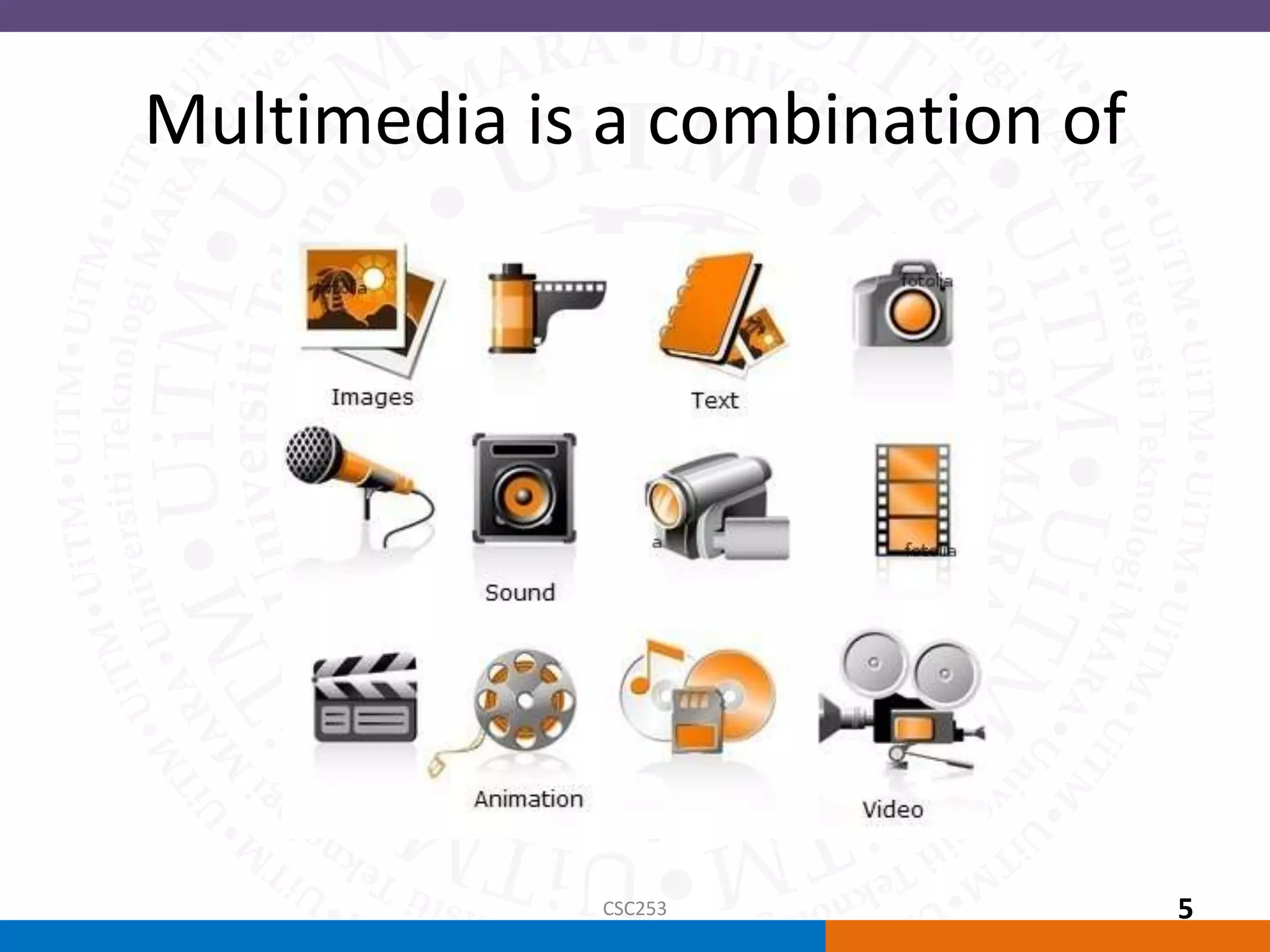
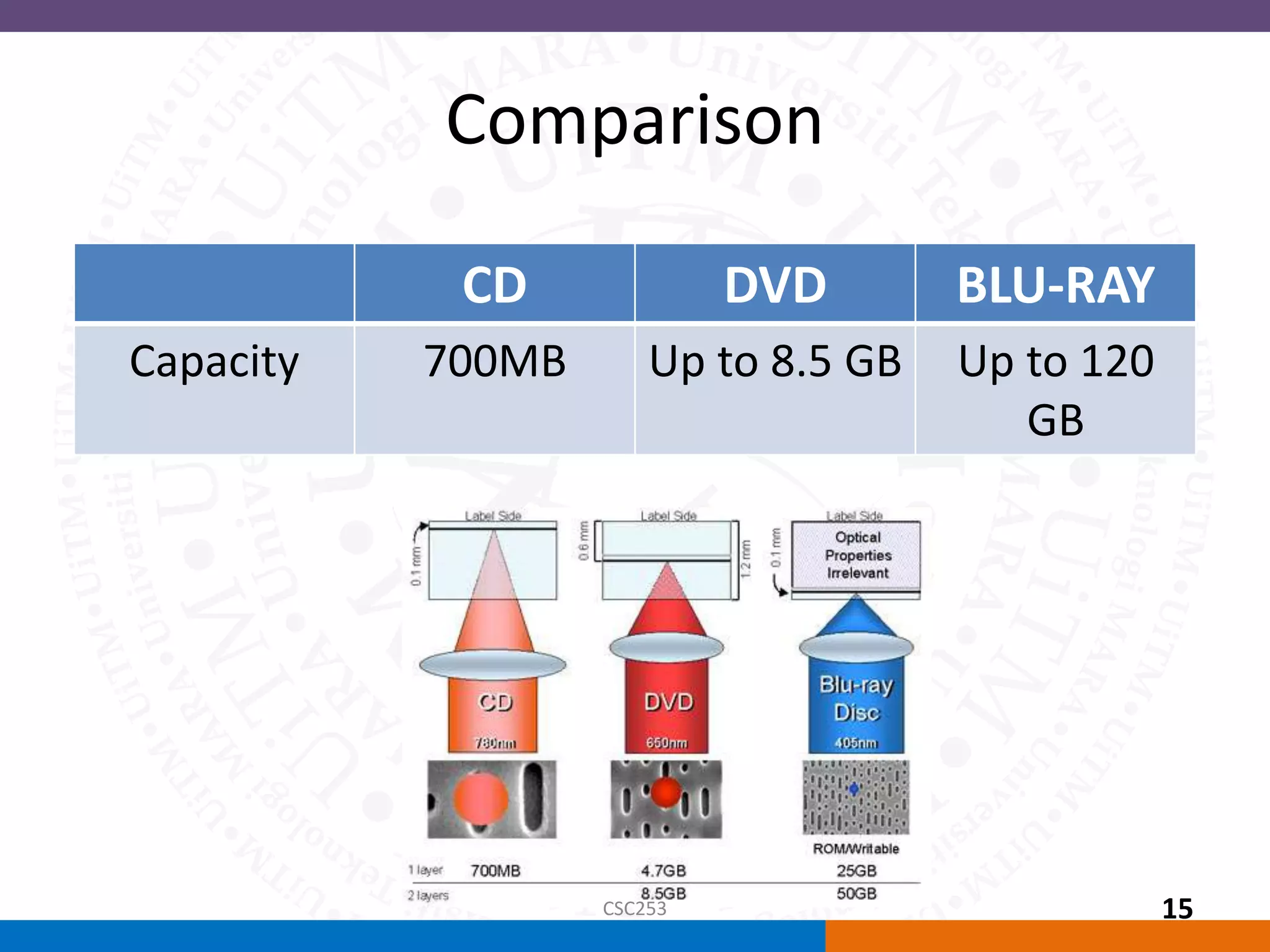
Multimedia is a combination of different media types that can be delivered via computer. It was defined as any combination of text, art, sound, animation, and video. The document discussed the types of linear and non-linear multimedia, applications in different domains like education, business, and virtual reality which is an extension of multimedia using 3D environments.