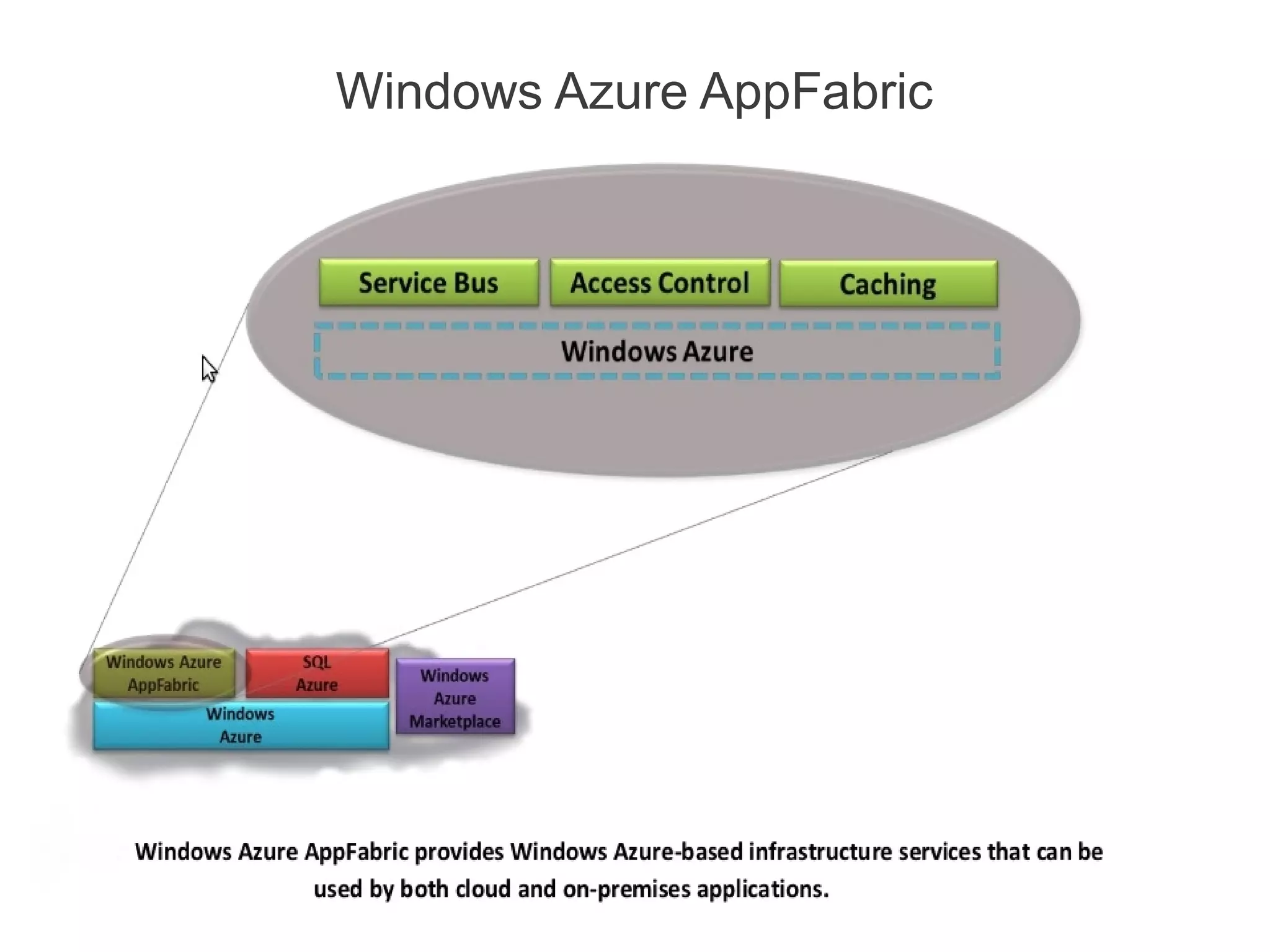
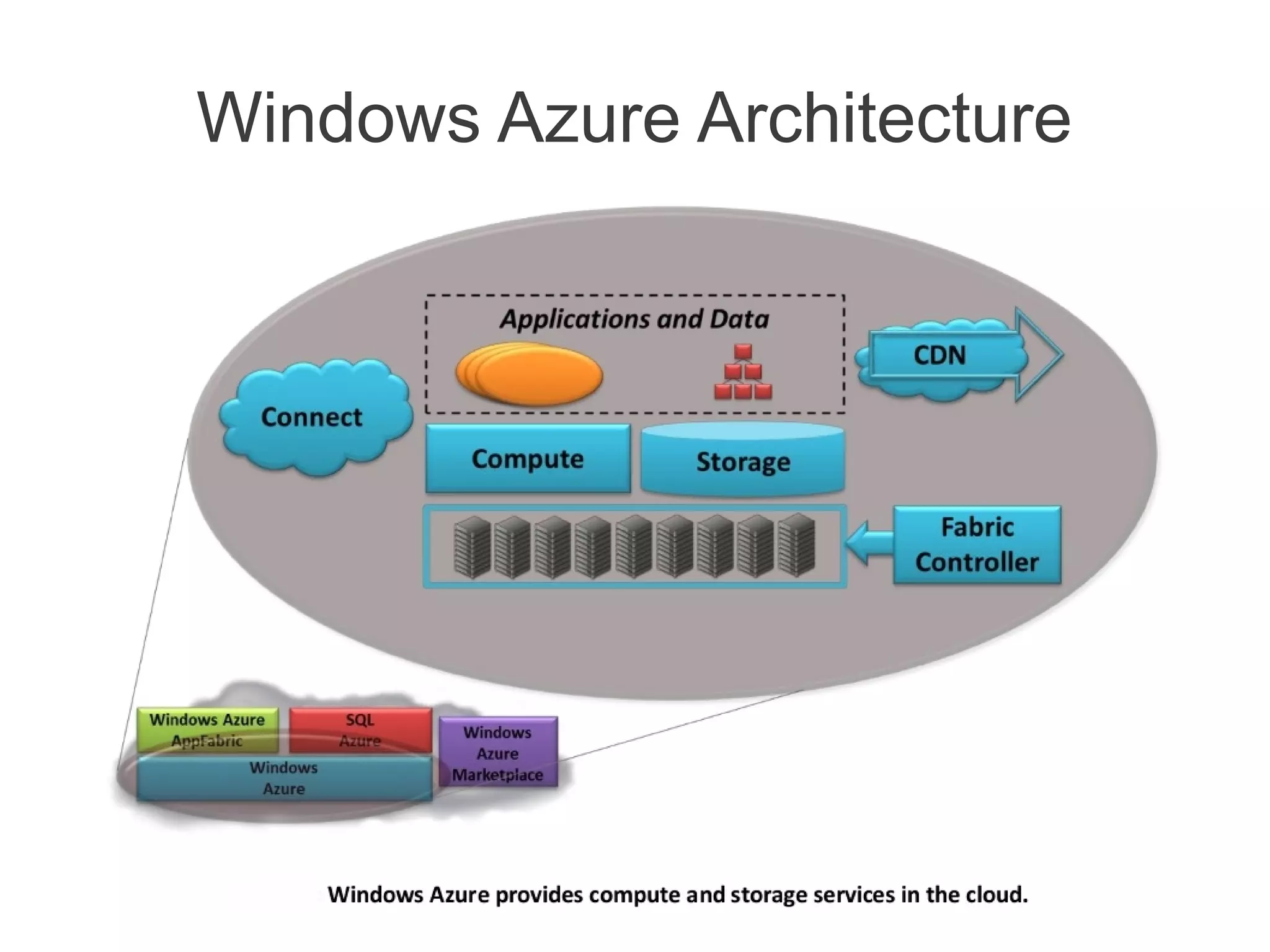
The document provides an overview of cloud computing concepts and the specific features of Microsoft's Windows Azure platform, which includes various services such as infrastructure, platform, software, and storage as a service. It discusses architecture, including web roles and worker roles, along with Azure's storage capabilities and SQL Azure for database management. Additionally, it highlights considerations for migrating ASP.NET applications to Azure and the importance of caching and access control mechanisms.



