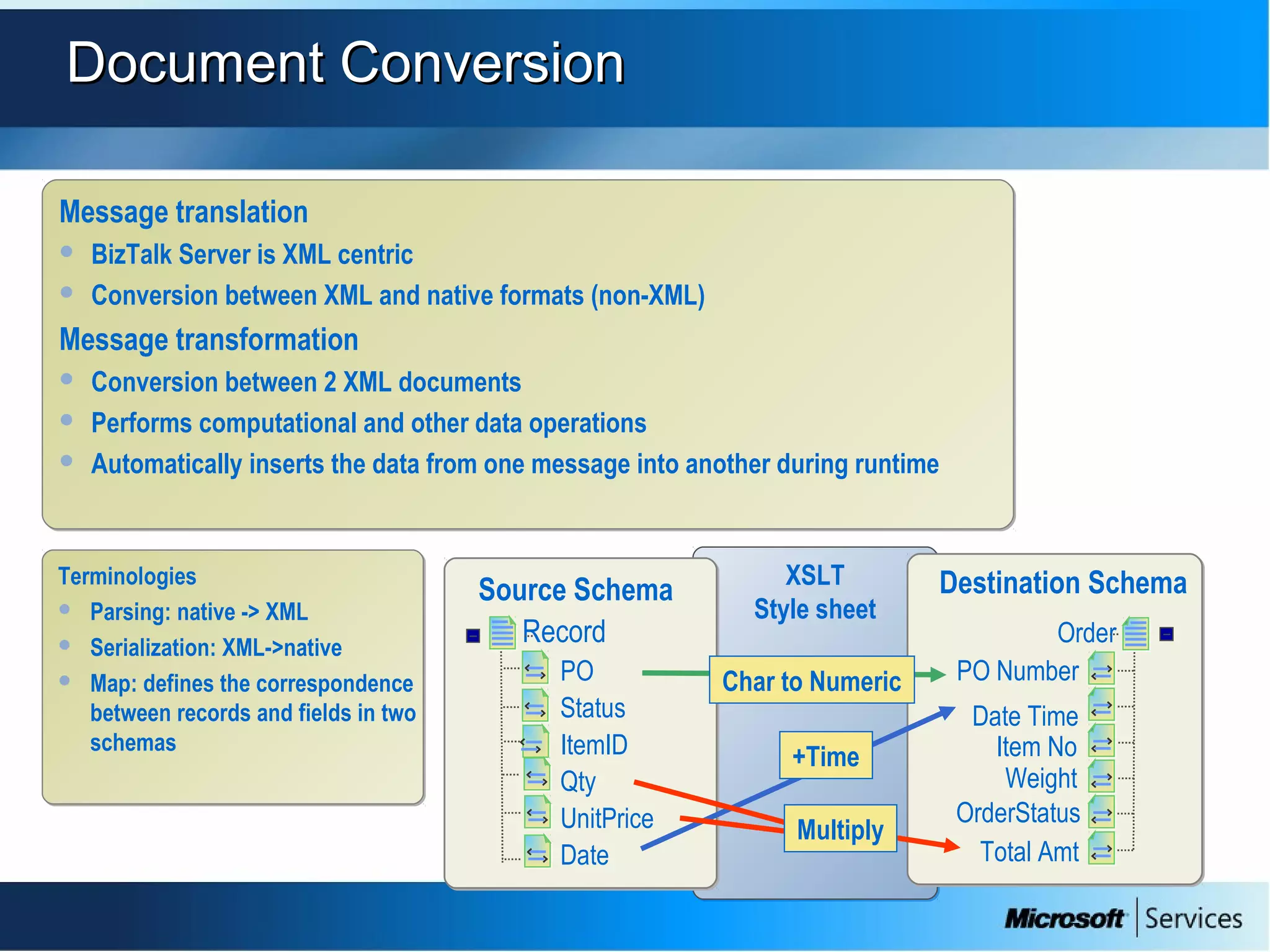
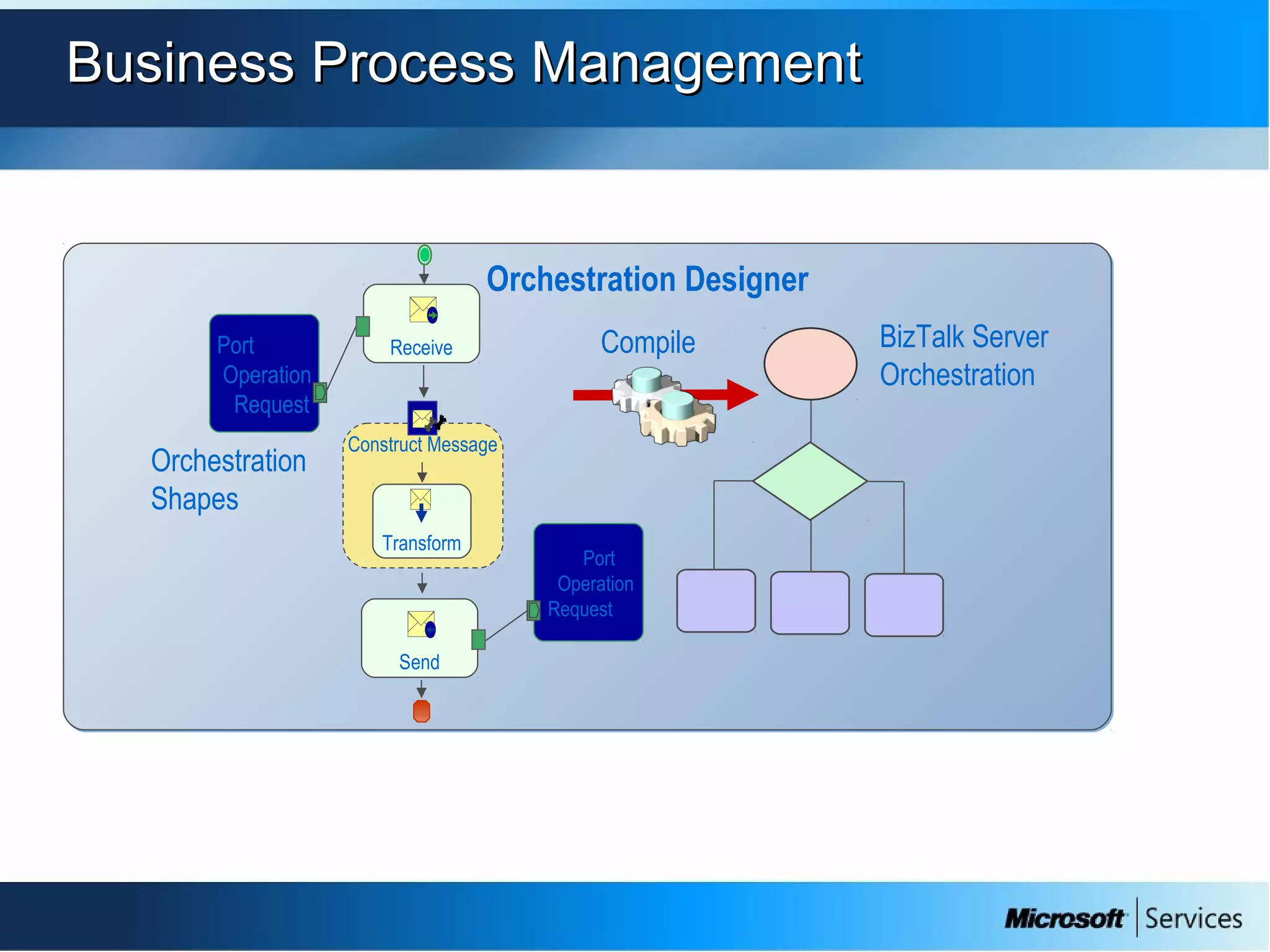
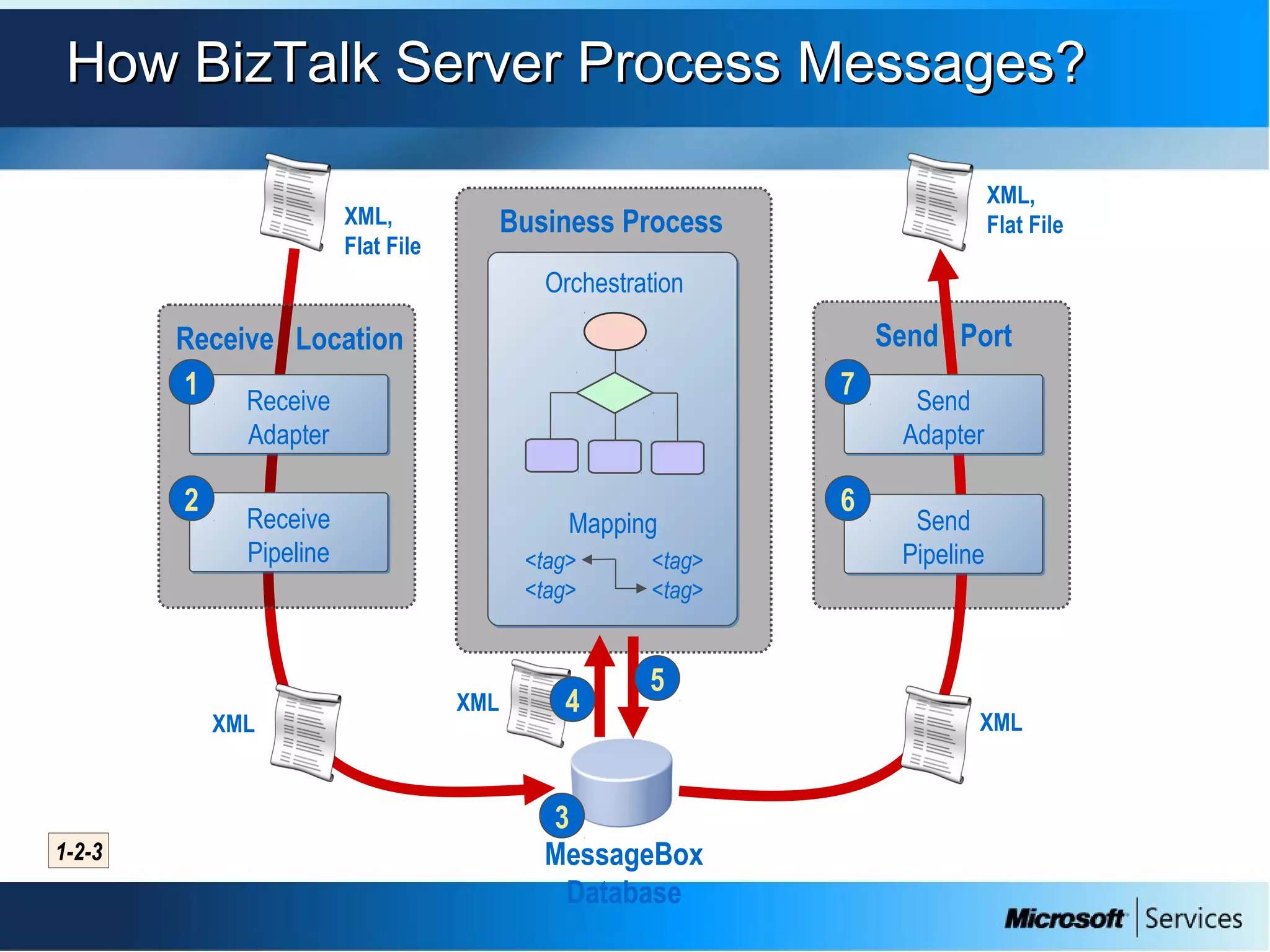
