The document provides information about PHP including what it is, where it is used, why it is used, its power and capabilities, and how to install and run PHP code. PHP is introduced as a server-side scripting language designed for web development. It is used by many popular websites and content management systems. PHP code can be embedded into HTML and is commonly used as a server-side language. Basic instructions are provided on installing PHP and running a "Hello World" PHP program. An overview of PHP syntax, variables, constants, and strings is also given.




![Let's Install the server
Here are the steps.
Installing Web Server (Here we will use Apache)
Installing PHP
However, you can do both of the above steps at once by
installing one of the following web development environments.
WAMP Server - Only Windows
XAMPP Server- Supports Windows, Linux, OS X
Installing a text editor
You need a good text editor to write and edit PHP files. The following are some of
recommended text editors. Go to those websites and choose any editor you like.
Sublime Text
Atom [recommended]
Visual Studio Code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-5-320.jpg)















![Integers a number which is not a fraction; a whole number ( -2, -1, 0, 1, 2 )
Floats anumber that can contain a fractional part (2.56, 1.24)
Strings A string is any finite sequence of characters (letters, numerals,
symbols, punctuation marks, etc.)
Arrays is a series of values
There are two ways to declare an array:
An array can be declared using the array() function.
An array can be declared wrapping with [ and ].
Elements of the arrays should be separated with a comma. And, elements
can be any type
<?php
$array = array('Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange', 'Mango');
var_dump($array);
$array = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange', 'Mango'];
var_dump($array);
// output
array(4) { [0]=> string(5) "Apple" [1]=> string(6)
"Banana" [2]=> string(6) "Orange" [3]=> string(5)
"Mango" }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-21-320.jpg)
























![Function Arguments - Type Declaration
Type declaration can be used to specify a data type for each argument .
data type should be added before the argument to specify type declaration for it
Valid Types For Type Declaration
Array The argument must be an array
<?php
function myDetails(string $name, int $age, string $country) {
echo " My name is $name <br>
My age is $age <br>
My country is $country <br><br> ";
}
myDetails('Joe', 22, 'USA’);
myDetails('Adam', 25, 'United Kingdom’);
myDetails('David', 30, 'France’);
# myDetails('John', 'N/A', 'Australia'); this will cause an error
<?php
function dumpArray(array $arr) {
var_dump($arr);
}
$array = ['Joe', 'Adam', 'David'];
dumpArray($array);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-46-320.jpg)









