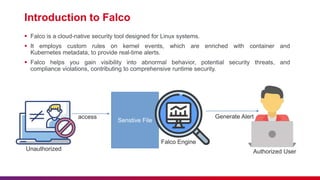
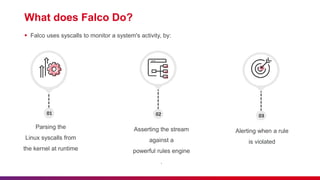
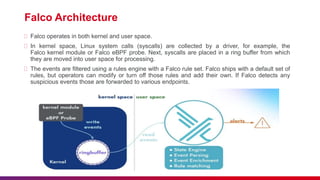
Falco is a cloud-native security tool for Linux systems that provides real-time alerts on abnormal behaviors and potential security threats by monitoring system calls with custom rules. Key features include threat detection, policy enforcement, compliance monitoring, and integration with DevSecOps practices. The document also outlines Falco's architecture, components, and best practices for etiquette during presentations.