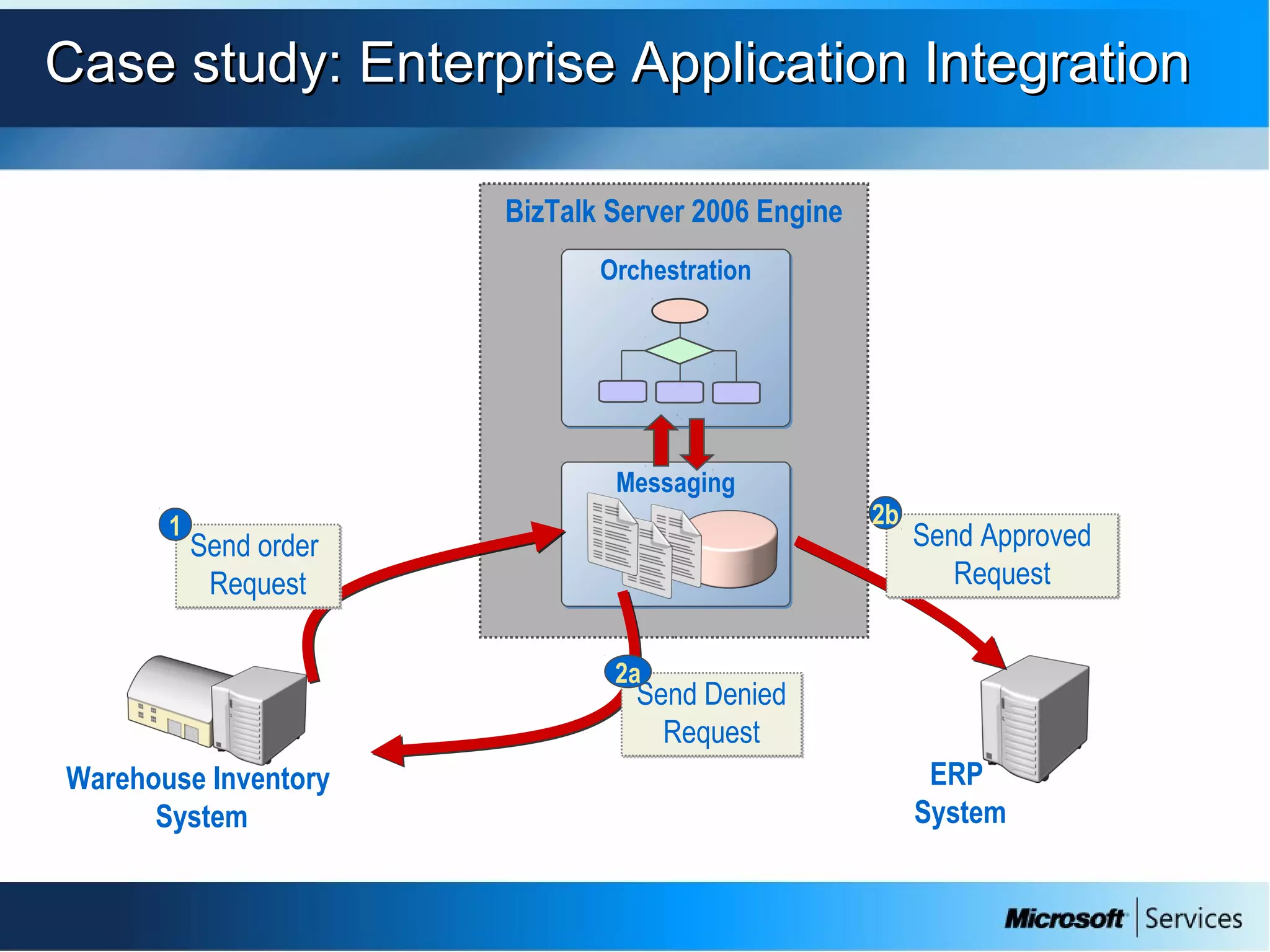
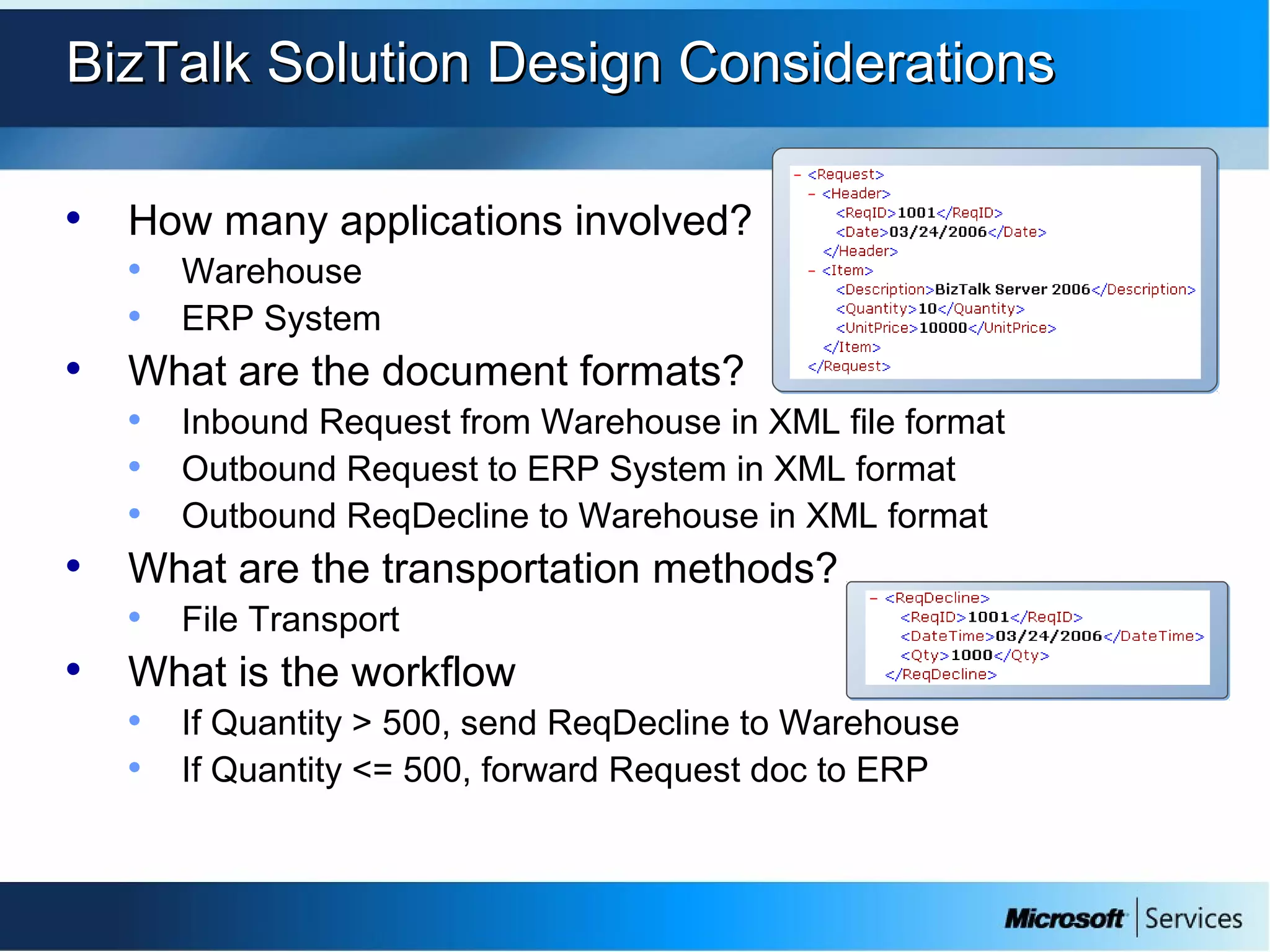
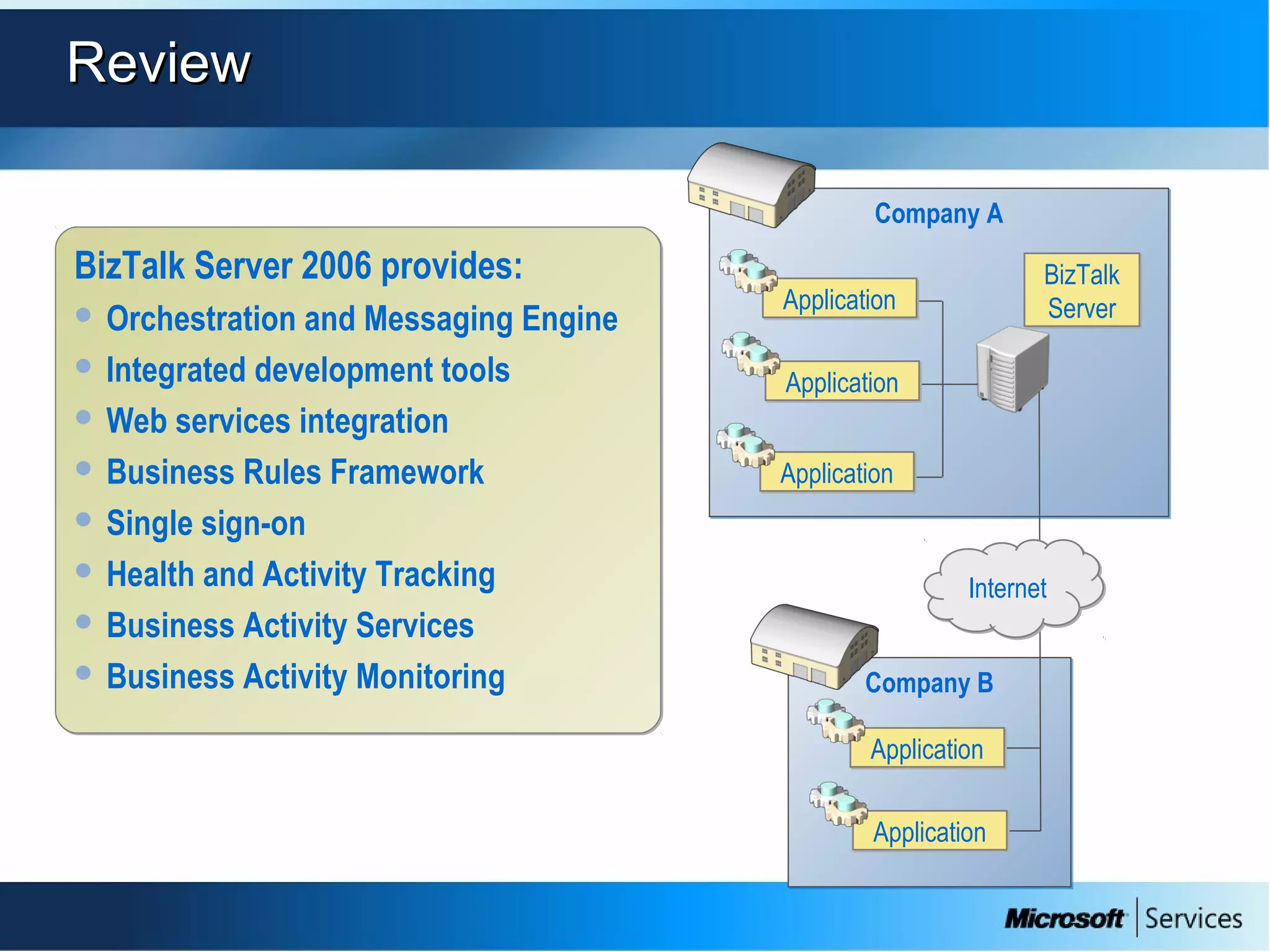