![Static Scope
As we discussed earlier, local scope variables are deleted after the end of the
execution of the function. But, sometimes we need to keep the variable alive.
<?php
$x = 'Hyvor’;
$y = 'Developer’;
function websiteName() {
echo $GLOBALS['x'], $GLOBALS['y’];
}
websiteName(); // outputs HyvorDeveloper
<?php
function test() {
static $number = 0; // declare static variable
echo $number . '<br>'; // echo number with line break
$number = $number + 5; // add five to $number
}
test(); // 0
test(); // 5
test(); // 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-58-320.jpg)
![PHP Arrays
Arrays are variables that store multiple values.
Arrays are really useful when we work with lists (or data) of similar types.
Arrays are commonly used for many purposes. An array in PHP can be
considered as mapping a value to a key.
Arrays can have key/value pairs.
The key can either be an integer or string. If it was a float, boolean it will
be cast to integer.
Values can be any data type.
Declaring an Array
there are two ways to declare an array:
An array can be declared using the array() function.
An array can be declared wrapped with [ and ].
<?php
$array = array('Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange', 'Mango');
var_dump($array);
$array = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange', 'Mango'];
var_dump($array);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-59-320.jpg)
![Types of Arrays
There are three types of arrays in PHP.
Indexed Arrays: Arrays with numeric indexes (keys).
Associative Arrays: Arrays with named keys.
Multidimensional arrays: Arrays of array.
Indexed Arrays
Indexed arrays have numeric indexes or keys
You can refer an element of the array as: $arrayName[index].
<?php
$fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange', 'Mango'];
<?php
$fruits[0] = 'Apple’;
$fruits[1] = 'Banana’;
$fruits[2] = 'Orange’;
$fruits[3] = 'Mango';
<?php
$fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange', 'Mango’];
echo "First Fruit is $fruits[0]" . '<br>’;
echo "Second Fruit is $fruits[1]" . '<br>’;
echo "Third Fruit is $fruits[2]" . '<br>’;
echo "Forth Fruit is $fruits[3]" . '<br>';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-60-320.jpg)
![Associative Arrays
Associative arrays have named keys.
There are two ways to declare associative arrays.
1. An associative array can be declared using the array() function or []
2. An associative array can be declared manually by adding keys.
<?php
$age = array( 'Joe' => 22,
'Adam' => 25,
'David' => 30
);
// or
$age = [ 'Joe' => 22,
'Adam' => 25,
'David' => 30
];
<?php
$age['Joe'] = 22;
$age['Adam'] = 25;
$age['David'] = 30;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-61-320.jpg)
![Array keys can also be integers.
The difference between indexed arrays and the above
associative arrays is that associative array is
constructed by adding keys explicitly by us without
any order (We didn't start from index 0).
<?php
$age = array('Joe' => 22,
'Adam' => 25,
'David' => 30
);
$age['Peter'] = 22;
$age['Christina'] = 25;
var_dump($age);
<?php
$schedule = [
16 => 'My Birthday’,
20 => 'Special Dinner’,
25 => 'PHP Conference’
];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-62-320.jpg)
![Multidimensional Arrays
Multidimensional arrays are arrays of arrays.
you can store an array as the value of an array element. These types of
arrays are called Multidimensional arrays
Foreach Loop loop is used to loop through arrays.
Syntax
foreach with Indexed Arrays
foreach ($array as $key => $value) { code to execute }
<?php
$people = [
'Joe' => [ 'age' => 22, 'country' => 'USA’ ],
'Adam' => [ 'age' => 25, 'country' => 'United Kingdom' ],
'David' => [ 'age' => 30, 'country' => 'France’ ]
];
<?php
$fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange', 'Mango’];
// foreach loop
foreach ($fruits as $fruit) {
echo $fruit . '<br>’;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-63-320.jpg)
![foreach with Associative Arrays
foreach with Multidimensional Arrays
<?php
$people = [ 'Joe' => 22, 'Adam' => 25, 'David' => 30 ]; foreach
($people as $name => $age) {
echo "My name is $name, and age is $age" . '<br>’;
}
<?php
$data = [
'Game of Thrones' => ['Jaime Lannister', 'Catelyn Stark', 'Cersei Lannister’],
'Black Mirror' => ['Nanette Cole', 'Selma Telse', 'Karin Parke’]
];
echo '<h1>Famous TV Series and Actors’;
foreach ($data as $series => $actors) {
echo "<h2>$series</h2>";
foreach ($actors as $actor) {
echo "<div>$actor</div>";
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-64-320.jpg)
![Playing with Arrays
1. Adding New Elements to Arrays (Using Brackets)
2. Adding New Elements to Arrays (Using array_push)
The array_push() function can be used to add new elements to an array. In this
function, you can add multiple elements at the end at the same time
3. Prepending New Elements to Arrays
The array_unshift() function is used to prepend elements to an array. After
prepending, array indexes will be changed accordingly. See this example
<?php
$fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange', 'Mango']; // add new elements to the end
$fruits[] = 'Pears’;
$fruits[] = 'Watermelon’;
var_dump($fruits);
<?php
$fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange', 'Mango']; # add new elements
array_push($fruits, 'Pears', 'Watermelon’);
var_dump($fruits);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-65-320.jpg)
![4. PHP Getting the Length of an Array
The count() function is used to get the length of an Array in PHP.
5. PHP Merging Two Arrays
The array_merge() function can be used to merge two arrays.
<?php
$indexedArray = ['USA', 'UK', 'Canada’];
var_dump($indexedArray); // 0 => USA
array_unshift($indexedArray, 'Australia', 'New Zealand');
var_dump($indexedArray); // 0 => Australia
<?php
$fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange', 'Mango’];
echo count($fruits); // will return 4
echo '<br>’;
$age = array( 'Joe' => 22, 'Adam' => 25, 'David' => 30 );
echo count($age); // will return 3;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-66-320.jpg)
![Note:This function will add new indexes for indexed arrays, and it will
overwrite the same keys for associative arrays.
The array union operator (+) can be used to merge two arrays when you have
different keys.
<?php
$array1 = ['red', 'blue’];
$array2 = ['yellow', 'green’];
$arrayMerged = array_merge($array1, $array2);
var_dump($arrayMerged);
<?php
$array1 = ['name' => 'John', 'age' => 24];
$array2 = ['country' => 'UK’];
$arrayMerged = $array1 + $array2;
var_dump($arrayMerged);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-67-320.jpg)
![6. PHP is_array()
is_array() checks if a variable is an array.
7. PHP Check if an element exists in an array - in_array()
checks if a specific element is there in the given array.
<?php
$int = 1;
$string = 'String’;
$array = ['This', 'is', 'an', 'array’];
var_dump(is_array($int)); // false
var_dump(is_array($string));// false
var_dump(is_array($array)); // true
<?php
$array = ['James', 'Doe', 'John’];
if (in_array('James', $array)) {
echo "James is in the array";
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-68-320.jpg)
![8. Check if a key exists in an array - array_key_exists()
function checks if a specific key exists in an array.
9. Get the Array Keys - array_keys()
function is used to get the array keys as an indexed array.
10. Get the Array Values - array_values()
function is used to get the array values as an indexed array.
<?php
$array = [ 'name' => 'William', 'age' => 25, 'country' => 'N/A' ];
var_dump( array_key_exists('name', $array) ); // true
var_dump( array_key_exists('birthday', $array) ); // false
<?php
$array = [ 'name' => 'William', 'age' => 25, 'country' => 'N/A' ];
$keys = array_keys($array);
var_dump($keys);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-69-320.jpg)
![11. A Function on Each Element - array_map()
We can perform a function on each element and return a new array
<?php
$array = [ 'name' => 'William', 'age' => 25, 'country' => 'N/A' ];
$values = array_values($array);
var_dump($values);
<?php
$array1 = [24, 12, 45, 23];
$array2 = array_map(function($val) {
return $val * 2;
}, $array1);
var_dump($array2);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-70-320.jpg)
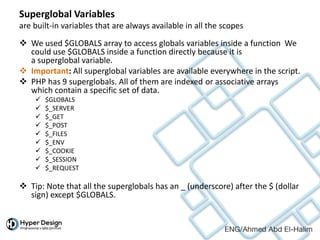