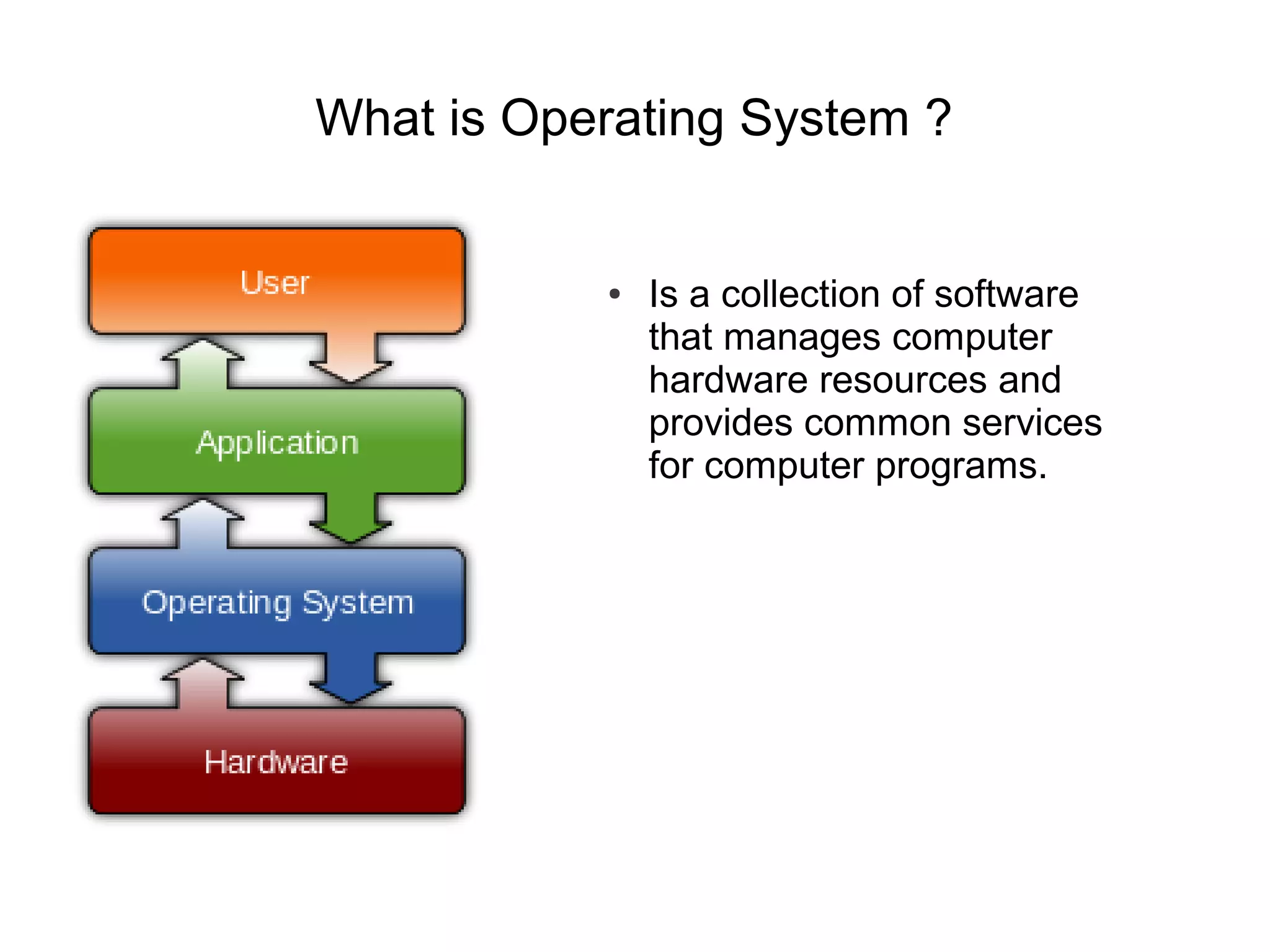
![What is distributed System ? [contd.]