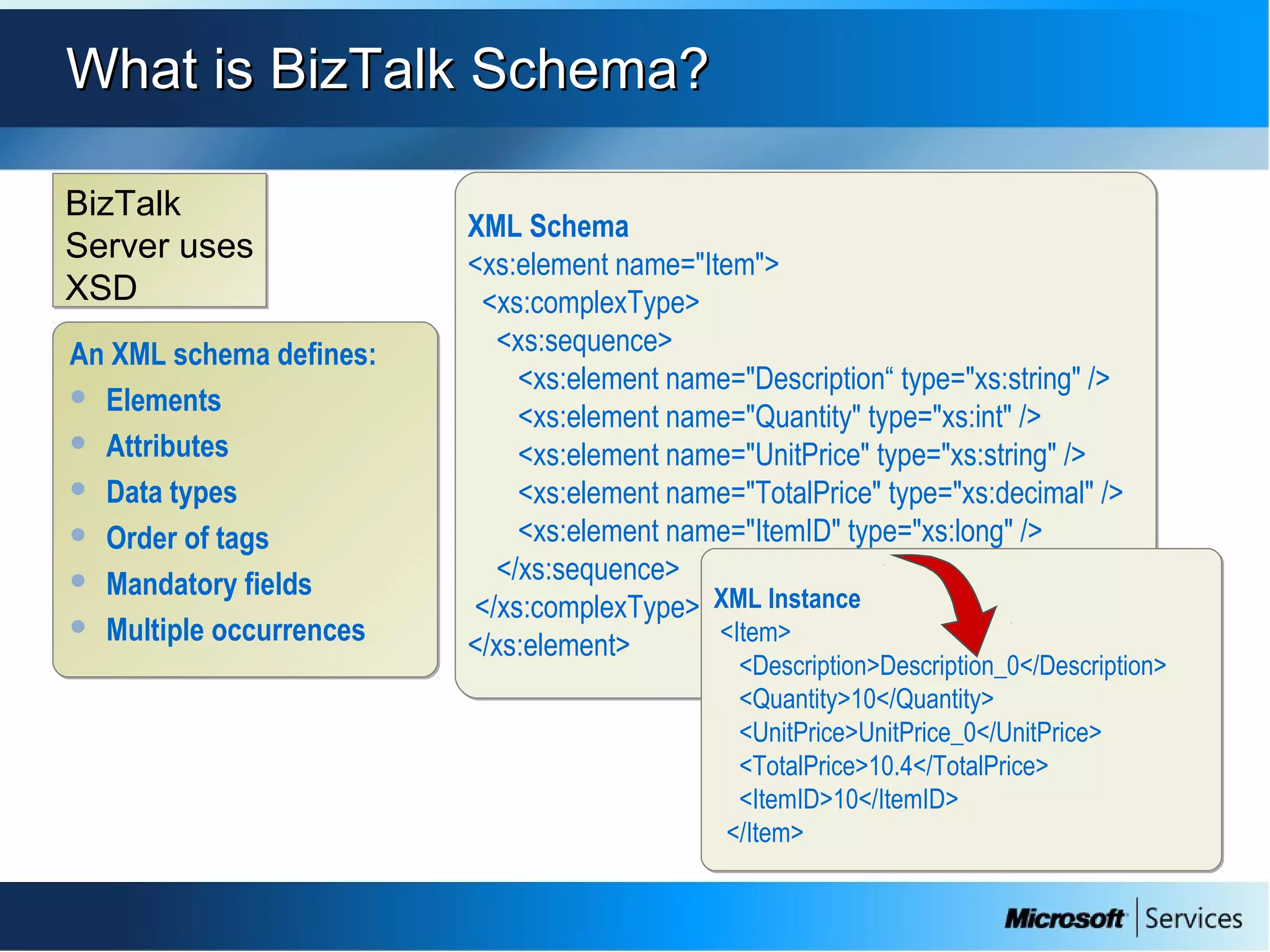
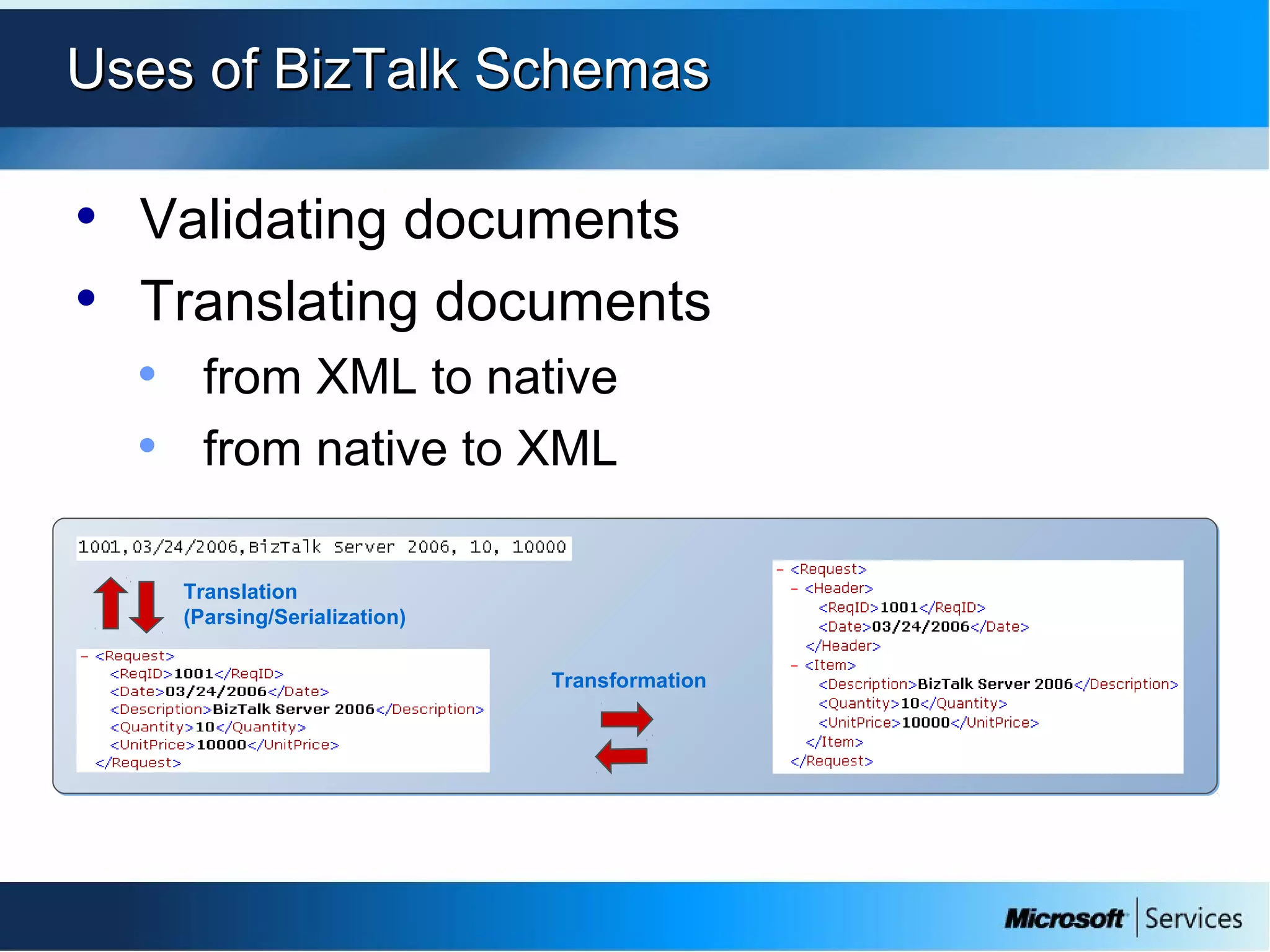
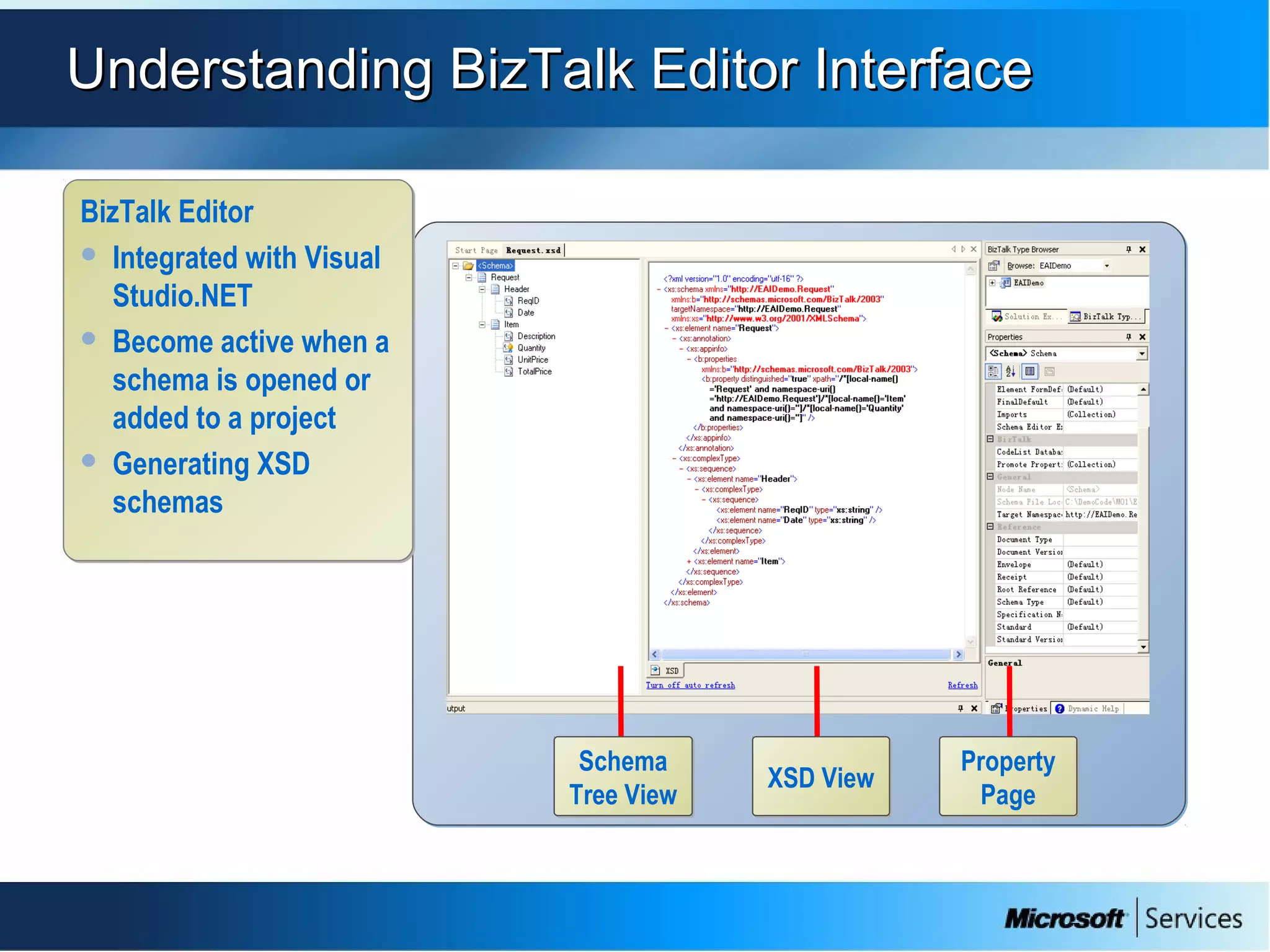
