The document provides an overview of research and review articles, detailing their types, structures, and purposes. It discusses the importance of citation indexing and impact factors in evaluating research papers, along with resources for publication and citation databases. Additionally, it outlines the peer review process, criteria for acceptance and rejection of papers, and tasks for further research engagement.



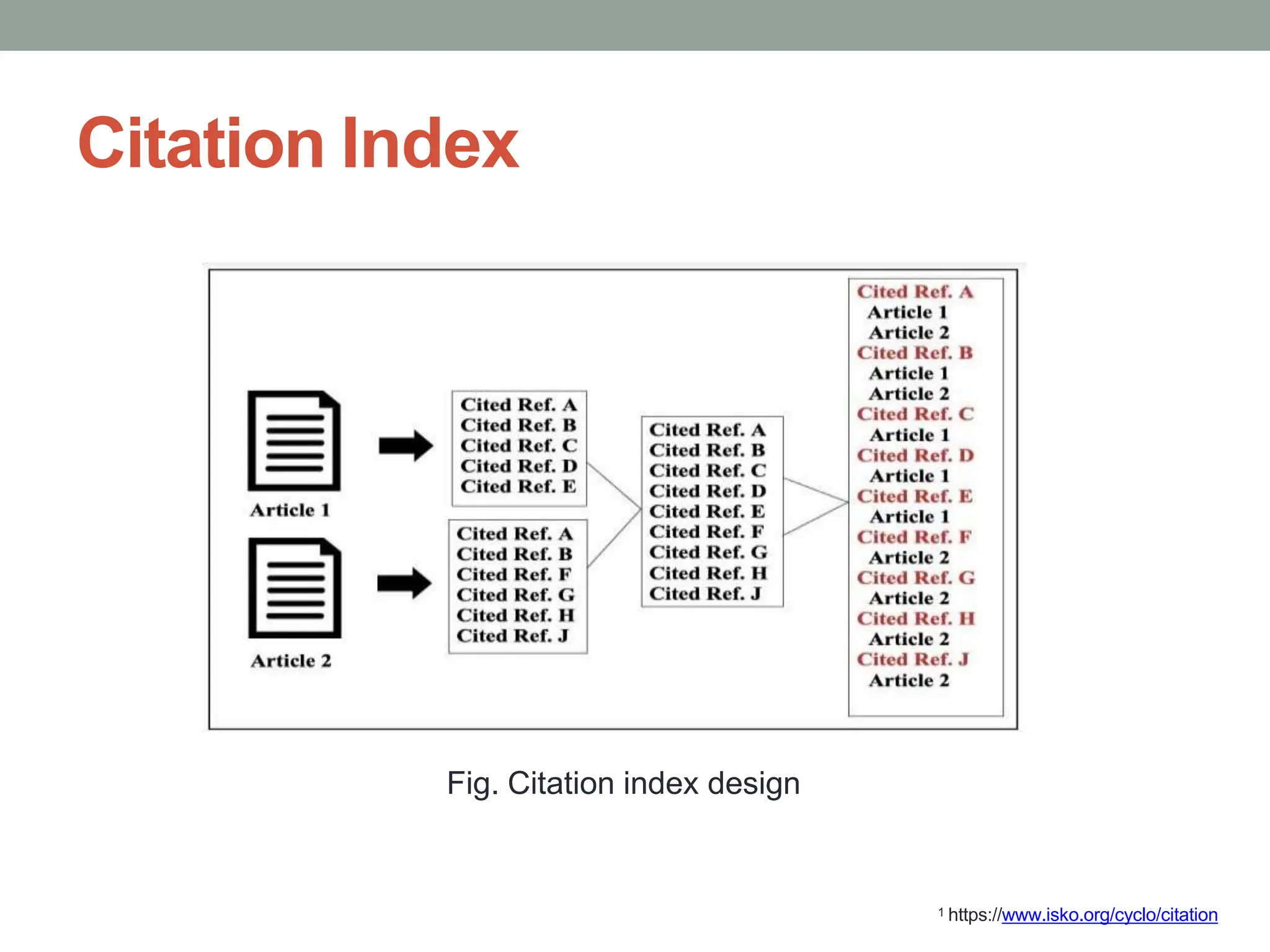
![Indexing and Impact Factor
Scientific and scholarly authors normally
cite other publications. If Paper R
contains a bibliographic footnote using
and describing Paper C, then
– R contains a reference to C,
– C has a citation from R.
• The number of references a paper has
is measured by the number of items in
its bibliography as endnotes, footnotes,
etc.,
• The number of citations a paper has is
found by looking it up [in a] citation
index and seeing how many others
papers mention it.“
Source: Price D. J. D. Little science, big science. and beyond. New York: Columbia University Press, 1986.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoresearch-240130090221-e8c62f9c/75/Introduction-to-research-and-its-different-aspects-5-2048.jpg)