This document provides an overview of PHP, including:
- PHP is a server-side scripting language used for web development. It allows querying databases, file uploads/downloads, and member areas.
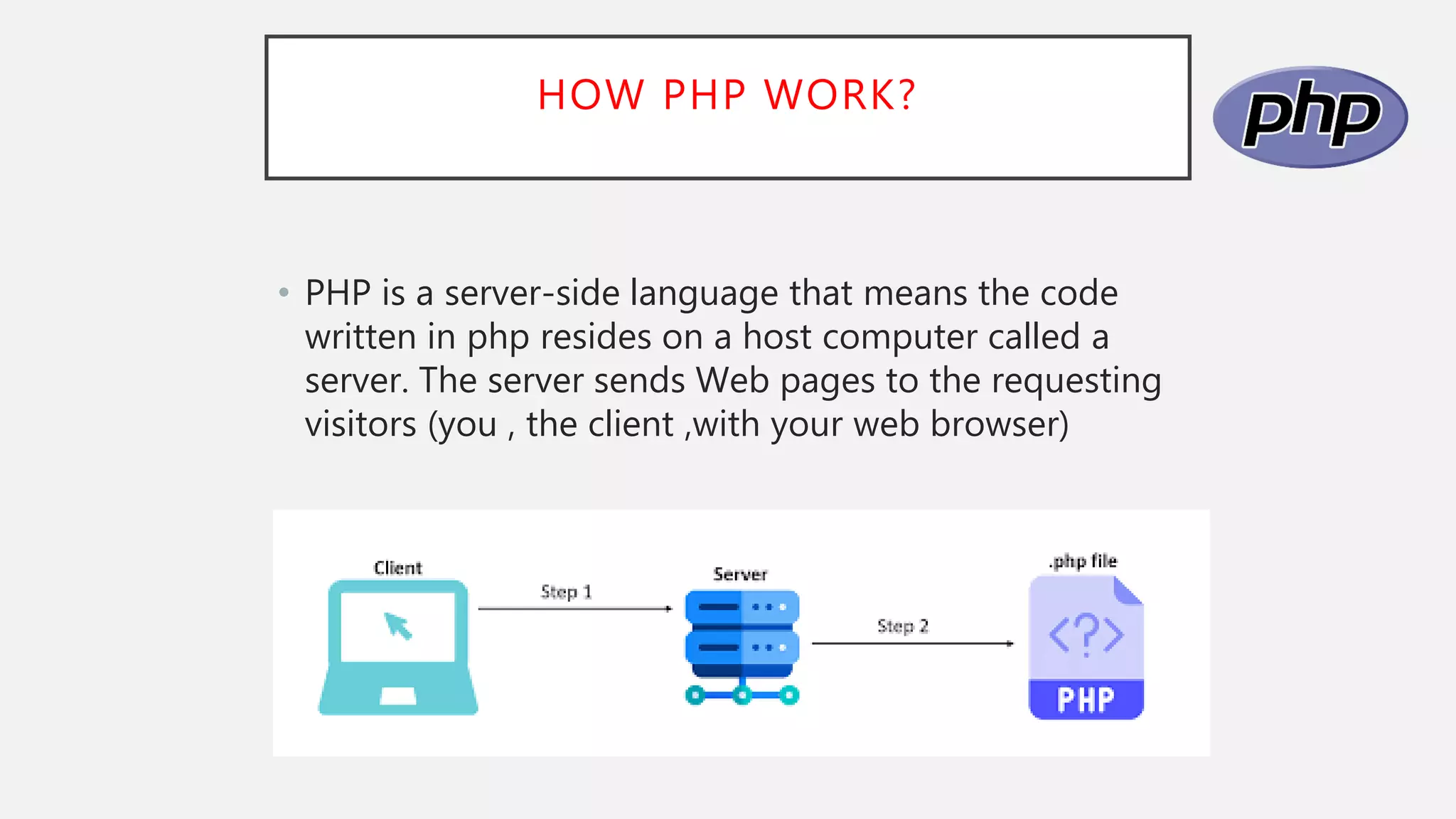
- PHP code is embedded into HTML files and executed on the server before the page is sent to the browser. It uses variables, control structures, and outputs to the browser.
- The basics of PHP include syntax, variables, data types, operators, and control structures like if/else statements and loops. Examples show how to output text and conditionally display messages.