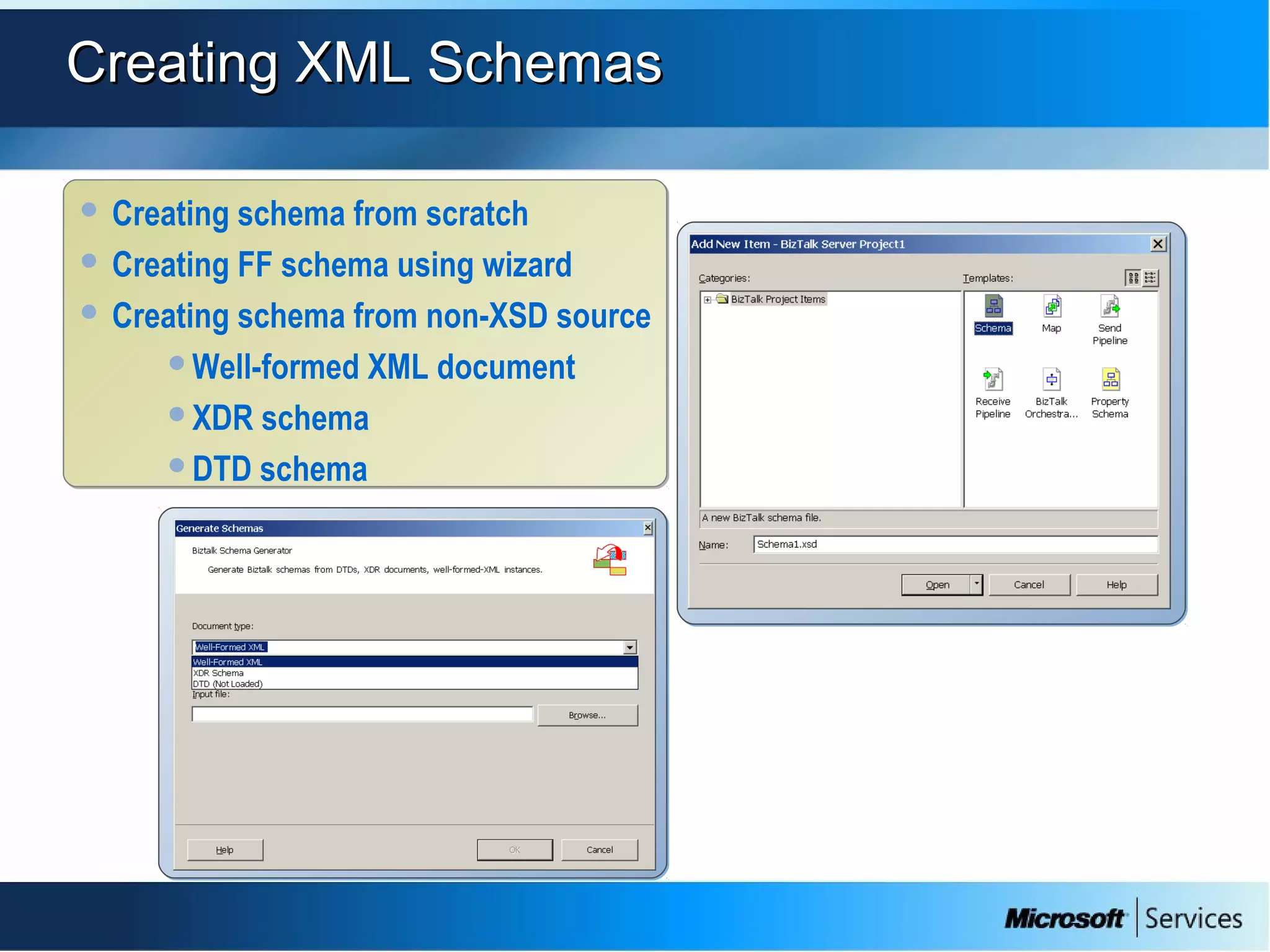
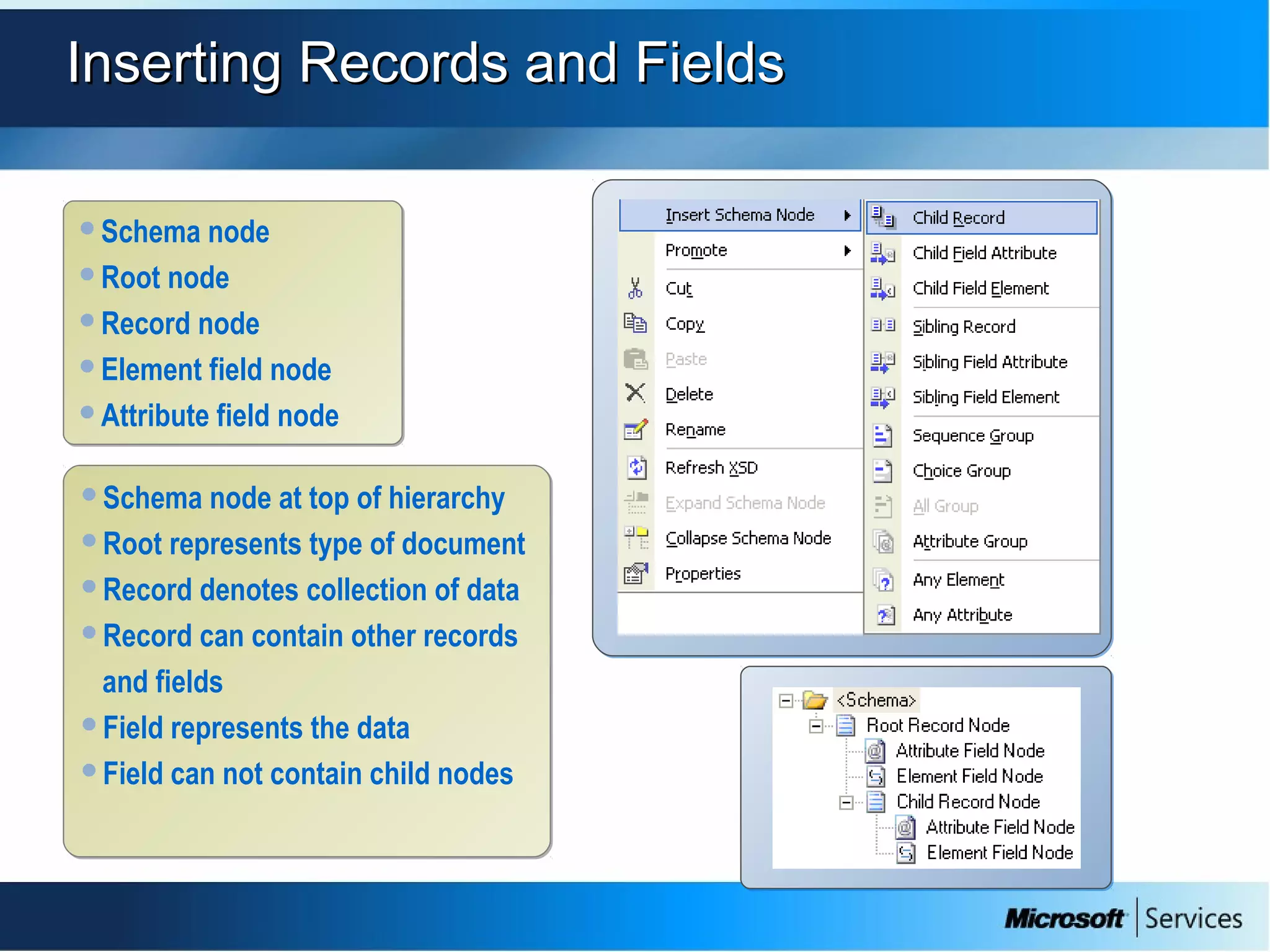