● A distributed operating system is the logical aggregation of operating
system software over a collection of independent, networked,
communicating, and physically separate computational nodes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windowsazureoverview-121023142533-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-Windows-Azure-6-2048.jpg)


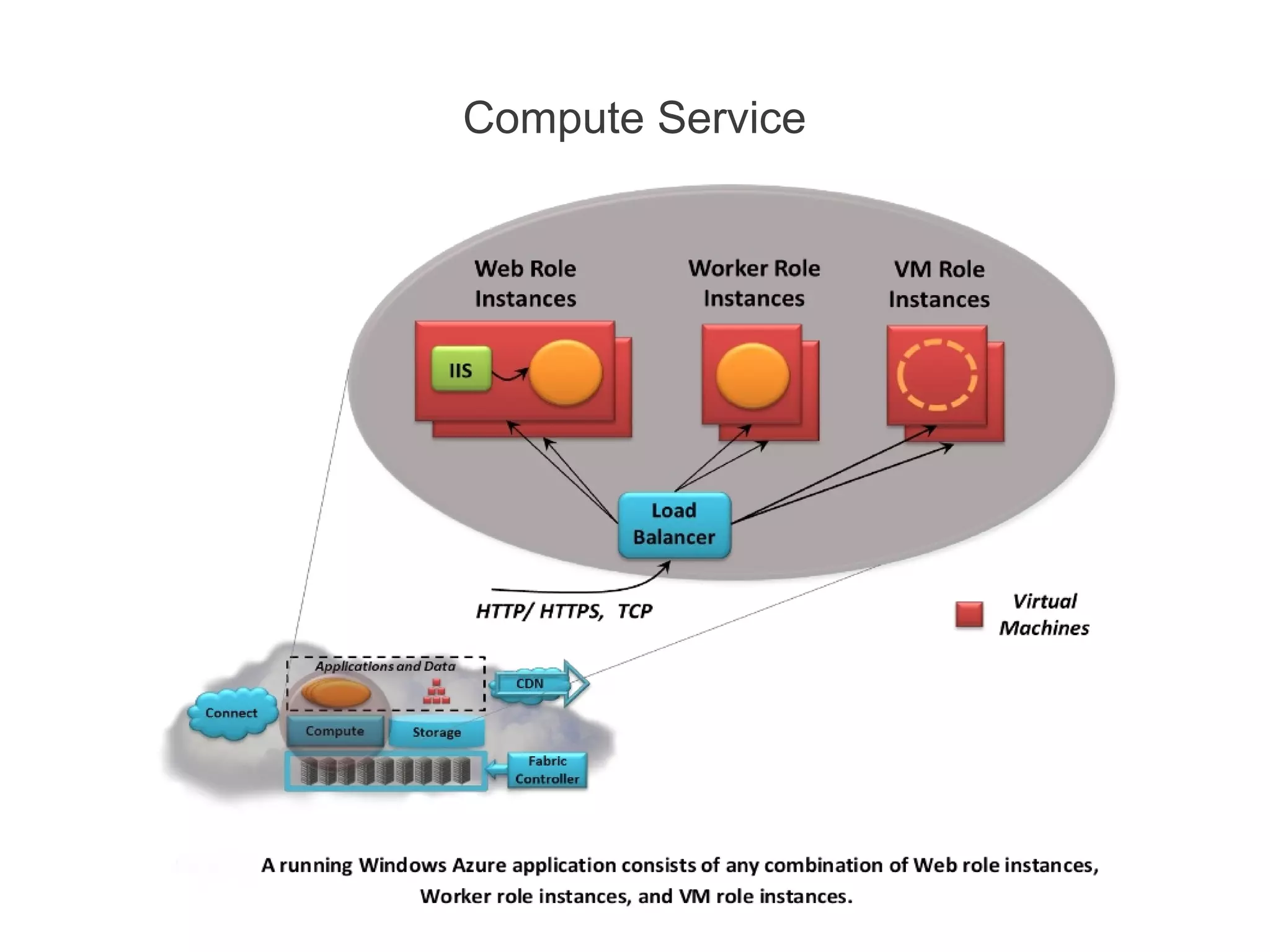
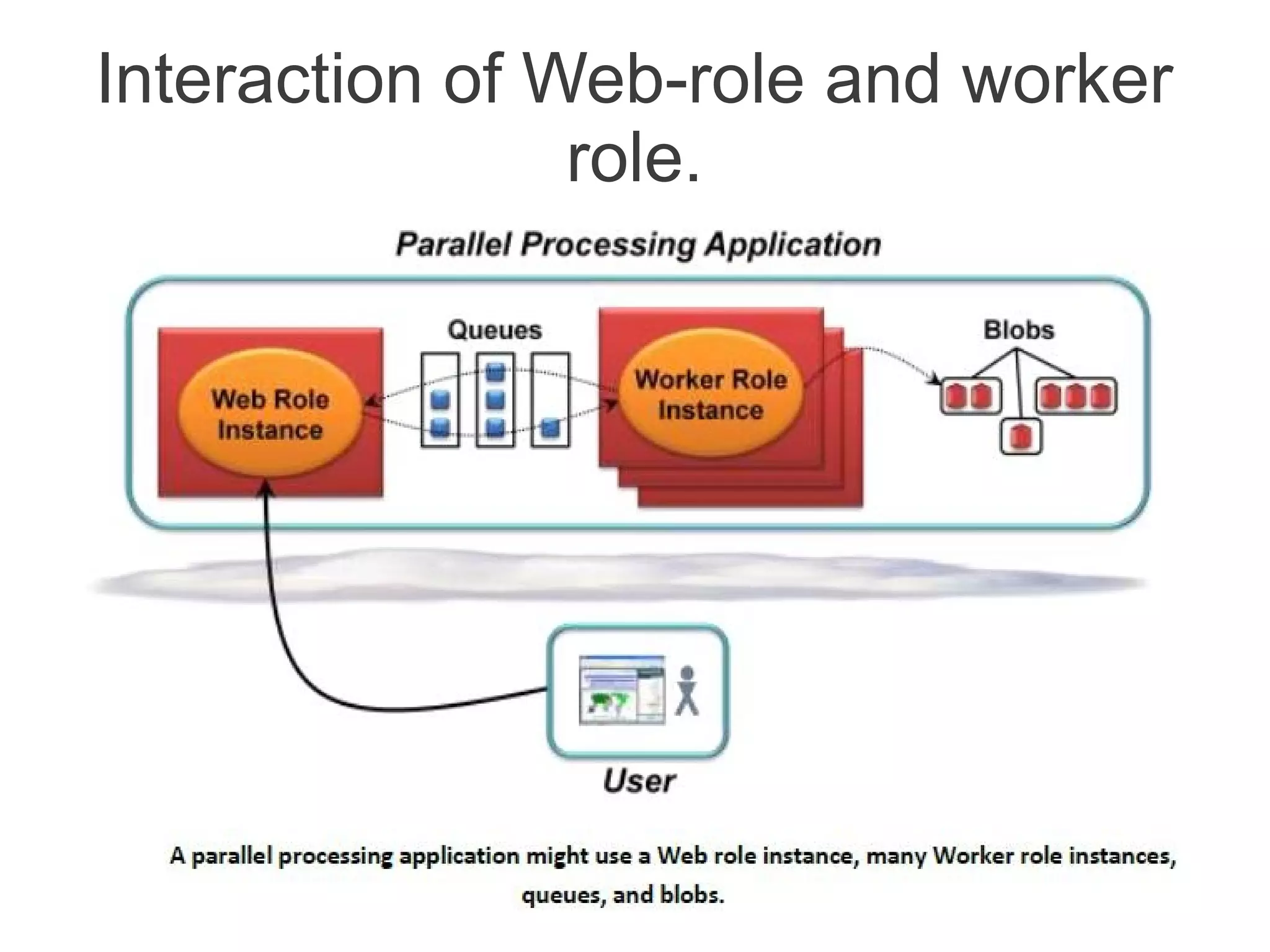
![Compute Service [contd.]
• A Web role instance can accept incoming HTTP or HTTPS
requests
• By running multiple instances of an application, Windows
Azure helps to scale application.
• Web role instances are stateless.
• Worker role instances can’t accept requests from the outside
world. Their VMs don’t run IIS, and a Worker application can’t
accept any incoming network connections.
• Instead, a Worker role instance initiates its own requests for
input.
