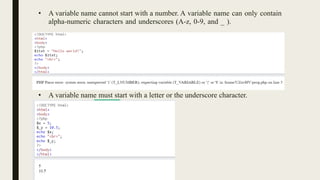
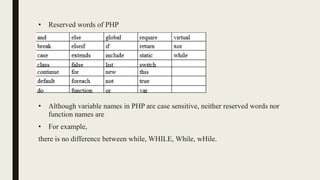
The document provides a comprehensive overview of PHP, detailing its origins, uses, and syntactic characteristics. It discusses PHP's operation modes, variable naming conventions, data types, output methods, and control statements, including examples for better understanding. Additionally, it highlights how PHP integrates with XHTML and outlines essential programming constructs like loops and conditionals.