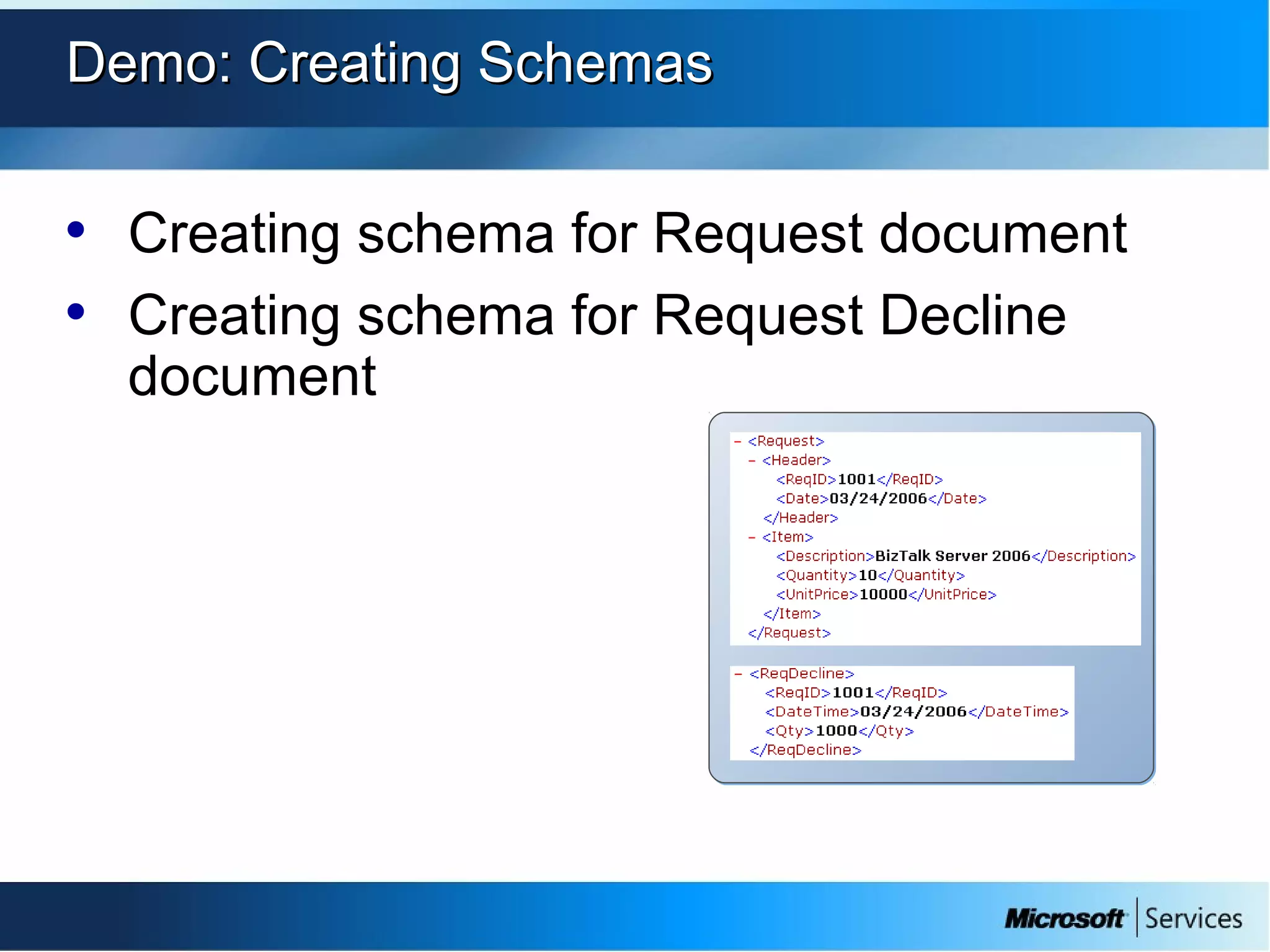
The document provides an overview of BizTalk Server 2009, covering application integration, server functions, components, document transportation, and business process management. It details architecture types, advantages and disadvantages, as well as message processing and the use of schemas in BizTalk. Additionally, it includes a case study on enterprise application integration and offers guidance on creating schemas using BizTalk Editor.