• It can read messages from a queue and it can open
connections with the outside world.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windowsazureoverview-121023142533-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-Windows-Azure-15-2048.jpg)

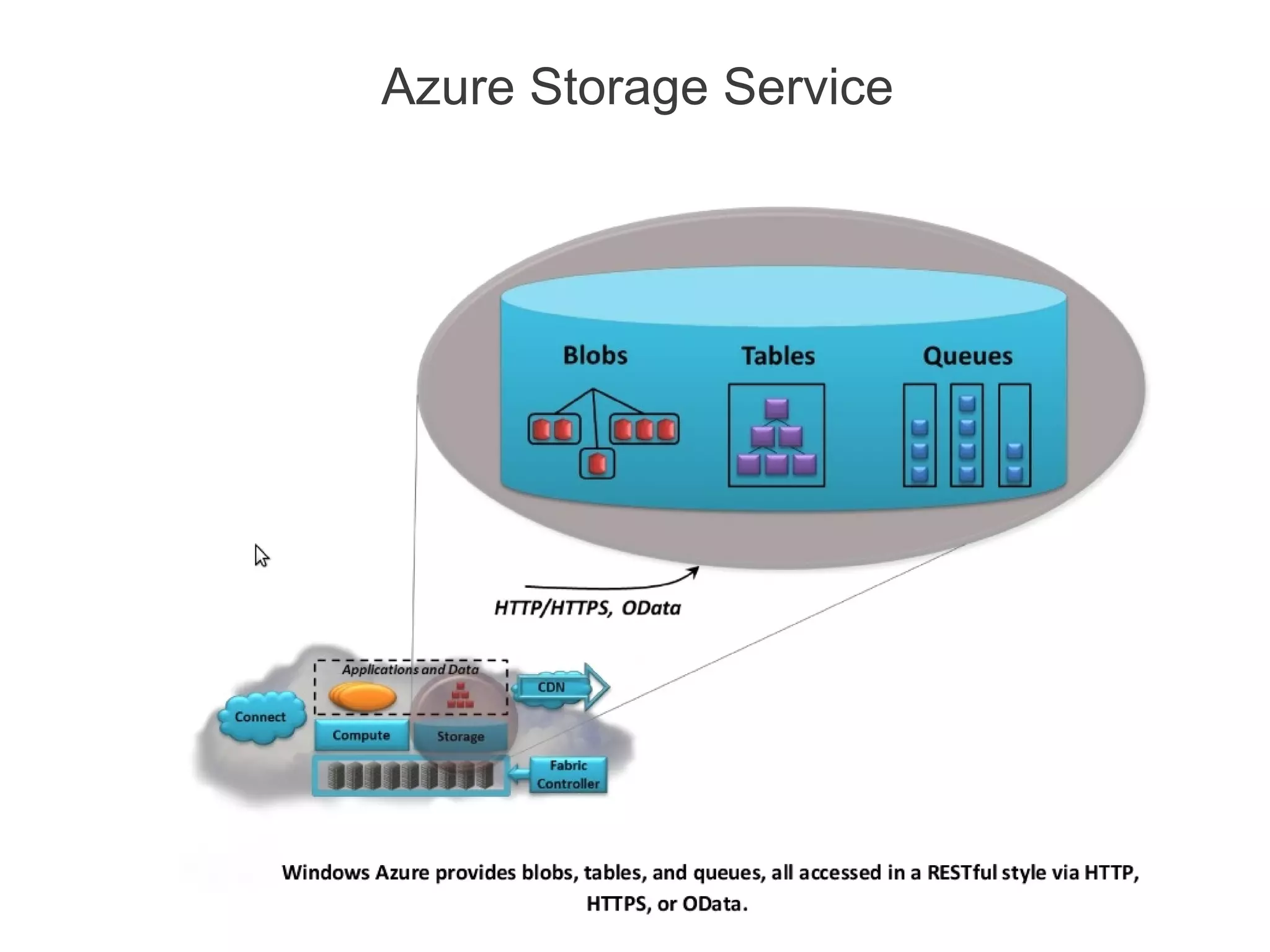


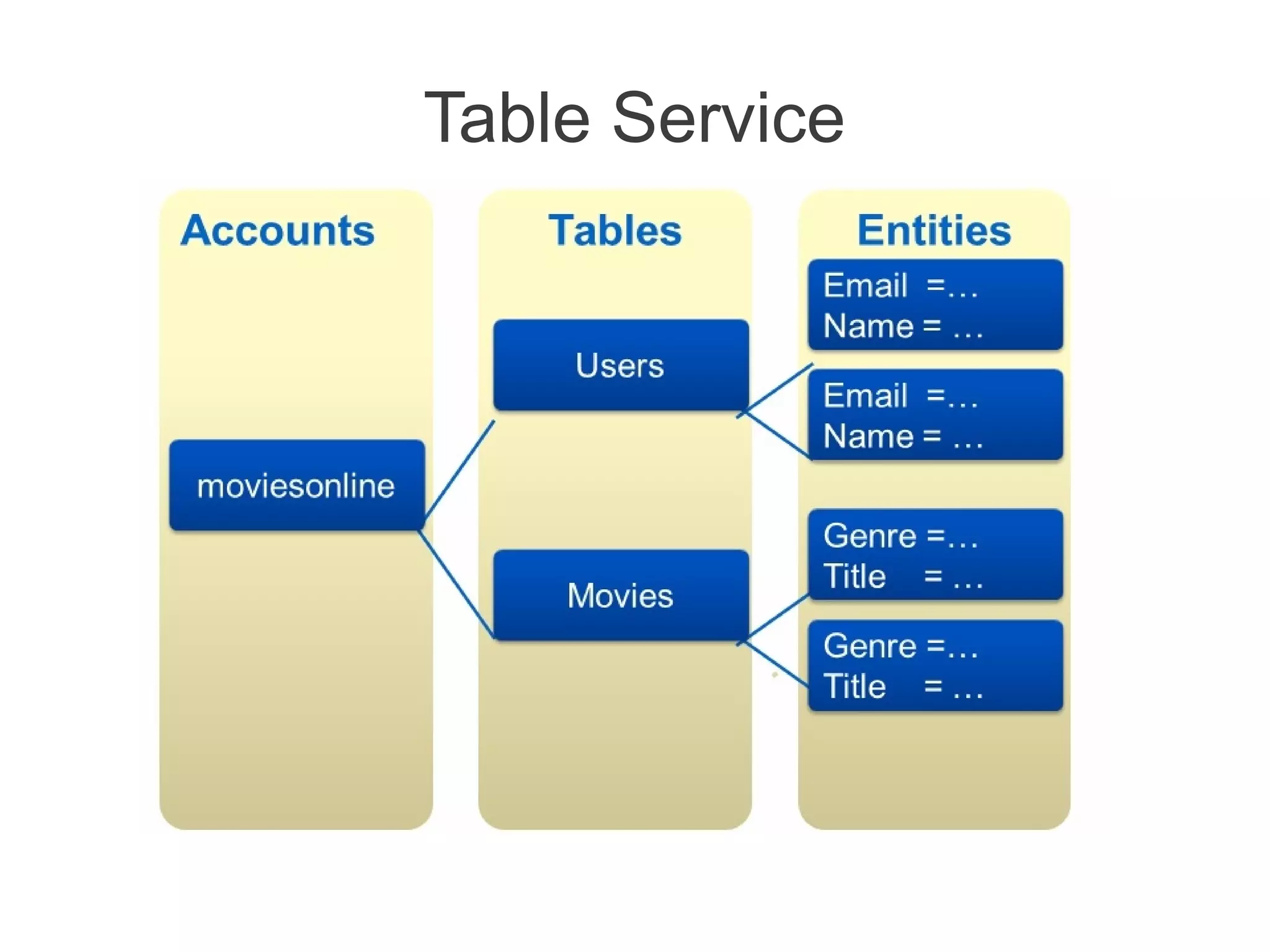