![$GLOBALS
$_SERVER
a very useful and huge array which holds the data about the currently
executing script, network addresses, paths, locations, etc.
<?php
$x = 'Hyvor’;
$y = 'Developer’;
function websiteName() {
echo $GLOBALS['x'], $GLOBALS['y’];
}
websiteName(); // outputs HyvorDeveloper](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-73-320.jpg)
![• Quiz 1:
1- write a php program that output
2- write a php program that draw table
Using
$array = [
['Joe', 'joe@hmail.com', 24],
['Doe', 'doe@hmail.com', 25],
['Dane', 'dane@hmail.com', 20]
];
<?php
echo $_SERVER['PHP_SELF'] . '<br>’;
echo $_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT'] . '<br>’;
echo $_SERVER['SERVER_ADDR'] . '<br>’;
echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'] . '<br>’;
echo $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] . '<br>’;
echo $_SERVER['REQUEST_TIME'] . '<br>’;
echo $_SERVER['HTTP_USER_AGENT'] . '<br>’;
echo $_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-74-320.jpg)
![<?php
$array = [
['Joe', 'joe@hmail.com', 24],
['Doe', 'doe@hmail.com', 25],
['Dane', 'dane@hmail.com', 20]
];
?>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Email</th>
<th>Age</th>
</tr>
<?php foreach ($array as $person) : ?>
<tr>
<?php foreach ($person as $detail) : ?>
<td><?php echo $detail ?></td>
<?php endforeach; ?>
</tr>
<?php endforeach; ?>
</table>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-php-191208195449/85/Introduction-to-php-75-320.jpg)