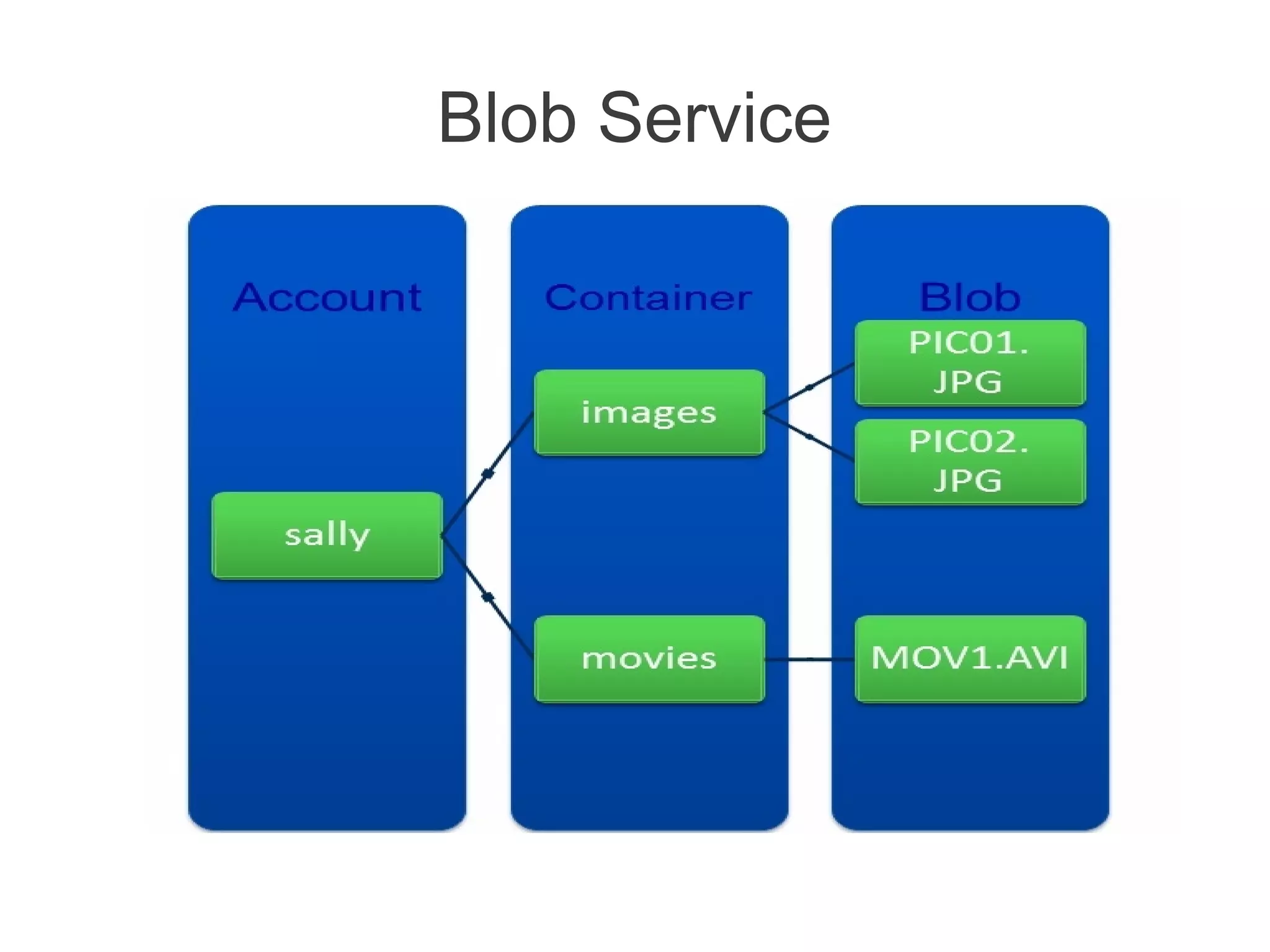

![Azure Drive (X-Drive)
• Access to a Local Drive in Azure
• Enables existing applications using NTFS to easily migrate to the cloud
• Essentially a Page Blob formatted as NTFS
• Remote Access via Page Blob Interface
• Durable NTFS volume [upto 1TB] for Windows Azure Applications
• Drives in the Cloud are only mountable by VMs within Cloud
• Mounted by one VM at a time for read/write
• A VM can dynamically mount up to 16 drives](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windowsazureoverview-121023142533-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-Windows-Azure-24-2048.jpg)